
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Related Documents
- •Typographic and Syntax Conventions
- •Introduction to the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Editing Your Technology File for Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Sample Technology File
- •Virtuoso XL Technology File Requirements
- •Layer Rules
- •Devices
- •Physical Rules
- •Virtuoso XL Rules (lxRules)
- •Compactor Rules
- •Preparing Your Connectivity Source for the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Placing Design Elements
- •Using Design Variables
- •Netlist Processor Expressions
- •Analog Expression Language Expressions
- •Simulation Design Variables
- •Using One-to-Many Mapping
- •Iterated Instances and Bus Pins
- •Multiplication Factor (mfactor)
- •Series-Connection Factor (sfactor)
- •One-to-Many Assignment with the Update Device Correspondence
- •Using Many-to-Many or Many-to-One Mapping
- •Modifying Many-to-Many or Many-to-One Mapping Between Components
- •Deleting Many-to-Many or Many-to-One Mapping Between Components
- •Using Virtuoso XL Properties
- •Using the lxUseCell Property to Specify Layout Devices to Use
- •Using the lvsIgnore Property to Exclude Schematic Symbols
- •Using the lxlgnoredParams Property to Exclude Device Properties
- •Using the lxRemoveDevice property to Ignore Parasitic Devices
- •Using the lxViewList and lxStopList Properties to Prepare Hierarchical Designs
- •Using the lxCombination Property to Build Complex Devices
- •Preparing Instances and Pins in Your Layout for the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Preparing Pins for the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Preparing Pins for Permutability
- •Search Order Variable
- •Syntax
- •Macros
- •Setting the permuteRule Property in the Symbol Master
- •Setting the permuteRule Property in the Device Master
- •Setting the permuteRule Property in the Symbol Instance
- •Setting the permuteRule Property in the Device Instance
- •Setting the permuteRule Property in the Component Description Format
- •Preparing Instances for Hierarchical Connectivity Checking
- •Setting Up Your Desktop
- •Customizing Your Desktop Layout
- •Using Multiple Cellviews
- •Printing to the Command Interpreter Window
- •Changing Display Colors
- •Using Bindkeys
- •Displaying Bindkeys
- •Loading Virtuoso XL Bindkeys
- •Setting Environment Variables
- •Information About Online Forms
- •Layout XL Options Form
- •Introduction to Abutment
- •Abutment Requirements
- •Setting Up Cells for Abutment
- •abutAccessDir
- •abutClass
- •Steps in Auto-Abutment
- •Sample Parameterized Cells Set Up for Abutment
- •Example 1
- •Example 2
- •Creating CMOS Pcells to Use with Abutment
- •autoAbutment Properties
- •The abutMosStretchMat Property
- •abutMosStretchMat Rules for MOS Abutment
- •Example Code Setting MOS Abutment Properties
- •Setting Environment Variables for Abutment
- •Move Together
- •Constraint Assisted
- •Using Device Abutment
- •Generating Your Layout with Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Starting Virtuoso XL from the Schematic
- •Importing a Netlist for a Connectivity Reference
- •Starting Virtuoso XL from the Layout View
- •Connectivity Reference as a Netlist
- •Mapping File Structure
- •Working with Template Files
- •Saving Form Contents
- •Loading Template Files
- •Modifying Templates
- •Loading Template Files
- •Creating Template Files
- •Template File Syntax
- •General Syntax Rules
- •Boundaries Section
- •I/O Pins Section
- •Sample Template
- •Generating a Layout with Components Not Placed (Gen From Source)
- •Moving Components from the Schematic into the Layout (Pick from Schematic)
- •Placing a Group of Schematic Elements Together
- •Placing Individual Components
- •Generating Pins
- •Viewing Unplaced Instances/Pins
- •Viewing in Place
- •Manually Abutting Devices Using Pick from Schematic
- •Cloning Components
- •Cloning
- •Troubleshooting
- •Cloning Using Multiple Cellviews
- •Using Correspondence Points
- •Information About Online Forms
- •Add Correspondence Pairs Form
- •Cloning Form
- •Correspondence Pairs Form
- •Import XL Netlist Form
- •Layout Generation Options Form
- •Open File Form
- •Pick from Schematic Form
- •Remove Correspondence Components Form
- •Set Pin Label Text Style Form
- •Startup Option Form
- •Template File Form
- •Editing Your Layout with Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Identifying Incomplete Nets
- •Moving Objects Manually in the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Moving Objects Using Move Options
- •Setting the Move Form to Appear Automatically
- •Aligning Objects
- •Post Selecting Devices
- •PreSelecting Devices
- •Swapping Components
- •Permuting Component Pins
- •Permuting Pins Manually
- •Checking Permutation Information
- •Using Device Locking
- •Using Automatic Spacing
- •Using Interactive Device Abutment
- •Setting Component Types
- •About Component Types
- •MOS Transistor Stacking and Folding Parameters
- •Modifying a Component Type
- •Using Transistor Chaining
- •Using Transistor Folding
- •Controlling the Folding Grid
- •Folding Transistors
- •Adding Instances to a Layout
- •Adding Pins to a Layout
- •Assigning Pins to a Net
- •Maintaining Connectivity When Editing a Flattened Pcell
- •Information About Online Forms
- •Assign Nets Form
- •Edit Component Types Form
- •Move Form
- •Set Transistor Folding Form
- •Show Incomplete Nets Form
- •Stretch Form
- •Virtuoso XL Alignment Form
- •Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
- •Overview
- •Main Features
- •Place Menu Command Summary
- •Other Commands Used with the Virtuoso custom placer
- •Placement Styles
- •Setting Up the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor for Placement
- •Identifying the Placement Translation Rules
- •Setting Cadence Design Framework II Environment Variables
- •Setting Environment Variables for the Virtuoso Custom Router and Placer
- •Setting MOS Chaining and Folding Parameters
- •Abutting Standard Cells
- •Using Auto-Abutment During Placement
- •Placement Constraints
- •Constraint Manager Geometric Constraints
- •Pin Placement Constraints
- •Constraint Limitations
- •Placement Parameters and Component Types
- •MOS Transistor Chaining and Folding Parameters
- •Pin Placement
- •Assigning Pins to an Edge
- •Assigning Pins to a Fixed Position
- •Railing Pins
- •Loading the Template File
- •Assigning Spacing Between Pins
- •Saving Pin Placement to a Template File
- •Partitioning the Design
- •Creating a Partition
- •Loading the Template File
- •Saving Partitions to a Template File
- •Setting Placement Planning
- •Assisted CMOS Placement
- •Choose Component Types Form
- •Running the Virtuoso Custom Placer
- •Prerequisites to Placement
- •Running the Virtuoso Custom Placer: Initial Placement
- •Stopping the Placer
- •Running Load Balancing Service (LBS)
- •Troubleshooting Placement Results
- •Running the Virtuoso Custom Placer: Detailed Placement
- •Showing Congestions
- •Information About Forms
- •Auto Placer Form
- •Partitioning Form
- •Choose Component Types Form
- •Pin Placement Form
- •Load Template File Form
- •Placement Planning Form (Assisted CMOS)
- •Placement Planning Form (Assisted Standard Cell)
- •Placement Planning Form (Assisted Mixed CMOS/Standard-Cell)
- •Preparing Your Design for Routing in the Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •Understanding Connectivity
- •Pseudo-Parallel Connections
- •Selecting Layers
- •Changing Layers
- •Connecting Nets
- •Creating Paths
- •Connecting Nets with Path Stitching
- •Connecting Nets with Design Shapes
- •Checking Connectivity with Flight Lines
- •Checking Connectivity with Markers
- •Finding Markers
- •Explaining Markers
- •Deleting Single Markers
- •Deleting All Markers
- •Using the Virtuoso Compactor on a Routed Design
- •Overview
- •Main Features
- •Wire Editing Commands
- •Virtuoso Custom Router to Virtuoso XL Command Mapping
- •Prerequisites
- •Rule Information
- •Net Connectivity Information
- •Routing Area Boundary
- •Enabling Wire Editing
- •Toggling Between Virtuoso XL and Wire Editing Enabled
- •Loading ASCII Rules Files
- •The Wire Editing Environment
- •Status Banner
- •Preview Wires and Routing Aids
- •Mouse Button Behavior
- •Using Environment Variables
- •Routing Paths
- •Routing a Single Path
- •Routing Multiple Paths
- •Preventing and Checking Design Rule Violations
- •Interactive Checking
- •Same Net Checking
- •Checking Regions
- •Checking Route and Pin Violations
- •Routing Options and Styles
- •Matching Path Width and Pin Widths
- •Matching Path Width and Pin Widths for Multiple Paths
- •Gathering Bus Wires
- •Spacing for Gathered Bus Wires
- •Overriding Bus Spacing
- •Rotating the Bus Cursor
- •Cycling the Control Wire
- •Allowing Redundant Wiring
- •Allowing Orthogonal Jogs
- •Route To Cursor
- •Allow Floating Nets
- •Connecting Multiple Component Pins
- •Pushing Routes and Components
- •Routing Shielded Nets
- •Routing Tandem Layer Pairs
- •Using Vias
- •Changing Layers and Adding Vias
- •Using Vias Patterns on Multiple Paths
- •Legal Via Sites
- •Rotating Vias
- •Pseudo Vias
- •Editing Routed Connections
- •Stretching Paths and Vias
- •Splitting and Stretching Paths
- •Copying Routes
- •Using Critic Wire
- •Compacting Paths Using Pull
- •Displaying Reports
- •Displaying Routing Status Reports
- •Displaying Network Reports
- •Displaying Component Reports
- •Displaying Net Reports
- •Creating Rules Reports
- •Search Reports
- •Saving Reports
- •Setting Constraints
- •Using the Virtuoso Constraint Manager
- •Using .do Files
- •About the Forms
- •Add Via Form
- •Check Routes Form
- •Create Path Form
- •Find File Form
- •Layout
- •Reports Form
- •Route Options Form
- •Save As Form
- •Search Form
- •Split Form
- •Via Pattern Pop-up
- •Reports
- •Route Status Report Window
- •Network Report Window
- •Instance Report Window
- •Net Report Window
- •Rules Report Window
- •Setting Environment Variables
- •Troubleshooting
- •Finding Design Elements (Probing)
- •Probing Hierarchical Designs
- •Removing Probes
- •Exiting the Probe Command
- •Showing the Options Form
- •Checking Shorts and Opens
- •Comparing Design Elements and Parameters (Checking against the Connectivity Source)
- •Information About Online Forms
- •Probe Options Form
- •Updating Design Data in Virtuoso XL
- •Updating Layout Parameters
- •Updating Schematic Parameters
- •Updating Device Correspondence
- •Creating Device Correspondence
- •Needed Mode
- •Computer Aided Mode
- •Updating the Connectivity Reference
- •Changing the Device (Instance) View
- •Information About Online Forms
- •Change Instance View Form
- •Create Device Correspondence
- •Problems with the Interface
- •Invalid Markers from Previous Software Versions
- •Options Form Does Not Appear
- •Virtuoso XL Performance Is Slow
- •Problems with Editing
- •Components Move Slowly
- •Extra Probes Appear
- •Layout Generation Options Form Does Not Keep Values from the Last Entry
- •Parameters Not Updated
- •Schematic Not Editable
- •Warning to Update Your Design Appears at Startup
- •Problems with Connectivity
- •Connections Not Made
- •Incomplete Nets Command Does Not Recognize Connected Pins and Nets
- •Markers for Nonexistent Overlaps and Shorts Appear
- •Path Ends Not Accepted
- •Placement and Routing Do Not Run
- •Virtuoso XL Does Not Recognize Physical Vias
- •Moving Software Executables To a New Location
- •Environment Variables
- •Virtuoso XL Layout Editor
- •alignApplySeparation
- •alignApplySpacings
- •alignDirection
- •alignLayer
- •alignMethod
- •alignSelectionMode
- •alignSeparation
- •allowRotation
- •autoAbutment
- •autoArrange
- •autoPermutePins
- •autoSpace
- •checkTimeStamps
- •ciwWindow
- •compTypeRefLibs
- •constraintAssistedMode
- •createBoundaryLabel
- •crossSelect
- •extractEnable
- •extractStopLevel
- •globalPlacement
- •ignoredParams
- •ignoreNames
- •incNetCycleHilite
- •incNetHiliteLayer
- •infoWindow
- •initAspectRatio
- •initAspectRatioOption
- •initBoundaryLayer
- •initCreateBoundary
- •initCreateInstances
- •initCreateMTM
- •initCreatePins
- •initDoFolding
- •initDoStacking
- •initEstimateArea
- •initGlobalNetPins
- •initIOLabelType
- •initIOPinLayer
- •initIOPinName
- •initPinHeight
- •initPinMultiplicity
- •initPinWidth
- •initPrBoundaryH
- •initPrBoundaryW
- •initSymbolicPins
- •initUtilization
- •layoutWindow
- •lswWindow
- •lxAllowPseudoParallelNets
- •lxDeltaWidth
- •lxFingeringNames
- •lxGenerationOrientation
- •lxGenerationTopLevelOnly
- •lxInitResetSource
- •lxStackMinimalFolding
- •lxStackPartitionParameters
- •lxWidthTolerance
- •maintainConnections
- •mfactorNames
- •mfactorSplit
- •moveAsGroup
- •openWindow
- •optimizePlacement
- •paramTolerance
- •pathProbe
- •pathPurposeList
- •pathSwitchLayer
- •pathSwitchPurpose
- •preserveTerminalContacts
- •probeCycleHilite
- •probeDevice
- •probeHiliteLayer
- •probeInfoInCIW
- •probeNet
- •probePin
- •rowGroundLayer
- •rowGroundName
- •rowGroundWidth
- •rowPowerLayer
- •rowPowerName
- •rowPowerWidth
- •rowSupplyPosition
- •rowSupplySpacing
- •rowMOSSupplyPattern
- •rowSTDAllowFlip
- •rowSTDSupplyPattern
- •rulesFile
- •runTime
- •saveAs
- •saveAsCellName
- •saveAsLibName
- •saveAsViewName
- •schematicWindow
- •setPPConn
- •sfactorNames
- •sfactorParam
- •showIncNetEnable
- •stopList
- •templateFileName
- •traverseMixedHierarchies
- •updateReplacesMasters
- •updateWithMarkers
- •vcpConductorDepth
- •vcpKeepoutDepth
- •viewList
- •Wire Editor
- •allowFloatingNets
- •allowJogs
- •allowRedundantWiring
- •autoAdjustLength
- •autoShield
- •busOverride
- •busOverrideValue
- •busWireSpacing
- •busWireSpacingType
- •checkCornerCorner
- •checkCrosstalk
- •checkLength
- •checkLimitWay
- •checkMaxProcessWireWidth
- •checkMaxStackViaDepth
- •checkMaxTotalVia
- •checkMinMaskEdgeLength
- •checkMinProcessWireWidth
- •checkMiter
- •checkNetOrder
- •checkOffManGridPin
- •checkOffWireGridPin
- •checkPinSpacing
- •checkPolygonWire
- •checkProtected
- •checkReentrantPath
- •checkRegion
- •checkSameNet
- •checkSegment
- •checkStub
- •checkUseLayers
- •checkUseVias
- •checkWireExtension
- •doFile
- •enableBusRouting
- •enableTandemPair
- •gatherBusWires
- •inaccessiblePin
- •interactiveChecking
- •matchPinWidth
- •matchPinWidthValue
- •matchWireWidth
- •multiplePinsConnection
- •pinLargerMaxProcessWidth
- •pinSmallerMinProcessWidth
- •pushComponent
- •pushRouting
- •routeAsManyAsPossible
- •routeToCursor
- •routeToCursorStyle
- •sameNetChecking
- •showTimingMeter
- •showTimingOctagon
- •snapToPinOrigin
- •useDoFile
- •useRulesFile
- •viaAssistance
- •viaPattern
- •Private Environment Variables
- •Virtuoso XL Command Quick Reference
- •Using Spice and CDL For Netlist Driven Layout Generation
- •Introduction
- •Specifying Spice Designs
- •Cell Creation Rules
- •Character Considerations
- •Spice Statements
- •File Level Statements
- •Statements Allowed at File Level or within a Subckt Cell or a Top Level Cell
- •Statements Allowed within a Subckt Cell or a Top Level Cell
- •Spice Design Example
- •CDL Design Example
- •Parameter Resolution
- •Parameter Levels
- •Resolving Parameters
- •Putting the Rules Together (Examples)
- •Parameter Scaling
- •Complete ibuf Example Results
- •Virtuoso XL .do File Commands
- •Rule Hierarchy
- •circuit
- •Syntax
- •Example
- •Syntax
- •Example
- •limit
- •Syntax
- •Example
- •rule
- •Syntax
- •Example
- •Syntax

Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
rule errors between each standard cell. The placer does not spend countless cycles on design rule checking between internal objects of one standard cell to another, just between the boundaries of adjacent standard cells. Using this method, the placer can use the boundary of each cell as the abutment edge for standard cells.
Note: Full design rule checking does occur between STDCELL component classes and all other devices.
The placer determines the cell boundary for each standard cell by the following precedence;
■Layer purpose pair = prBoundary drawing
■Layer purpose pair = prBoundary boundary
■Layer purpose pair = instance drawing
If any of the above layer purpose pairs do not exist in the cell, a boundary is derived equal in size to all objects within the cell. Due to the nature of standard cell design and the desire to share/overlap objects between adjacent standard cells, defining a boundary is the preferred method to ensure proper cell abutment.
Using Auto-Abutment During Placement
Auto-abutment, if enabled in Virtuoso XL, is automatically performed during layout generation for assisted MOS. In order to use auto-abutment,
■Your components (including your MOS device parameterized cells) need to be set up correctly with abutment properties
For an example of such a parameterized cell, see the spcnmos and spcpmos devices in the sample parameterized cells library. For more information, see the Sample Parameterized Cells Installation and Reference.
■Auto-abutment needs to be enabled in the Layout XL Options form
For more information, refer to Chapter 6, “Setting Up Device Abutment.”
Placement Constraints
You can create geometric constraints using the Virtuoso® Constraint Manager or the constraint manager SKILL functions to constrain devices or pins. You can also create constraints through the Virtuoso XL Pin Placement form to constrain pins.
■Geometric Constraints
December 2002 |
264 |
Product Version 5.0 |

Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
Geometric constraints are used to control the placement of objects. There are various types of geometric constraints that can be created through the constraint manager. For information about the types of constraints and how they are supported by Virtuoso XL and the placer, see “Constraint Manager Geometric Constraints” on page 265.
For more information about setting constraints through the constraint manager, refer to the Virtuoso Constraint Manager User Guide.
For more information about setting constraints using the constraint manager SKILL functions, refer to the Custom Layout SKILL Functions Reference Manager User.
■Pin Placement Constraints
Creating pin constraints through the Pin Placement form lets you place different types of constraints on multiple pins at one time and automatically moves the pins to their assigned locations. Conversely, when creating pin constraints through the constraint manager, different types of pin constraints must be created separately and placement is not automatic.
For more information about pin constraints, see “Pin Placement Constraints” on page 270.
Some of the procedures in this chapter suggest that you set certain types of constraints at certain points in the design flow, but generally this is not a strict requirement. You can constrain any device in the layout at any time, except while the placer is running. For example, you can use the placer iteratively, setting increasingly strict constraints as you refine the placement.
Constraint Manager Geometric Constraints
You can create the following constraints in the constraint manager for placement: of objects
■Distance
■Alignment
■Grouping
■Symmetry
■Fixed
December 2002 |
265 |
Product Version 5.0 |

Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
Caution |
The Virtuoso custom placer does not recognize constraint weights for alignment, fixed, symmetry, and distance constraints. Only grouping constraint weights with a fence is recognized by the placer.
Distance Constraints
The placer will honor distance constraints between two devices. When using the nearest edge option two devices or more can be constrained. Devices can be constrained in the X or Y direction but not both. In addition the placer will align the devices in the orthogonal direction.The placer will interpret the distance constraint between a pair of objects.
Table 9-1 Distance Constraint Handling in Virtuoso XL and Virtuoso Custom Placer
Distance Constraint Option |
Virtuoso XL |
Virtuoso custom placer |
|
|
|
Max X |
Yes |
Yes |
Min X |
Yes |
Yes |
Max Y |
Yes |
Yes |
Min Y |
Yes |
Yes |
Reference X |
Yes |
Yes |
Reference Y |
Yes |
Yes |
Support for more than two |
Between any pair in the set |
Two or more objects are |
objects |
|
supported for Nearest Edge |
|
|
reference. |
|
|
|
December 2002 |
266 |
Product Version 5.0 |

Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
Alignment Constraints
The placer supports all alignment references on any layer or the instance bounding box. The
first object is the alignment reference object and the rest of the objects are aligned to that reference. Relative orientation is also supported.
Table 9-2 Alignment Constraint Handling in Virtuoso XL and Virtuoso Custom Placer for two or more objects
Alignment Constraint |
Virtuoso XL |
Virtuoso custom placer |
|
Option |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Relative Orientation |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Align |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Reference Layer or Bounding |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Box |
|
|
|
Ordering |
No |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Grouping Constraints
Grouping constraint restricts a group of components to a rectilinear region (“fence”). A fence can optionally exclude all other, or specified, components.
The placer moves instances as necessary to implement confinement constraints even if they are not properly positioned in the preplaced view.
Table 9-3 Grouping Constraint Handling in Virtuoso XL and Virtuoso Custom Placer
Grouping Constraint |
Virtuoso XL |
Virtuoso custom placer |
|
Option |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Preserve Relative Position |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Fence |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Exclude |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Note: A grouping constraint with a fence that has a weight of 255 is translated as a hard fence. Any other weight between 1 and 254 is translated as a soft fence.
December 2002 |
267 |
Product Version 5.0 |
Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
Firm Grouping Constraints
When creating constraints in the schematic view and you want to preserve the relative position of components in the layout view, you can use the Preserve Relative Position to create a firm grouping constraint (also called a firm group).
To create a firm group,
Use the constraint manager to create a grouping constraint and choose Preserve
Relative Position.
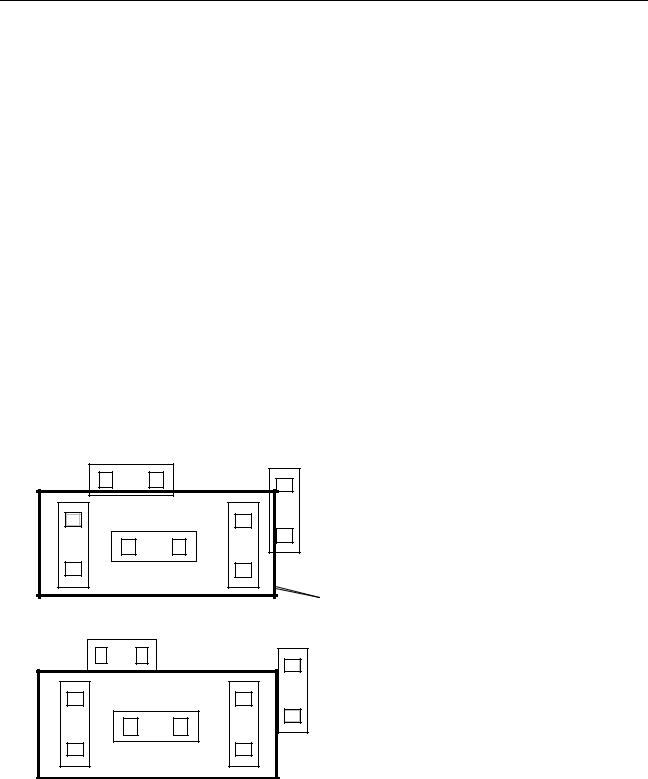
Soft Grouping Constraints
A soft grouping constraint keeps a group of components close together within the cell boundary, but it does not constrain the group.
The placer moves instances as necessary to implement soft group constraints even if they are not properly positioned in the preplaced view.
To create a soft grouping constraint,
Use the constraint manager to create a grouping constraint with the cell boundary as the fence.
Grouping constraints with Preserve
Relative Position
 group
group
Grouping constraints with a
Fence
 fence
fence
December 2002 |
268 |
Product Version 5.0 |

Virtuoso XL Layout Editor User Guide
Using the Virtuoso Custom Placer
Symmetry Constraints
The placer implies an order between the pairs involved in the constraint. For example, if Q1 and Q2 are constrained along their horizontal line, then the constraint implies that Q1 is below the line and Q2 is above.
The placer has the ability of defining a line of symmetry, self-symmetries and for a given pair (pairwise symmetries). The symmetry axis can be floating as well as fixed.
Table 9-4 Symmetry Constraint Handling in Virtuoso XL and Virtuoso custom placer
Symmetry Constraint |
Virtuoso XL |
Virtuoso custom placer |
|
Option |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Floating line |
No |
Yes |
|
Fixed line |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Horizontal/vertical direction |
Yes |
Yes (see Note below) |
|
Self-symmetry |
Only on fixed axis |
Yes, bounding box center |
|
|
|
|
Note: The Virtuoso custom placer interprets a symmetry constraint on a pair of objects such that the first object must be placed below a horizontal line of symmetry or to the left of a vertical line of symmetry. The other object would be placed on the opposite side of the line of symmetry.
Fixed Constraints
You can define a fixed constraint with an allowable set of orientations on one or more named components to a required x, y location. The User Movable option in the Create Fixed Constraint form can affect the description of pin position constraints. Components can also be temporarily locked to a fixed location and orientation through theEdit – Other – Lock Selected command.
Table 9-5 Fixed Constraint Handling in Virtuoso XL and Virtuoso custom placer
Fixed Constraint Option |
Virtuoso XL |
Virtuoso custom placer |
|
|
|
X |
Yes |
Yes |
Y |
Yes |
Yes |
Orientation |
Yes |
Yes |
Reference |
Yes |
Yes |
December 2002 |
269 |
Product Version 5.0 |
