
- •Dedication
- •Editors and Contributors
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •PREPARING FOR THE SURGERY CLERKSHIP
- •SURGICAL NOTES
- •COMMON ABBREVIATIONS YOU SHOULD KNOW
- •RETRACTORS (YOU WILL GET TO KNOW THEM WELL!)
- •SUTURE MATERIALS
- •WOUND CLOSURE
- •KNOTS AND EARS
- •INSTRUMENT TIE
- •TWO-HAND TIE
- •COMMON PROCEDURES
- •NASOGASTRIC TUBE (NGT) PROCEDURES
- •CHEST TUBES
- •NASOGASTRIC TUBES (NGT)
- •FOLEY CATHETER
- •CENTRAL LINES
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •THIRD SPACING
- •COMMON IV REPLACEMENT FLUIDS (ALL VALUES ARE PER LITER)
- •CALCULATION OF MAINTENANCE FLUIDS
- •ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCES
- •ANTIBIOTICS
- •STEROIDS
- •HEPARIN
- •WARFARIN (COUMADIN®)
- •MISCELLANEOUS AGENTS
- •NARCOTICS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ATELECTASIS
- •POSTOPERATIVE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
- •PULMONARY EMBOLISM
- •ASPIRATION PNEUMONIA
- •GASTROINTESTINAL COMPLICATIONS
- •ENDOCRINE COMPLICATIONS
- •CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK
- •SEPTIC SHOCK
- •CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
- •NEUROGENIC SHOCK
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI)
- •CENTRAL LINE INFECTIONS
- •WOUND INFECTION (SURGICAL SITE INFECTION)
- •NECROTIZING FASCIITIS
- •CLOSTRIDIAL MYOSITIS
- •SUPPURATIVE HIDRADENITIS
- •PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS
- •PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTICS
- •PAROTITIS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •CHEST
- •ABDOMEN
- •MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •OVERVIEW
- •CHOLECYSTOKININ (CCK)
- •SECRETIN
- •GASTRIN
- •SOMATOSTATIN
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •GROIN HERNIAS
- •HERNIA REVIEW QUESTIONS
- •ESOPHAGEAL HIATAL HERNIAS
- •PRIMARY SURVEY
- •SECONDARY SURVEY
- •TRAUMA STUDIES
- •PENETRATING NECK INJURIES
- •MISCELLANEOUS TRAUMA FACTS
- •PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD)
- •DUODENAL ULCERS
- •GASTRIC ULCERS
- •PERFORATED PEPTIC ULCER
- •TYPES OF SURGERIES
- •STRESS GASTRITIS
- •MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME
- •ESOPHAGEAL VARICEAL BLEEDING
- •BOERHAAVE’S SYNDROME
- •ANATOMY
- •GASTRIC PHYSIOLOGY
- •GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
- •GASTRIC CANCER
- •GIST
- •MALTOMA
- •GASTRIC VOLVULUS
- •SMALL BOWEL
- •APPENDICITIS
- •CLASSIC INTRAOPERATIVE QUESTIONS
- •APPENDICEAL TUMORS
- •SPECIFIC TYPES OF FISTULAS
- •ANATOMY
- •COLORECTAL CARCINOMA
- •COLONIC AND RECTAL POLYPS
- •POLYPOSIS SYNDROMES
- •DIVERTICULAR DISEASE OF THE COLON
- •ANATOMY
- •ANAL CANCER
- •ANATOMY
- •TUMORS OF THE LIVER
- •ABSCESSES OF THE LIVER
- •HEMOBILIA
- •ANATOMY
- •PHYSIOLOGY
- •PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- •DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
- •BILIARY SURGERY
- •OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE
- •CHOLELITHIASIS
- •ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS
- •ACUTE ACALCULOUS CHOLECYSTITIS
- •CHOLANGITIS
- •SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS
- •GALLSTONE ILEUS
- •CARCINOMA OF THE GALLBLADDER
- •CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS CONDITIONS
- •PANCREATITIS
- •PANCREATIC ABSCESS
- •PANCREATIC NECROSIS
- •PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST
- •PANCREATIC CARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ANATOMY OF THE BREAST AND AXILLA
- •BREAST CANCER
- •DCIS
- •LCIS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •MALE BREAST CANCER
- •BENIGN BREAST DISEASE
- •CYSTOSARCOMA PHYLLODES
- •FIBROADENOMA
- •FIBROCYSTIC DISEASE
- •MASTITIS
- •BREAST ABSCESS
- •MALE GYNECOMASTIA
- •ADRENAL GLAND
- •ADDISON’S DISEASE
- •INSULINOMA
- •GLUCAGONOMA
- •SOMATOSTATINOMA
- •ZOLLINGER-ELLISON SYNDROME (ZES)
- •MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA
- •THYROID DISEASE
- •ANATOMY
- •PHYSIOLOGY
- •HYPERPARATHYROIDISM (HPTH)
- •PARATHYROID CARCINOMA
- •SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS
- •LYMPHOMA
- •SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
- •BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS SKIN LESIONS
- •STAGING
- •INTENSIVE CARE UNIT (ICU) BASICS
- •INTENSIVE CARE UNIT FORMULAS AND TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW
- •SICU DRUGS
- •INTENSIVE CARE PHYSIOLOGY
- •HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING
- •MECHANICAL VENTILATION
- •PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE
- •LOWER EXTREMITY AMPUTATIONS
- •ACUTE ARTERIAL OCCLUSION
- •ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSMS
- •MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA
- •MEDIAN ARCUATE LIGAMENT SYNDROME
- •CAROTID VASCULAR DISEASE
- •CLASSIC CEA INTRAOP QUESTIONS
- •SUBCLAVIAN STEAL SYNDROME
- •RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS
- •SPLENIC ARTERY ANEURYSM
- •POPLITEAL ARTERY ANEURYSM
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •PEDIATRIC IV FLUIDS AND NUTRITION
- •PEDIATRIC BLOOD VOLUMES
- •FETAL CIRCULATION
- •ECMO
- •NECK
- •ASPIRATED FOREIGN BODY (FB)
- •CHEST
- •PULMONARY SEQUESTRATION
- •ABDOMEN
- •INGUINAL HERNIA
- •UMBILICAL HERNIA
- •GERD
- •CONGENITAL PYLORIC STENOSIS
- •DUODENAL ATRESIA
- •MECONIUM ILEUS
- •MECONIUM PERITONITIS
- •MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME
- •ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
- •HIRSCHSPRUNG’S DISEASE
- •MALROTATION AND MIDGUT VOLVULUS
- •OMPHALOCELE
- •GASTROSCHISIS
- •POWER REVIEW OF OMPHALOCELE AND GASTROSCHISIS
- •APPENDICITIS
- •INTUSSUSCEPTION
- •MECKEL’S DIVERTICULUM
- •NECROTIZING ENTEROCOLITIS
- •BILIARY TRACT
- •TUMORS
- •PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
- •OTHER PEDIATRIC SURGERY QUESTIONS
- •POWER REVIEW
- •WOUND HEALING
- •SKIN GRAFTS
- •FLAPS
- •SENSORY SUPPLY TO THE HAND
- •CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
- •ANATOMY
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUSES
- •ORAL CAVITY AND PHARYNX
- •FACIAL FRACTURES
- •ENT WARD QUESTIONS
- •RAPID-FIRE REVIEW OF MOST COMMON CAUSES OF ENT INFECTIONS
- •THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (TOS)
- •CHEST WALL TUMORS
- •DISEASES OF THE PLEURA
- •DISEASES OF THE LUNGS
- •DISEASES OF THE MEDIASTINUM
- •DISEASES OF THE ESOPHAGUS
- •ACQUIRED HEART DISEASE
- •CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
- •CARDIAC TUMORS
- •DISEASES OF THE GREAT VESSELS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •BASIC IMMUNOLOGY
- •CELLS
- •IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
- •OVERVIEW OF IMMUNOSUPPRESSION MECHANISMS
- •MATCHING OF DONOR AND RECIPIENT
- •REJECTION
- •ORGAN PRESERVATION
- •KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
- •LIVER TRANSPLANT
- •PANCREAS TRANSPLANT
- •HEART TRANSPLANT
- •INTESTINAL TRANSPLANTATION
- •LUNG TRANSPLANT
- •TRANSPLANT COMPLICATIONS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TERMS
- •TRAUMA GENERAL PRINCIPLES
- •FRACTURES
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA
- •DISLOCATIONS
- •THE KNEE
- •ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
- •ROTATOR CUFF
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTIONS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TUMORS
- •ARTHRITIS
- •PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS
- •HEAD TRAUMA
- •SPINAL CORD TRAUMA
- •TUMORS
- •VASCULAR NEUROSURGERY
- •SPINE
- •PEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY
- •SCROTAL ANATOMY
- •UROLOGIC DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- •RENAL CELL CARCINOMA (RCC)
- •BLADDER CANCER
- •PROSTATE CANCER
- •BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA
- •TESTICULAR CANCER
- •TESTICULAR TORSION
- •EPIDIDYMITIS
- •PRIAPISM
- •ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
- •CALCULUS DISEASE
- •INCONTINENCE
- •URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI)
- •MISCELLANEOUS UROLOGY QUESTIONS
- •Rapid Fire Power Review
- •TOP 100 CLINICAL SURGICAL MICROVIGNETTES
- •Figure Credits
- •Index
214 Section II / General Surgery |
|
|
What are the boundaries of |
1. |
Inferior epigastric vessels |
Hesselbach’s triangle? |
2. |
Inguinal ligament (Poupart’s) |
|
3. Lateral border of the rectus sheath |
|
|
Floor consists of internal oblique and the |
|
|
|
transversus abdominis muscle |
What are the layers of the |
Skin |
|
abdominal wall? |
Subcutaneous fat |
|
|
Scarpa’s fascia |
|
|
External oblique |
|
|
Internal oblique |
|
|
Transversus abdominus |
|
|
Transversalis fascia |
|
|
Preperitoneal fat |
|
|
Peritoneum |
|
|
Note: All three muscle layer aponeuroses |
|
|
|
form the anterior rectus sheath, with |
|
|
the posterior rectus sheath being |
|
|
deficient below the arcuate line |
What is the differential |
Hernia, ENDOMETRIOMA |
|
diagnosis for a mass in a |
|
|
healed C-section incision? |
|
|
GROIN HERNIAS |
|
|
|
|
|
What is the differential |
Lymphadenopathy, hematoma, seroma, |
|
diagnosis of a groin mass? |
abscess, hydrocele, femoral artery |
|
|
aneurysm, EIC, undescended testicle, |
|
|
sarcoma, hernias, testicle torsion |
|
DIRECT INGUINAL HERNIA |
|
|
|
|
|
What is it? |
Hernia within the floor of Hesselbach’s |
|
|
triangle, i.e., the hernia sac does not |
|
|
traverse the internal ring (think directly |
|
|
through the abdominal wall) |
|
What is the cause?
What is the incidence?
What nerve runs with the spermatic cord in the inguinal canal?
Acquired defect from mechanical breakdown over the years
1% of all men; frequency increases with advanced age
Ilioinguinal nerve

Chapter 36 / Hernias 215
INDIRECT INGUINAL HERNIA
What is it?
What is the cause?
What is the incidence?
How is an inguinal hernia diagnosed?
Hernia through the internal ring of the inguinal canal, traveling down toward the external ring; it may enter the scrotum upon exiting the external ring (i.e., if complete); think of the hernia sac traveling indirectly through the abdominal wall from the internal ring to the external ring
Internal ring
External ring
Patent processus vaginalis (i.e., congenital)
5% of all men; most common hernia in both men and women
Relies mainly on history and physical exam with index finger invaginated into the external ring and palpation of hernia; examine the patient standing up if diagnosis is not obvious
(Note: if swelling occurs below the inguinal ligament, it is possibly a femoral hernia)
What is the differential diagnosis of an inguinal hernia?
What is the risk of strangulation?
Lymphadenopathy, psoas abscess, ectopic testis, hydrocele of the cord, saphenous varix, lipoma, varicocele, testicular torsion, femoral artery aneurysm, abscess
Higher with indirect than direct inguinal hernia, but highest in femoral hernias
216 Section II / General Surgery |
|
What is the treatment? |
Emergent herniorrhaphy is indicated |
|
if strangulation is suspected or acute |
|
incarceration is present; otherwise, elective |
|
herniorrhaphy is indicated to prevent the |
|
chance of incarceration/strangulation |
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIRS |
|
|
|
Define the following |
|
procedures: |
|
Bassini |
Sutures approximate reflection of |
|
inguinal ligament (Poupart’s) to the |
|
transversus abdominis aponeurosis/ |
|
conjoint tendon |
McVay |
Cooper’s ligament sutured to transversus |
|
abdominis aponeurosis/conjoint tendon |
Lichtenstein |
“Tension-free repair” using mesh |
Shouldice |
Imbrication of the floor of the inguinal |
|
canal (a.k.a. “Canadian repair”) |
Plug and patch |
Placing a plug of mesh in hernia defect |
|
and then overlaying a patch of mesh over |
|
inguinal floor (requires few if any sutures |
|
in mesh!) |
High ligation |
Ligation and transection of indirect |
|
hernia sac without repair of inguinal floor |
|
(used only in children) |
TAPP procedure |
TransAbdominal PrePeritoneal inguinal |
|
hernia repair |
TEPA procedure |
Totally ExtraPeritoneal Approach |
What are the indications for |
1. Bilateral inguinal hernias |
laparoscopic inguinal hernia |
2. Recurring hernia |
repair? |
3. Need to resume full activity as soon as |
|
possible |
CLASSIC INTRAOPERATIVE INGUINAL HERNIA QUESTIONS |
|
|
|
What is the first identifiable |
Scarpa’s fascia (thin in adults) |
subcutaneous named layer? |
|
|
Chapter 36 / Hernias 217 |
What is the name of the sub- |
Superficial epigastric vein |
cutaneous vein that is ligated? |
|
What happens if you cut the |
Numbness of inner thigh or lateral |
ilioinguinal nerve? |
scrotum; usually goes away in 6 months |
From what abdominal |
Internal oblique muscle |
muscle layer is the cremaster |
|
muscle derived? |
|
From what abdominal muscle layer is the inguinal ligament (a.k.a. Poupart’s ligament) derived?
To what does the inguinal (Poupart’s) ligament attach?
Which nerve travels on the spermatic cord?
Why do some surgeons deliberately cut the ilioinguinal nerve?
What is in the spermatic cord (6)?
What is the hernia sac made of?
What attaches the testicle to the scrotum?
What is the most common organ in an inguinal hernia sac in men?
External oblique muscle aponeurosis
Anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle
Ilioinguinal nerve
First they obtain preoperative consent and cut so as to remove the risk of entrapment and postoperative pain
1.Cremasteric muscle fibers
2.Vas deferens
3.Testicular artery
4.Testicular pampiniform venous plexus
5.hernia sac
6.Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
Peritoneum (direct) or a patent processus vaginalis (indirect)
Gubernaculum
Small intestine
What is the most common |
Ovary/fallopian tube |
organ in an inguinal hernia |
|
sac in women? |
|

218 Section II / General Surgery |
|
What lies in the inguinal |
Round ligament |
canal in the female instead |
|
of the VAS? |
|
Where in the inguinal canal |
Anteromedially |
does the hernia sac lie in rela- |
|
tion to the other structures? |
|
What is a “cord lipoma”?
Preperitoneal fat on the cord structures (pushed in by the hernia sac); not a real lipoma; remove surgically, if feasible
What is a small outpouching of testicular tissue off of the testicle?
What action should be taken if a suture is placed through the femoral artery or vein during an inguinal herniorrhaphy?
Testicular appendage (a.k.a. the appendix testes); remove with electrocautery
Remove the suture as soon as possible and apply pressure (i.e., do not tie the suture down!)
What nerve is found on top |
Ilioinguinal nerve |
|
of the spermatic cord? |
|
|
What nerve travels within |
Genital branch of the genitofemoral |
|
the spermatic cord? |
nerve |
|
What are the borders of |
1. |
Epigastric vessels |
Hesselbach’s triangle? |
2. |
Inguinal ligament |
|
3. |
Lateral border of the rectus |
1. Epigastric vessels
3. Rectus
2.Inguinal ligament
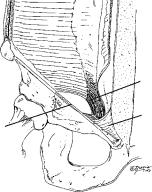
|
Chapter 36 / Hernias 219 |
What type of hernia goes |
Direct hernia due to a weak abdominal |
through Hesselbach’s |
floor |
triangle? |
|
What is a “relaxing |
Incision(s) in the rectus sheath to relax |
incision”? |
the conjoint tendon so that it can be |
|
approximated to the reflection of the |
|
inguinal ligament without tension |
What is the conjoint tendon? |
Aponeurotic attachments of the |
|
“conjoining” of the internal oblique and |
|
transversus abdominis to the pubic tubercle |
Define inguinal anatomy.
1.Inguinal ligament (Poupart’s ligament)
2.Transversus aponeurosis
3.Conjoint tendon
2
3
1
How tight should the new internal inguinal ring be?
Should allow entrance of the tip of a Kelly clamp but not a finger (the new external inguinal ring should not be tight and should allow entrance of a finger)
What percentage of the |
ZERO |
strength of an inguinal floor |
|
repair does the external |
|
oblique aponeurosis |
|
represent? |
|
FEMORAL HERNIA |
|
|
|
What is it? |
Hernia traveling beneath the inguinal |
|
ligament down the femoral canal medial |
|
to the femoral vessels (Think: FM radio, |
|
or Femoral hernia Medial) |
