
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •Brain Tumor Imaging
- •1 Introduction
- •1.1 Overview
- •2 Clinical Management
- •3 Glial Tumors
- •3.1 Focal Glial and Glioneuronal Tumors Versus Diffuse Gliomas
- •3.3 Astrocytomas Versus Oligodendroglial Tumors
- •3.4.1 Diffuse Astrocytoma (WHO Grade II)
- •3.5 Anaplastic Glioma (WHO Grade III)
- •3.5.1 Anaplastic Astrocytoma (WHO Grade III)
- •3.5.3 Gliomatosis Cerebri
- •3.6 Glioblastoma (WHO Grade IV)
- •4 Primary CNS Lymphomas
- •5 Metastatic Tumors of the CNS
- •References
- •MR Imaging of Brain Tumors
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Brain Tumors in Adults
- •2.1 Questions to the Radiologist
- •2.2 Tumor Localization
- •2.3 Tumor Malignancy
- •2.4 Tumor Monitoring
- •2.5 Imaging Protocol
- •Computer Tomography
- •2.6 Case Illustrations
- •3 Pediatric Brain Tumors
- •3.1 Standard MRI
- •3.2 Differential Diagnosis of Common Pediatric Brain Tumors
- •3.3 Early Postoperative Imaging
- •3.4 Meningeal Dissemination
- •References
- •MR Spectroscopic Imaging
- •1 Methods
- •1.1 Introduction to MRS
- •1.2 Summary of Spectroscopic Imaging Techniques Applied in Tumor Diagnostics
- •1.3 Partial Volume Effects Due to Low Resolution
- •1.4 Evaluation of Metabolite Concentrations
- •1.5 Artifacts in Metabolite Maps
- •2 Tumor Metabolism
- •3 Tumor Grading and Heterogeneity
- •3.1 Some Aspects of Differential Diagnosis
- •4 Prognostic Markers
- •5 Treatment Monitoring
- •References
- •MR Perfusion Imaging
- •1 Key Points
- •2 Methods
- •2.1 Exogenous Tracer Methods
- •2.1.1 Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI
- •2.1.2 Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI
- •3 Clinical Application
- •3.1 General Aspects
- •3.3 Differential Diagnosis of Tumors
- •3.4 Tumor Grading and Prognosis
- •3.5 Guidance for Biopsy and Radiation Therapy Planning
- •3.6 Treatment Monitoring
- •References
- •Diffusion-Weighted Methods
- •1 Methods
- •2 Microstructural Changes
- •4 Prognostic Marker
- •5 Treatment Monitoring
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •1 MR Relaxometry Techniques
- •2 Transverse Relaxation Time T2
- •4 Longitudinal Relaxation Time T1
- •6 Cest Method
- •7 CEST Imaging in Brain Tumors
- •References
- •PET Imaging of Brain Tumors
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Methods
- •2.1 18F-2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-d-Glucose
- •2.2 Radiolabeled Amino Acids
- •2.3 Radiolabeled Nucleoside Analogs
- •2.4 Imaging of Hypoxia
- •2.5 Imaging Angiogenesis
- •2.6 Somatostatin Receptors
- •2.7 Radiolabeled Choline
- •3 Delineation of Tumor Extent, Biopsy Guidance, and Treatment Planning
- •4 Tumor Grading and Prognosis
- •5 Treatment Monitoring
- •7 PET in Patients with Brain Metastasis
- •8 Imaging of Brain Tumors in Children
- •9 Perspectives
- •References
- •1 Treatment of Gliomas and Radiation Therapy Techniques
- •2 Modern Methods and Strategies
- •2.2 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy
- •2.4 Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Radiotherapy
- •2.5 Interstitial Brachytherapy
- •2.6 Dose Prescription
- •2.7 Particle Radiation Therapy
- •3 Role of Imaging and Treatment Planning
- •3.1 Computed Tomography (CT)
- •3.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- •3.3 Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- •4 Prognosis
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •1 Why Is Advanced Imaging Indispensable for Modern Glioma Surgery?
- •2 Preoperative Imaging Strategies
- •2.4 Preoperative Imaging of Function and Functional Anatomy
- •2.4.1 Imaging of Functional Cortex
- •2.4.2 Imaging of Subcortical Tracts
- •3 Intraoperative Allocation of Relevant Anatomy
- •Conclusions
- •References
- •Future Methods in Tumor Imaging
- •1 Special Editing Methods in 1H MRS
- •1.1 Measuring Glycine
- •2 Other Nuclei
- •2.1.1 Spatial Resolution
- •2.1.2 Measuring pH
- •2.1.3 Measuring Lipid Metabolism
- •2.1.4 Energy Metabolism
- •References
MR Imaging of Brain Tumors |
33 |
|
|
Fig. 28 The astrocytoma WHO grade II 2 years after surgery with residual peri-insular tumor on FLAIR (a) and T2WI (b): Some tumor areas (arrows) might be missed on FLAIR due to the T1-effect yielding intermediate signal in contrast to the hyperintense signal on T2WI
The most attention apart from contrast enhancement is given to Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
(FLAIR) sequences. Isovolumetric 3D FLAIR sequences allow for multiplanar reconstructions and obviate partial volume effects or artifacts of sequential 2D FLAIR. However, some basic physics of this sequence should be considered: FLAIR signal is not only influenced by the T2 relaxation time (T2-weighted) but also by the Tl relaxation time (Tl-weighted). Further, the contrast between gray and white matter and thus the delineation of anatomical structures may be inferior to T2WI. Therefore, signal changes may be more ambiguous on FLAIR than on T1WI and T2WI, and subtle infiltration of gray matter (cortical ribbon sign) may be less obvious compared to T2WI (Fig. 28), yielding
differentiation between tumor and vasogenic edema more difficult. Therefore, FLAIR should not replace but supplement T2WI.
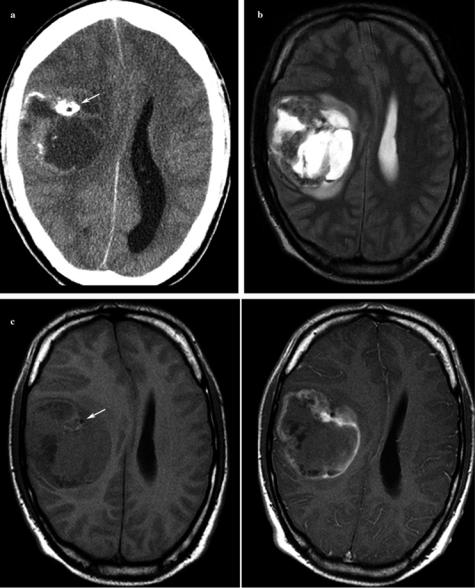
Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) detects small veins and extravascular blood products including tumorassociated microhemorrhages. Recently, it has been shown that SWI after i.v. application of contrast agent visualizes architecture of tumor vessels. Increasing numbers of small vessels and intratumoral susceptibility signals seem to be hallmarks of high-grade gliomas (Pinker et al. 2007) and help to distinguish them from lymphomas.
Computer Tomography
CCT may be indicated to detect calcification which narrows the differential diagnosis. 70–90 % of oligodendrogliomas
