
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgements
- •Contents
- •The Team
- •The Instruments
- •Patient Positioning
- •Setup for Upper Abdominal Surgery
- •Setup for Lower Abdominal Surgery
- •The Working Environment
- •Appraisal of Surgical Instruments
- •Trocars
- •Other Instrumental Requirements
- •Troubleshooting Loss of Pneumoperitoneum
- •Principles of Hemostasis
- •Control of Bleeding of Unnamed Vessels
- •Control of Bleeding of a Main Named Vessel
- •Selected Further Reading
- •2 Cholecystectomy
- •Impacted Stone (Hydrops, Empyema, Early Mirizzi)
- •Adhesions Due to Previous Upper Midline Laparotomy
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Selected Further Reading
- •The Need for Specialized Equipment
- •Access to the Liver
- •Maneuvers Common to All Laparoscopic Liver Surgery
- •Resection of Liver Tumors
- •Limited Resection of Minor Lesions
- •Left Lateral Segmentectomy
- •Right Hepatectomy
- •Patient Selection
- •Principles of Surgical Therapy in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- •Patient Positioning
- •Technique
- •Postoperative Course
- •Management of Complications
- •Paraesophageal Hernia
- •Esophageal Myotomy for Achalasia
- •Vagotomies
- •Bilateral Truncal Vagotomy
- •Highly Selective Vagotomy
- •Lesser Curvature Seromyotomy and Posterior Truncal Vagotomy
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Pyloroplasty
- •Vagotomy with Antrectomy or any Distal Gastrectomy
- •Port Placement
- •Technique
- •Locating the Perforation
- •Abdominal Washout
- •Closure of the Perforation with an Omental Patch
- •Postoperative Course
- •Selected Further Reading
- •7 Appendectomy
- •OR Setup and Port Placement
- •Technique
- •Gangrenous or Perforated Appendicitis
- •Laparoscopic Assisted Appendectomy
- •Left Hemicolectomy
- •Reversing the Hartmann Procedure
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Transabdominal Preperitoneal Repair (TAPP)
- •Patient and Port Positioning
- •Dissection of the Preperitoneal Space
- •Dissection of the Cord Structures and the Vas Deferens
- •Placement of the Mesh and Fixation
- •Closure of the Peritoneum
- •Indications
- •Technique
- •Positioning
- •Pneumoperitoneum
- •Port Placement
- •Adhesiolysis
- •Measurement of the Hernia Defect
- •Placement of Mesh
- •Difficult Ventral or Incisional Hernias
- •Pain Following Laparoscopic Ventral or Incisional Hernia Repair
- •Preoperative Requirements and Workup
- •Patient Positioning
- •Port Placement
- •Surgical Anatomy
- •Surgical Principles
- •Technique
- •Division of the Short Gastric Vessels and Exposure of the Tail of the Pancreas
- •Division of the Hilar Vessels and Phrenic Attachments
- •Extraction of the Spleen in a Bag
- •Final Steps of the Procedure
- •Control of an Unnamed Vessel
- •Control of a Major Vessel
- •Splenic Injury
- •Maneuver of Last Resort During Bleeding of the Hilar Vessels
- •Distal Splenopancreatectomy
- •Selected Further Reading
- •13 Adrenalectomy
- •Principles
- •Patient Positioning
- •Technique
- •Immediate Postoperative Complications
- •Late Postoperative Complications
- •Laparoscopic Adjustable Band
- •Technique
- •Complications
- •Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- •Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- •Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
- •Selected Further Reading
- •Monitors
- •OR Table
- •Trocar Placement and Triangulation
- •Equipment
- •Needle Holders
- •Graspers
- •Suture Material
- •Intracorporeal Knot-Tying
- •Interrupted Stitch
- •Running Stitch
- •Pirouette
- •Extracorporeal Knot-Tying
- •Roeder’s Knot
- •Endoloop
- •Troubleshooting
- •Lost Needle
- •Short Suture
- •Subject Index

Splenectomy 12
(Total and Partial) and
Splenopancreatectomy
Preoperative Requirements and Workup
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a difficult procedure that should only be performed by an experienced laparoscopic surgeon or under the direct supervision of such a surgeon. As always, the entire team should be adequately prepared.
The surgeon should check the instrument set personally to ensure that everything is available, specifically clip appliers, atraumatic graspers, liver fan retractors, and an irrigation suction machine with the capacity for hydrodissection. An open tray with a number 10 or 20 blade should be immediately available in case there is a need for conversion. Harmonic shears (Ethicon Endosurgery Inc.) are especially useful because they can reduce the number of clips used during division of the short gastric vessels, and can also function as a grasper.
It is essential that patients presenting with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) are worked up appropriately by the referring hematologists. The anesthesiologist must make sure that there is a suitable blood and platelet supply in the operating room prior to the start of the procedure.An orogastric tube is placed to decompress the stomach.
The patient should be vaccinated against pneumococcus, H. influenza and menningococcus (triple vaccine) at least 2 weeks prior to surgery.
Classic
Laparoscopic
Splenectomy
N. Katkhouda, Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery,
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-74843-4_12, © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2011
182 |
Chapter 12 Splenectomy (Total and Partial) and Splenopancreatectomy |
Patient Positioning
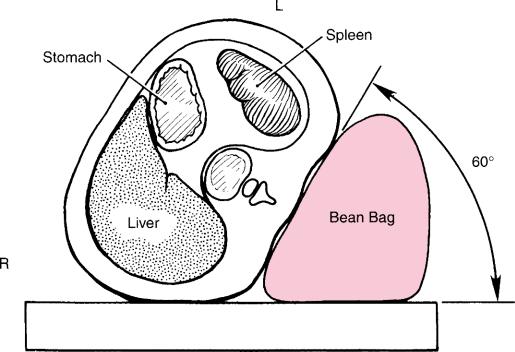
Proper patient positioning is a critical step. The patient is safely secured on a bean-bag with the left side up at a 60° angle in reverse Trendelenberg and the left arm positioned as for a left lateral thoracotomy (Fig. 12.1). This allows gravity to retract the abdominal organs and maximize the working space.This is the“hanging spleen”technique described by Delaitre and Gagner. The surgeon stands on the patient’s right side facing the left monitor, with the camera assistant on the same side sitting on a stool to his left to avoid a conflict with the elbows of the surgeon. The first assistant is on the opposite side, but the three members of the team all look at the left monitor to avoid mirror imaging and discoordination of the critical first assistant (Fig. 12.2).
When the trocars are inserted, the patient is positioned in reverse Trendelenburg. Combined with a 60° tilt, this position has two important effects. First, gravity pulls the stomach and small bowel in a rostral direction out of the operative field.Second,the spleen is kept hanging from the diaphragm by its phrenic attachments, thus placing the gastrosplenic vessels under tension, simplifying dissection and division of the vessels later in the operation (Fig. 12.3). In the anterior approach, the hilar vessels are controlled first, and the phrenic attachments are divided at the end of the operation. In contrast, with a posterior approach, the lateral attachments are divided first, the spleen is mobilized laterally and the hilar vessels are controlled later, as done in open surgery (Fig. 12.4).
Fig. 12.1 The patient’s position for laparoscopic splenectomy

Classic Laparoscopic Splenectomy |
183 |
Fig. 12.2 Operating room set up for laparoscopic splenectomy. S surgeon; FA first assistant; CA camera assistant sitting on a chair

184 |
Chapter 12 Splenectomy (Total and Partial) and Splenopancreatectomy |
a
b
c
Fig. 12.3 Effects of reverse Trendelenburg and 60° elevation: (a) splenic pedicle put under tension; (b) stomach falls down; (c) splenic flexure put under strain

Classic Laparoscopic Splenectomy |
185 |
a
b
Fig. 12.4 (a) Open splenectomy, and (b) laparoscopy (The “hanging spleen” technique). Numbers depict stages of the operation
