
- •Сontents
- •Введение
- •Introduction
- •Unit I. Introductory part
- •1. Fill in the table:
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •3. Scan the text. Political Situation in Russia in the 17th Century and Prerequisites for the Exploration of the Far East
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •5. Complete the sentences:
- ••Moscow was occupied by ___________________________ .
- •Unit II. Movement to the far east Lesson 1. Expeditions of Ivan Moskvitin and Vasily Poyarkov
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •3. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •4. Complete the sentences with the correct key vocabulary item:
- •5. Translate into English:
- •7. Scan the table. Analyze the peculiarities of the expeditions. What differences and similar features have you found?
- •9. Explain the meaning of the following expressions from the text.
- •Lesson 2. Yerofey Pavlovich Khabarov: a Successful Commercial Man and “Getter” of Russia
- •1. History test. Choose the correct variant to complete the sentences:
- •2. Read the text and explain the meaning of the word “khabar”. What does the word “khabar” mean?
- •3. Study the key vocabulary:
- •4. Match the following word-combinations with their definitions:
- •5. Make up sentences with the key phrases.
- •6. Scan the table. The Most Important Periods of y. P. Khabarov’s Biography
- •11. Find out about his Amur trip. What other trips did he undertake?
- •12. Explain why his way was shorter and better. Use maps.
- •13. Translate into Russian. Which natural riches of the Far East was Khabarov impressed by?
- •14. On your own. Use the Internet and other resources to find information about the character of y.P.Khabarov. Prove that he was a successful Russian commercial man.
- •15. Read the text and analyze all achievements of y. P. Khabarov. Explain why historians name him the “getter” of Russia.
- •Importance of Khabarov’s discoveries
- •16. Say what impressed you most in Khabarov’s fate.
- •17. Imagine you are a guide-interpreter. Make a presentation about the monument to y. Khabarov. Use the information from the text.
- •Vocabulary:
- •18. Write an essay on the following theme: “The city of Khabarovsk was named so because …”.
- •1. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Replace the following words and word-combinations by the synonyms:
- •3. Make up the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •4. Scan the text and translate into Russian the sentences with the key vocabulary. Semеn Ivanovich Dezhnev
- •5. Answer the following questions:
- •6. Complete the sentences:
- •7. True or false? Write “t” if true, “f”, if false:
- •Part II
- •Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov
- •5. Prove that:
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Fill in the table:
- •8. Look at the map. Speak how the territory of Russia changed in the 17th century due to expeditions of famous Russian explorers.
- •9. Make a presentation about one of five famous explorers of the Far East.
- •1. Study the key-vocabulary:
- •2. Replace the following words and word-combinations by the synonyms:
- •3. Fill in the correct key word or word-combination:
- •3. Make up the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •4. Scan the text and translate into Russian the sentences with the key vocabulary. Albazin Fortress
- •Lesson 5. Fatal Consequences of the Nerchinsk Treaty
- •Нерчинский трактат
- •9. Replace the following words and word-combinations by the antonyms:
- •10. Complete the following sentences with the correct key word or word-combination:
- •11. Make up the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •12. Scan the text. Political Situation in the Far East
- •13. Look at the picture by a Chinese artist: “a battle for Albazin between Russian Cossacks and Daurs”. Explain what you see there.
- •14. Answer the following sentences:
- •Unit IV. Peter’s age in the far east
- •Alexey Mikhailovich and Nataliya Naryshkina
- •Alexey Mikhailovich and Maria Miloslavskaya
- •Lesson 6. Development of the Far Eastern Lands by Peter I
- •1. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Complete the following sentences with the correct key word or word-combination:
- •3. Translate into English:
- •4. Make up the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •5. Scan the text. Achievements of Peter I in the Far East
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •Lesson 7. Okhotsk: the Major Russian Port in the Pacific
- •6. Scan the text. Okhotsk Foundation
- •Lesson 8. Expeditions of Vitus Bering
- •4. Translate into English:
- •5. Scan the text.
- •Vitus Bering
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Complete the following sentences:
- •9. Translate into Russian:
- •10. Find on map №12 the places:
- •12. Give a summary of V. Bering’s life. Lesson 9. The First Steps to Explore the American Coast
- •1. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Explain the meaning of the following key vocabulary:
- •3. Match the words and word-combinations with their definitions:
- •4. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •5. Translate the sentences into Russian:
- •6. Scan the text. Problems with the Locals during the First Steps to Explore the American Coast
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •Unit V. Russian america Lesson 10. Political Situation in the Pacific at the End of the 18th Century
- •Influenced the appearance of the new indigenous peoples in America.
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •3. Match the following columns:
- •4. Translate into English:
- •5. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •6. Scan the text. Russian and American Frontiers
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Find in the text the sentences with the key vocabulary and translate them into Russian.
- •9. Complete the sentences:
- •Lesson 11. Functions of Russian Trade Stations on the American Shores
- •2. Replace the following words and word-combinations by the synonyms:
- •3. Match the following columns:
- •4. Find the words from the key vocabulary to match the following definitions:
- •5. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •6. Scan the text. Grigory Ivanovich Shelikhov – the Founder of Russian Business in NorthAmerica
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Write if the statement is true (t) or false (f):
- •Lesson 12.The Work of the Russian-American Company (rac)
- •Основание Российско-Американской компании
- •Vocabulary:
- •7. Make up the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •8. Scan the text. The First Russian Joint-stock Commercial Enterprise in America
- •9. Answer the following questions:
- •16. Give a summary of the text.
- •17. A) Scan the table of persons who were the Governors of the Russian American Company. B) Find on map №16 places named by them. Governors of the Russian American Company
- •Lesson 13. Reforms of Nikolay Petrovich Rezanov in Russian America
- •1. Study the key vocabulary
- •9. Answer the following questions:
- •10. Write if the statement is true (t) or false (f):
- •Lesson 14. Decline of the rac and Sale of Russian Estates in America
- •2. Replace the following words by the antonyms:
- •6. Scan the text. Why Were the Colonial Possessions of Russian America Sold?
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Prove that the territory of Russian America was practically uninhabited.
- •11. Complete the sentences:
- •Исторические факты
- •Vocabulary:
- •Популярные мифы и заблуждения о продаже Аляски
- •1.Утверждается, что в связи с известными нарушениями договора, сделка может быть оспорена и по сей день.
- •3.В российской публицистике распространяется еще один миф, который гласит, что Аляска на самом деле была не продана, а сдана в аренду на 99 лет, но ссср по каким-то причинам не потребовал её обратно.
- •Vocabulary:
- •16. Read the newspaper article. Share your point of view about the perspectives of Russian-American business relations. From Russia with Love: Tunnel to Link Siberia and Alaska
- •Vocabulary:
- •1. What do you know about the settlement of the Amur area in the 19th century? Choose a correct answer to complete a sentence.
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •3. Replace the following words with the synonyms:
- •7. Scan the text. Return of Russia to the Amur
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Complete the sentence:
- •Lesson 16. Important Discoveries of Captain Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy
- •3. Complete the sentences with the word or word-combinations from the key vocabulary :
- •4. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •5. Scan the text. The Life and Activities of the “Amur Admiral” Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Translate into Russian the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •8. Think why the first Russian ports at the Amur estuary and Sakhalin were named as Petrovsky, Nikolaevsky, Ilyinsky and Muravyovsky.
- •9. Say if the statement is true (t) or false (f):
- •10. Scan map №17. Describe the rout of the expedition of Captain g.I. Nevelskoy.
- •11. Translate an extract below. Explain what g.I. Nevelskoy guaranteed to the local population.
- •Vocabulary:
- •12. Fill in the table about the life and discoveries of Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy:
- •Lesson 17. The Activities of the Governor - General Nikolay Nikolaevich Muravyov- Amursky during His Reign in the Far East
- •2. Replace the word-combinations by the key vocabulary:
- •3. Match the following columns:
- •4. Make up sentences with the phrases from ex.3.
- •5. Scan the text. Nikolay Nikolaevich Muravyov-Amursky* - a Great Reformer of the Russian Far East
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Translate the sentences with the key vocabulary into Russian.
- •8. Complete the sentences:
- •Lesson 18. The First Raftings of the Russian People down the Amur River
- •5. Scan the text: Measures to Consolidate and Secure the Far East
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Translate into Russian sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •8. Complete the following sentences:
- •Дважды открытый
- •Lesson 19.Difficult Life of the First Russian Settlers
- •Амурское казачье войско
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Replace the following words by the antonyms:
- •3. Match the following columns:
- •4. Complete the sentence:
- •5. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •6. Scan the text. Difficult Life of the First Russian Settlers
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •A) Описание жизни первых переселенцев Николаем Михайловичем Пржевальским
- •Vocabulary:
- •B) The “World's End” Lost in Taiga
- •1. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Replace the following words by the synonyms:
- •3. Make up sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •4. Complete the sentences:
- •5. Scan the text: Demand, Design and Importance of the Trans-Siberian Railway*
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •17. Scan the articles. Prove that these educational institutions played an important role in the designing the Trans-Siberian railway. A)Khabarovsk Railway College of the Ministry of Railways
- •Far Eastern State Transportation University
- •18. Read the text. Speak about the importance of the Amur Bridge for the Far East. Amur Bridge
- •1. Study the key vocabulary:
- •2. Match the following columns:
- •3. Make up sentences with the phrases from exercise 2.
- •4. Translate into English:
- •5. Scan the text: Prerequisites for the Rapid Growth and Decay of Some Far Eastern Territories
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Translate into Russian the sentences with the key vocabulary.
- •8. Complete the following sentences:
- •The First Freemen of Khabarovsk
- •17. On your own. Use the Internet and other sources to make a list of the most popular honorable citizens of modern Khabarovsk.
- •18. A)Scan the text: Merchants’ Khabarovsk
- •19. Read the text. Династия Плюсниных
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Николай Иванович Тифонтай
- •Vocabulary:
- •Торговый Дом «Кунст и Альберс»
- •Vocabulary:
- •Lesson 22. Contribution of Governors-General to the Development of the Far Eastern Lands
- •Protected person b) maker of somebody’s ideas in reality c)successor
- •5. Scan the text: General - Governorship in the Far East
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •6. Speak about the Governors-General of Eastern Siberia.
- •7. Study the table. Which Governors-General are familiar to you? Why?
- •8. Explain why the initials of some Governors-General are italicized.
- •9. Read the article about Nikolay Ivanovich Grodekov. Nikolay Ivanovich Grodekov (1843 – 1913)
- •Andrey Nikolayevich Korf (1831-1893)
- •14. Prove that Andrey Nikolayevich Korf was a worthy person and had not got the title of the Honorable Citizen of Khabarovsk in vain.
- •15. Write the translation of the text. Николай Львович Гондатти (1863—1945)
- •Lesson 23. Main Discoveries of Russian Scientists in the Far East
- •In the 19th –20th Centuries
- •Activity of the Priamurskiy Department of the Imperial Russian Geographic Society
- •6. Answer the following questions:
- •7. Translate into English. Исследование Сибири и Дальнего Востока
- •8. Speak about the importance of the scientific research for the development of the Far East.
- •9. Scan the texts. Richard Karlovich Maack (1825-1886)
- •Alexander Fedorovich Middendorf (1815–1894)
- •Karl Ivanovich Maximowicz (1827 - 1891)
- •Plants named after Maximowicz
- •Vladimir Klavdievich Arsenyev (1972 - 1930)
- •Arsenyev’s family home in Vladivostok has been made into a museum. The town of Arsenyev, located in Primorskiy Territory, was named after him. Dersu Uzala
- •Венюков Михаил Иванович (1832-1901)
- •11. Make up a table of scientific discoveries in the Far East.
- •1. Scan the text. The History of Khabarovsk
- •5. Give a key sentence to each paragraph and retell the text.
- •Герб города Хабаровска
- •Vocabulary:
- •11. Have a look at photos of old Khabarovsk on pages 163-171. Can you guess which modern buildings are these?
- •12. Make a presentation or a slide-show about several old and modern buildings of Khabarovsk. Compare them and tell about differences.
- •Lesson 25. The Importance of the Amur River for the Region
- •1. Scan the Statistical Data. Name the peculiarities of the Amur River. Statistical Data:
- •2. Study the key vocabulary:
- •3. Match the following columns:
- •4. Make up sentences with the word-combinations from ex.3.
- •5. Translate into English:
- •6. Scan the text: Amur River History
- •Economy of the Amur Basin
- •Major Amur tributaries are:
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Translate sentences with the key vocabulary into Russian.
- •9. Write all meanings of the word “Amur”:
- •10. Write the main dates of the Amur history and explain the events:
- •11. Speak about the history of the Amur River.
- •12. Fill in the table about the resources of the Amur River:
- •13. Watch map in the text and map №23. Determine the location of the the Amur River, its tributaties, and cities, located on its banks.
- •14. Read the articles.
- •Viktor Ishayev: “China Threatens Khabarovsk Region with New Ecological Catastrophe”
- •Китай пообещал закрыть все угрожающие загрязнением Амура заводы
- •Amur Needs un Clean-up Aid
- •15. Analyze the articles and make a list of main ecological problems of the river and measures to solve them.
- •16. Write an essay on the following topic:” Father Amur is the River of life in the Far East”. Lesson 26. Far Eastern Federal District
- •1. Scan the information.
- •Statiscical Data:
- •4. Speak about the presence of the Chinese at the Territory of the Far East. Is their presence here really dangerous?
- •5. Read the text. Khabarovsk Territory
- •Description of the flag of Khabarovsk Territory
- •Description of the Coat of Arms of Khabarovsk Territory
- •History
- •Geography
- •Economy
- •Demographics
- •Places Attractive for Tourists
- •Welcome to the Russian Far East!
- •10. Write an essay on the following theme: “What will happen to the Far East in 20 years?”
- •Vocabulary list
- •Appendix
- •Map № 8. Stanovoy Range
- •Map № 16. Russian America
- •Seminar № 2
- •Seminar № 3
- •Old buildings of khabarovsk
- •Reference sources
- •Www.Wikipedia.Org
Amur Needs un Clean-up Aid
 The United
Nations may allocate $7 million within a UN Environment Programme
(UNEP) budget for an ecological preserve on the Amur River.
On
November 24 the international supervisory board including the experts
for the UNEP project from Russia, China and Mongolia discussed in
China’s city of Harbin major issues to be addressed within the
project, named ‘Complex control in the Amur River basin’. Among
the project’s priorities, the Russian experts stressed the need to
provide ecological security to Primorye’s residents by increasing
the purity of the Amur River water and its fish resources.
The United
Nations may allocate $7 million within a UN Environment Programme
(UNEP) budget for an ecological preserve on the Amur River.
On
November 24 the international supervisory board including the experts
for the UNEP project from Russia, China and Mongolia discussed in
China’s city of Harbin major issues to be addressed within the
project, named ‘Complex control in the Amur River basin’. Among
the project’s priorities, the Russian experts stressed the need to
provide ecological security to Primorye’s residents by increasing
the purity of the Amur River water and its fish resources.
The specialists also expressed the necessity to frequently exchange information gathered on the Amur River and its tributaries.
Overall, Russian experts offered eight major ecological problems to be tackled within the project. All of the suggested items were accepted by Chinese and Mongolian experts for consideration.
“Russia took the initiative at the meeting since the country’s Kabarovsk region is located at the river’s lower course and we experience in full the negative effects of its pollution,” cited the Head of the region’s Department of Natural Resources Sergei Andriyenko.
To receive the money for the project, the three participating countries must conduct a cross-border analysis of the Amur River to receive the UN grant for the Amur clean-up. At the next working session to be held in the Chinese town of Heihe in January 2007, the project participants will choose the ecological issues which will top the agenda.
The river, according to experts, has been suffering from rampant pollution for many years. Public attention to ecological problems on the Amur River was greatly increased last December, when it became contaminated by a toxic slick of chemicals which reached it from the Songhua River.
The explosion at a petrochemical factory in the Chinese city of Jilin resulted in 100 tons of benzene spilling into the Songhua River. The previous UNEP ecological projects implemented in the Far East are those in Primorye’s Khanka Lake and in Mongolia’s Daurian Steppe zone, which are the parts of the Amur River basin. The neighboring countries of Mongolia, Russia and China participated in both projects, which did not, however, receive wide attention.
Combined reports
|
|
|
|
15. Analyze the articles and make a list of main ecological problems of the river and measures to solve them.
16. Write an essay on the following topic:” Father Amur is the River of life in the Far East”. Lesson 26. Far Eastern Federal District
1. Scan the information.
Statiscical Data:
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Siberia and the Pacific Ocean.
|
|
The Far Eastern Federal District is the largest of the seven federal districts of Russia. With a population of over 6, 8 million (4,7% of the total popularion in the RF), the Far Eastern FD is the least populated federal district of Russia.
The Far Eastern FD was established in 2000 by President Vladimir Putin and is being governed by a presidential envoy. The Far Eastern FD covers the territory of the Russian Far East and is subdivided into republics that enjoy a high degree of autonomy on most issues. Many of these correspond to some of Russia's ethnic minorities.
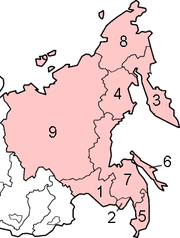 Federal
subjects
Federal
subjects
Subjects of the Far Eastern Federal District: 1.Amur Oblast (Blagoveshchensk), 2.Jewish Autonomous Oblast (Birobidzhan), 3.Kamchatka Territory (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky), 4.Magadan Oblast (Magadan), 5.Primorskiy Terrotory (Vladivostok), 6.Sakhalin Oblast (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk), 7.Khabarovsk Terrotory (Khabarovsk), 8.Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (Anadyr), 9.Sakha Republic (Yakutsk);
Интересные факты о Дальнем Востоке:
• С 1992 усилился отток населения Дальнего Востока в западные регионы России. За 14 лет население региона сократилось более чем на 1 млн. человек.
• В связи с сокращением населения на юг Дальнего Востока хлынула дешёвая рабочая сила — китайцы, в основном рабочие и крестьяне.
• На Дальнем Востоке ещё с начала 1990-х гг. намечалось построить 2 АЭС — близ Хабаровска и Уссурийска, чтобы обеспечивать дешёвой электроэнергией не только Россию, но и Китай, однако большинство населения отрицательно относится к подобным проектам.
• К 2008 году планируется завершить строительство газо - и нефтепровода «Восточная Сибирь — Тихий океан» (ВСТО).
• Самый большой по территории регион ДВ — Якутия, а самый маленький — Еврейская автономная область. Наиболее населён Приморский край, наименее — Чукотский автономный округ.
• На шельфе острова Сахалин найдены большие запасы нефти.
• В 1920—1922 на территории Российского Дальнего Востока (без Якутии) и Забайкалья существовала независимая Дальневосточная республика.
• Дальний Восток расположен во многих климатических поясах. Самая южная точка расположена на широте Дербента и Дубровника, а самая северная находится ещё севернее Барроу на Аляске.
• Если бы Дальний Восток России был независимым государством, это была бы 7-я страна мира по территории и только 97-я по численности населения.
• На всём Дальнем Востоке России проживает более, чем в 1,5 раза меньше жителей, чем в Москве.
2. Speak about the Far Eastern Federal District.
3. Read and discuss the article.
Chinese Diaspora
Facts say that there are only around 40 million Russians settled across the vast expanse of the Far East and Siberia, with only 7 million in the Far East itself. Yet now, for example, Russia’s main Pacific port and naval base of Vladivostok, once closed to foreigners, is bristling with Chinese markets, restaurants and trade houses. The expanding Chinese presence in the area has led to yellow peril-style fears of Chinese occupation. Russian newspapers publish fantastic estimates of between two and five million Chinese migrants in the Russian Far East, and predict that half of the population of Russia would be Chinese by 2050.
Russians understand hostile intent in the Chinese practice of using different names for local cities, such as Hǎishēnwǎi for Vladivostok, and a widespread folk belief states that the Chinese migrants remember the exact locations of their ancestors' ginseng patches, and seek to restore them.
The fear of the Chinese and talks about the Chinese influx are described as being less prevalent in the Russian Far East, where most of the Chinese shuttle trade is actually occurring, than in European Russia. The southern part of the Russian Far East, south of the Stanovoy Mountains, was yielded by China to Russia in the 19th century in the Treaty of Aigun and Treaty of Beijing.
Chinese historians present the treaties as being Unequal Treaties imposed on China by Russia by force, a presentation that also figures strongly in Chinese schools.



