
3troubleshootingjunos
.pdf
Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
ViewingReproductionBoot M ssag s
The slide shows an xample of an operator displaying the contents of the boot log by issuing a show syst m boot-messages command. JUNOS Software writes this file during the system boot, and the file contains the various boot-up messages
forgene ated during the last power cycle and boot or reboot.
In some cases, JUNOS Software reports hardware errors and device malfunctions at b t time. The truncated capture the slide does not show any abnormal events.
Not
JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting • Chapter 4–35
Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Not
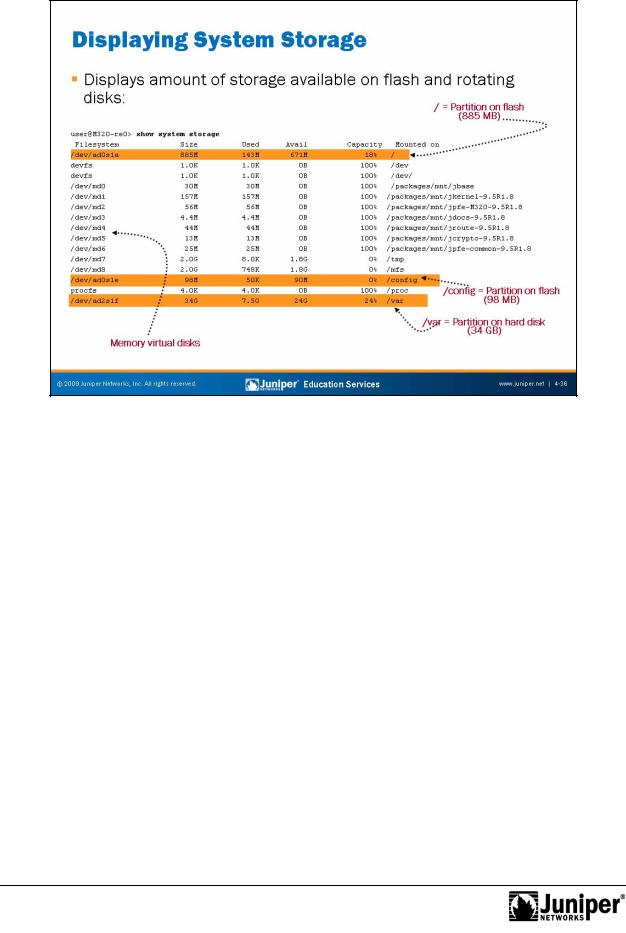
Displaying SystemReproductionStorage
The show system storage command displays the amount of storage available the flash and rotating disks. This command displays statistics about the amount of free disk space in the various file systems used by the device. Values display in 512 byte blocks. This command is equivalent to the UNIX df command.
forThe highlights on the slide indicate the device names used by the flash and rotating st age devices. In this case, the flash medium is device ad0s1a, while the hard disk is device ad2s1f. You can also see that JUNOS Software makes use of FreeBSD’s virtual ile system support to mount images of jbundle components on memory virtual disks. These RAM disk devices always indicate being 100% full because of their read-only nature.
Continued on next page.
Chapter 4–36 • JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Displaying System Storage (contd.)
Note that the output of the show system storage command might list the same flash and hard disk devices with different names due to changes in the underlying FreeBSD distribution on which the JUNOS Software version is based. For the curious, the device name ad0s1a has the following meaning:
Not |
for |
|
• ad = IDE hard disk (the flash device emulates an IDE disk).
• s1 = Slice 1 for PC BIOS partition 1.
• a = The root (/) partition. A b partition type is for swap space, while a partition type is used in dedicated mode (na ve BSD sl ce m de).
•Reproduction0 = The unit number for that device type—for example, the first IDE disk is unit 0.
Other partition types are for general use, su h as he e designation for the /config partition.
JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting • Chapter 4–37

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
|
|
|
bootedReproductionand how long it has been running; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Displaying Uptime |
|||
|
|
The show system uptime command displays the current time and information |
|||
|
|
about how long the vic , its software, and routing protocols have been running. The |
|||
|
|
following are the output fields: |
|||
|
|
• |
Cu ent time: Displays the current system time in UTC; |
||
|
|
• |
System booted: Displays the date and time when the device last |
||
|
|
• |
Protocols started: Displays the date and time when the routing |
||
Not |
|
protocols last started and how long they have been running; |
|||
• |
Last configured: Displays the date and time a configuration last |
||||
|
|
foractivated (either by booting the device or issuing the commit command |
|||
|
|
|
in configuration mode); |
||
|
|
• |
Time: Displays the current time, in the local time zone; |
||
|
|
• |
Up: Displays how long the device has been operational; |
||
|
|
• |
user: Displays the number of users logged into the device; and |
||
|
|
• |
load averages: Displays the load averages for the last 1 minute, 5 |
||
|
|
|
minutes, and 15 minutes. |
||
Continued on next page.
Chapter 4–38 • JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Display Users
|
The show system users command displays the currently logged in users, and |
|
|
displays what they are doing. The example on the slide shows that the root user is |
|
|
logged in at a c-shell while the lab user is in the CLI. Knowing that folks are actively |
|
|
logged into the device might factor in to a decision to perform disruptive actions like |
|
|
software upgrades. Note that the terminal name for a console port begins with d, |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
|
while virtual terminal (vty) ports, such as result from Telnet or SSH connections, use |
|
|
p-style tty connections. This information is helpful when the goal is to disco ect a |
|
|
user with the request system logout user command because you must specify |
|
|
both the user name and the related terminal port, unless you use the all keyword. |
|
Not |
for |
|
|
|
|
JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting • Chapter 4–39

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Not
Parsing SystemReproductionLogs
The slide shows exampl s of how you can use the CLI to rapidly locate signs of trouble within a given log file. The syslog samples shown the slide come from the messages file. The samples illustrate how you can use the CLI match function,
which allows you to easily and effectively parse the system log files. for
Chapter 4–40 • JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
|
|
|
Reproduction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Case Study |
|||
|
|
The slide highlights the topic we discuss next. |
|||
Not |
for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting • Chapter 4–41
Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
forhow a pa ticularReproductiontechnician decides to approach a problem always remains. Put another way, two individuals working with the same sets of tools and a common
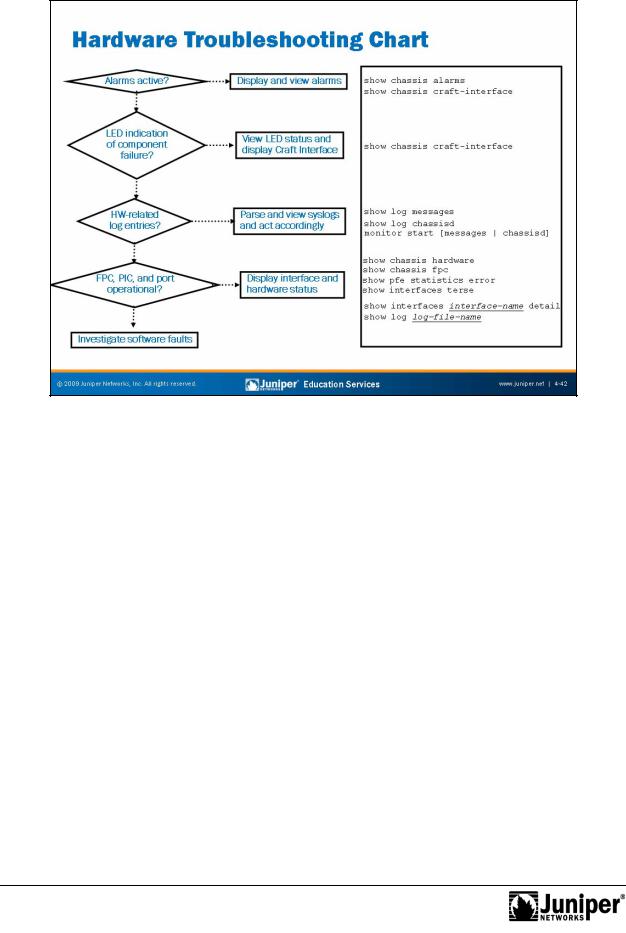
Hardware Troubl shooting Flow Chart
Troubleshooting is an artfully appli |
science. The intent of this statement is to |
highlight that even though many asp |
cts of fault isolation have a basis in |
straightforward facts and physics, a certain degree of artistic license that determines |
|
symptom might approach the act of fault analysis in completely different ways. For example, ne pe son might always start with visual inspection while another opts to begin with interface loopback tests. In the end, it is hard to say that one approach is better than another, assuming that both individuals arrive at a similar conclusion, in a similar am unt of time, with similar levels of minimal disruption.
Not The determination that troubleshooting is a mix of science and artwork is important
because most agree that art is a subjective concept that must come from within the artist; although artistic skills and concepts can be taught, the receipt of such edification does not imply the student will actually create master artworks.
Continued on next page.
Chapter 4–42 • JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Hardware Troubleshooting Flow Chart (contd.)
|
The artistic aspect of troubleshooting and the myriad ways in which a modern |
|
|
communications device might malfunction combine to make a definitive set of |
|
|
troubleshooting steps and procedures an unobtainable goal. The purpose of the |
|
|
hardware troubleshooting flow-chart shown on the slide is simply to provide a set of |
|
|
high-level steps designed to get you started with hardware fault analysis. Note that |
|
|
reasonable people might disagree the exact ordering of the steps or on the |
|
|
particulars of the CLI commands that you could use to help isolate a hardware failure |
|
|
(for example, some might prefer the extensive switch to the show i terfaces |
|
|
command, while the sample chart calls out the terse and detail switches). |
|
|
for |
Reproduction |
Not |
|
|
|
|
|
JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting • Chapter 4–43

Troubleshooting JUNOS Platforms
Not
The slide sets the stage for a sample hardware troubleshooting case study. We begin with the general description of the problem, which in this case indicates that you see high speed link (HSL) errors as reported in the system log file. The HSL interconnects
forthe FPC, the PFE, the SIB, and the midplane of the M320 router. In addition to HSL error messages, SIB 3 goes offline and becomes unusable for forwarding the traffic. In fact, a sho t time, all FPCs that are still trying to use SIB 3 to send traffic through the switch fab ic generate destination errors as illustrated the slide.
Hardware CaseReproductionStudy A: Part 1
Chapter 4–44 • JUNOS Platforms Hardware Troubleshooting
