
- •Методические указания для студентов по направлению
- •140100 Теплотехника и теплоэнергетика
- •1 The Paradigm Shift Reading
- •I. Read the following international words:
- •Idea, fundamental, theory, centre, system, mechanical, gravitation, industrial, energy, process, nature, revolution, construct, quantum, theory.
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •III. Guess if the following statements are true or false.
- •2 Mikchail Lomonosov
- •I. Read the following international words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •IV. Fill in the blanks with the following words:
- •Pronoun one Местоимение one
- •V. Translate the sentences. Mind one.
- •VI. Fill in the gaps with: one, ones.
- •VII. Discuss with your group-mates.
- •3 Fields and Forces
- •I. Read the following key words:
- •II. Guess if the following statements are true or false.
- •III. Read and translate the text.
- •4 Thomas Alva Edison
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VIII. Answer the following questions:
- •5 The science of electricity
- •I. Read the following key words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •6 Michael Faraday
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Translate into Russian. Mind no:
- •VII. Answer the following questions:
- •Faraday’s Law.
- •Faraday’s Law.
- •7 The Electric Charge Opposite Charges and Interactions
- •I. Read the following key words: lightning, characteristic, interaction, rod, positive, negative, opposite, comb, particles, cumulonimbus, thunder.
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VII. Read and remember the following instructions. What should you do to protect yourself from lightning?
- •8 Isaak Newton
- •I. Read the following international words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •IV. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the infinitive.
- •V. Translate the following sentences. Pay attention to the infinitive constructions.
- •VI. Discuss in the group.
- •2. The theory of gravity.
- •9 Energy and its forms
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •IV. Translate the following sentences:
- •V. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the passive voice:
- •VI. Translate into Russian in writing.
- •VIII. Discuss in the group.
- •10 Electricity
- •I. Read the following key words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VIII. Arrange the scrambled words to make up sentences.
- •11 Electric power
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •IV. Translate these sentences. Find predicates in the passive voice.
- •V. Complete the text with the correct form of the verb.
- •VI. Translate the following groups of words.
- •12 Direct current and alternating current
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Test. Choose the correct variant:
- •VII. Answer the following words:
- •13 Difference between a.C. And d.C.
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Define the following terms.
- •I. Read the following words:
- •I I. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Find antonyms among the following words:
- •VII. Complete the sentences using the correct variant.
- •VI. Give an English definition for the following terms:
- •Resistance and Resistivity
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •IV. Translate the following sentences.
- •V. State to what part of speech the following words belong and translate them:
- •VI. Translate the following sentences:
- •VII. Answer the following questions:
- •14 Sources of energy
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •III. Remember these words:
- •V. Now answer these questions.
- •VI. Match these different power plants to their description.
- •VII. Translate the following words and define their part of speech:
- •VIII. Translate the following sentences.
- •15 Alternative energy
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Read what people say about different fuels and energy sources. What text is mainly about the following? Match the appropriate statement and the text.
- •VII. Questions for discussion:
- •16 Wind power
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Match components 1-8 with their functions a-h with the help of this simplified diagram of a wind turbine.
- •Read the web page and answer the questions below.
- •VIII Try this quiz. What do you know about wind turbines?
- •17 Electric motors
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VI. Answer the following questions:
- •Inside an Electric Motor
- •18 Heating system
- •I. Read the following words:
- •19 Electric Shock Safety Electric System
- •I. Read the following words:
- •II. Read and translate the text.
- •VII. Test. Choose the correct variant:
- •VIII. Questions to the text:
- •I. Complete the warnings with the words in the box.
- •II. Work in pairs. Why do the signs below have different colours and shapes? Match the examples to the signs.
- •III. Complete the instructions with the words in the box.
- •IV. Write these signs in another way.
- •VII.Work in pairs. What safety rules are in your University?
- •Reference section Numbers, times and dates
- •Common Fractions (Простые дроби)
- •Decimal Fractions (Десятичные дроби)
- •Volume/Capacity
- •36.7 Find among the following words:
- •4. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the words in bold type:
- •4. Fill in the blanks with:
- •I. Read the manual for the solar panel…
4 Thomas Alva Edison
Reading
I. Read the following words:
technical, laboratory, due, humanity, throughout, further, contribution, public, genius, widespread.
II. Read and translate the text.
T he
name of Thomas Alva Edison is widely known throughout the world. The
most famous of all his contributions was the improvement of the
electric lamp. Thus, highly appreciating Lodygin’s invention,
Edison went further and worked out a more efficient incandescent
filament lamp that was durable, cheap and suitable for the
large-scale production. It is also owing to Edison that an efficient
system of electric distribution
he
name of Thomas Alva Edison is widely known throughout the world. The
most famous of all his contributions was the improvement of the
electric lamp. Thus, highly appreciating Lodygin’s invention,
Edison went further and worked out a more efficient incandescent
filament lamp that was durable, cheap and suitable for the
large-scale production. It is also owing to Edison that an efficient
system of electric distribution
Thomas Edison was carried out, due to which the widespread use of this
(1847-1931) lamp became possible. Edison was a self-taught man, his schooling being limited to three months in a public school. In spite of this, from early childhood he displayed an intense curiosity as well as a great capacity for work and study. He began to experiment at the age of ten or eleven. Instead of a laboratory he used the cellar of his parents’ house.
Later on, Edison had to overcome many difficulties because of the lack of money and assistance. Thanks to his native genius, his capacity for work, (for months he slept no more than one or two hours a day) he headed technical research in his country and enriched humanity with his numerous inventions.
Vocabulary
III. Remember these words:
incandescent, filament, distribution, to overcome, suitable, research, to enrich, capacity.
Grammar
IV. Read the words of the same root and translate them into Russian:
to differ, different, difference, indifferent, indifference;
to act, action, interaction, active, reaction;
to accelerate, acceleration, deceleration;
to calculate, calculation, calculator.
V. Form nouns using suffixes -or, -er.
Work, translate, act, speak, steam, boil, conduct, engine, fact, heat.
VI. Form verbs using the prefix over-.
Load, throw, grow, come, estimate, power, take, heat.
VII. Complete the table
Noun |
Verb |
Company/Person |
generation |
|
generator |
transmission |
|
|
|
|
producer |
|
distribute |
|
invention |
|
|
|
|
assistant |
regulation |
|
|
|
supply |
|
Speaking
VIII. Answer the following questions:
1. How did Thomas Alva Edison improve the electric lamp?
2. At what age did he begin to experiment?
3. What can you say about his education?
4. Why did he have to overcome many difficulties?
5 The science of electricity
Reading
I. Read the following key words:
universe, head, nucleus, protons, neutrons, electrical charge, positive, negative, electricity.
II. Read and translate the text.
I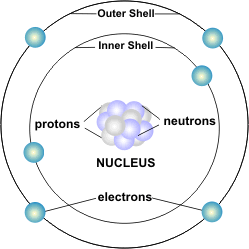 n
order to understand how electric charge moves from one atom to
another, we need to know something about atoms. Everything in the
universe is made of atoms — every star, every tree, every animal.
The human body is made of atoms. Air and water are, too. Atoms are
the building blocks of the universe. Atoms are so small that millions
of them would fit on the head of a pin.
n
order to understand how electric charge moves from one atom to
another, we need to know something about atoms. Everything in the
universe is made of atoms — every star, every tree, every animal.
The human body is made of atoms. Air and water are, too. Atoms are
the building blocks of the universe. Atoms are so small that millions
of them would fit on the head of a pin.
Atoms are made of even smaller particles. The center of an atom is called the nucleus. It is made of particles called protons and neutrons. The protons and neutrons are very small, but electrons are much, much smaller. Electrons spin around the nucleus in shells a great distance from the nucleus and are held in their shells by an electrical force.
The protons and electrons of an atom are attracted to each other. They both carry an electrical charge. An electrical charge is a force within the particle. Protons have a positive charge (+) and electrons have a negative charge (-). The positive charge of the protons is equal to the negative charge of the electrons. Opposite charges attract each other. When an atom is in balance, it has an equal number of protons and electrons. The neutrons carry no charge and their number can vary.
The number of protons in an atom determines the kind of atom, or element, it is. An element is a substance in which all of the atoms are identical (the Periodic Table shows all the known elements). Every atom of hydrogen, for example, has one proton and one electron, with no neutrons. Every atom of carbon has six protons, six electrons, and six neutrons. The number of protons determines which element it is.
Vocabulary
III. Remember these words:
particle, shell, empty, force, both, equal, to determine, hydrogen, carbon, to push, to apply.
IV. Translate the following sentences, paying attention to the words in bold type.
1. If the water is heated in a closed container, the temperature and the pressure both rise.
2. Both Lomonosov and his friend Rihman worked at atmospheric electricity. Both of them made experiments on that subject.
3. Take both a small cup of boiling water and a large container also full of boiling water; you will find that both of them have the same temperature.
Grammar
V. Find suitable attributes in (a) for the nouns in (b).
1.famous; 2.boiling; 3.glass; 4.cold; 5.scientific; 6.electrical; 7.mercury.
1.water; 2.problem; 3.thermometer; 4.device; bulb; 6.scientist; 7.point.
VI. Give the comparative and superlative forms of these adjectives.
Example: long – longer – the longest
fast __________
small __________
hot __________
dark __________
strong __________
VII. Use the comparative form of the adjectives to complete the sentences.
Example: A particle of light / small / an electron.
A particle of light is smaller than an electron.
The waves in white light /long / the waves in red light.
Maldacena’s theory of light /interesting/ Newton’s.
Nothing travels /fast/ than light.
Blue light /hot/ red light.
VIII. Complete with the comparative form of the adjectives below.
easy, famous, complete
Maldacena is an Argentine scientist. In the USA many scientists know him. He’s _______ there than in Argentina. He used other theories to make a new theory that is _______ than Newton’s and Einstein’s. Thanks to Maldacena, the structure of matter ______ to understand now than a few years ago.
IX. Read and translate the following pairs of words:
to use — use, to subject — subject, to present — present, to object — object, to increase — increase, to export —export, to transport — transport, to perfect — perfect.
