
- •TABLE OF CONTENTS
- •Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
- •The es-ice Environment
- •es-ice Meshing Capabilities
- •Tutorial Structure
- •Trimming Tutorial Overview
- •Required Files
- •Trimming Tutorial files
- •Automatic 2D Tutorial files
- •Wall Temperature Tutorial files
- •Mesh Replacement Tutorial files
- •Multiple Cylinder Tutorial files
- •Closed-Cycle Tutorial files
- •Sector Tutorial files
- •Two-Stroke Tutorial files
- •Mapping Tutorial files
- •ELSA Tutorial files
- •Chapter 2 SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+
- •Importing and Scaling the Geometry
- •Creating Features
- •Defining Surfaces
- •Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry
- •Chapter 3 GEOMETRY IMPORT AND VALVE WORK
- •Importing the Surfaces
- •Modelling the Valves
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 4 MESHING WITH THE TRIMMING METHOD
- •Modifying Special Cell Sets in the Geometry
- •Defining Flow Boundaries
- •Creating the 2D Base Template
- •Creating the 3D Template
- •Trimming the 3D Template to the Geometry
- •Improving cell connectivity
- •Assembling the Trimmed Template
- •Running Star Setup
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 5 CREATING AND CHECKING THE MESH
- •Chapter 6 STAR SET-UP in es-ice
- •Load Model
- •Analysis Set-up
- •Valve Lifts
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Cylinder
- •Port 1 and Port 2
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Cylinder
- •Port and Valve 1
- •Port and Valve 2
- •Global settings
- •Post Set-up
- •Cylinder
- •Port 1 and Port 2
- •Global settings
- •Time Step Control
- •Write Data
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 7 STAR SET-UP in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice Panel
- •Setting Solution and Output Controls
- •File Writing
- •Chapter 8 RUNNING THE STAR SOLVER
- •Running in Serial Mode
- •Running in Parallel Mode
- •Running in Parallel on Multiple Nodes
- •Running in Batch
- •Restarting the Analysis
- •Chapter 9 POST-PROCESSING: GENERAL TECHNIQUES
- •Creating Plots with the es-ice Graph Tool
- •Calculating Apparent Heat Release
- •Plotting an Indicator Diagram
- •Calculating Global Engine Quantities
- •Creating a Velocity Vector Display
- •Creating an Animation of Fuel Concentration
- •Creating an Animation of Temperature Isosurfaces
- •Chapter 10 USING THE AUTOMATIC 2D TEMPLATE
- •Importing the Geometry Surface
- •Defining Special Cell Sets in the Geometry
- •Modelling the Valves
- •Creating the Automatic 2D Template
- •Refining the 2D Template Around the Injector
- •Adding Features to the Automatic 2D Template
- •Using Detailed Automatic 2D Template Parameters
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Chapter 11 MULTIPLE-CYCLE ANALYSIS
- •Setting Up Multiple Cycles in es-ice
- •Setting Up Multiple Cycles in pro-STAR
- •Chapter 12 HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS
- •Resuming the es-ice Model File
- •Mapping Wall Temperature
- •Exporting Wall Heat Transfer Data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Cycle-averaging Wall Heat Transfer Data
- •Post-processing Wall Heat Transfer Data in pro-STAR
- •Plotting average wall boundary temperatures
- •Plotting average heat transfer coefficients
- •Plotting average near-wall gas temperature at Y-plus=100
- •Mapping Heat Transfer Data to an Abaqus Model via STAR-CCM+
- •Chapter 13 MESH REPLACEMENT
- •Preparing the File Structure
- •Rebuilding the Dense Mesh
- •Creating Ahead Files for the Dense Mesh
- •Defining Mesh Replacements
- •Setting Up Mesh Replacement in pro-STAR
- •Setting up the coarse model
- •Setting up the dense model
- •Chapter 14 MULTIPLE CYLINDERS
- •Resuming the es-ice Model File
- •Making, Cutting and Assembling the Template
- •Setting Up Multiple Cylinders
- •Checking the Computational Mesh
- •STAR Set-Up in es-ice
- •Analysis set-up
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Post Setup
- •Time Step Control
- •Write Data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Importing the Geometry
- •Generating the Closed-Cycle Polyhedral Mesh
- •Assigning shells to geometry cell sets
- •Specifying General, Events and Cylinder parameters
- •Creating a spray-optimised mesh zone
- •Importing a user intermediate surface
- •Checking the spray-optimised zone
- •Creating the closed-cycle polyhedral mesh
- •Running Star Setup
- •Creating and checking the computational mesh
- •Saving the Model File
- •Chapter 16 DIESEL ENGINE: SECTOR MODEL
- •Importing the Bowl Geometry
- •Defining the Bowl Shape
- •Defining the Fuel Injector
- •Creating the 2D Template
- •Creating the Sector Mesh
- •Creating and Checking the Mesh
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 17 DIESEL ENGINE: STAR SET-UP IN es-ice and pro-STAR
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Load model
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary conditions
- •Post setup
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the Model File
- •STAR Set-up in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice Panel
- •Selecting Lagrangian and Liquid Film Modelling
- •Setting up the Fuel Injection Model
- •Setting up the Liquid Film Model
- •Setting up Analysis Controls
- •Writing the Geometry and Problem Files and Saving the Model
- •Chapter 18 DIESEL ENGINE: POST-PROCESSING
- •Creating a Scatter Plot
- •Creating a Spray Droplet Animation
- •Chapter 19 TWO-STROKE ENGINES
- •Importing the Geometry
- •Meshing with the Trimming Method
- •Assigning shells to geometry cell sets
- •Creating the 2D template
- •Creating the 3D template
- •Trimming the 3D template to the geometry
- •Assembling the trimmed template
- •Running Star Setup
- •Checking the mesh
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary conditions
- •Post setup
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Chapter 20 MESHING WITH THE MAPPING METHOD
- •Creating the Stub Surface in the Geometry
- •Creating the 2D Base Template
- •Creating the 3D Template
- •General Notes About Edges and Splines
- •Creating Edges and Splines Near the Valve Seat
- •Creating the Remaining Edges and Splines
- •Creating Patches
- •The Mapping Process
- •Chapter 21 IMPROVING THE MAPPED MESH QUALITY
- •Creating Plastered Cells
- •Chapter 22 PISTON MODELING
- •Meshing the Piston with the Shape Piston Method
- •Chapter 23 ELSA SPRAY MODELLING
- •Importing the Bowl Geometry
- •Defining the Bowl Shape
- •Setting the Events and Cylinder Parameters
- •Creating the Spray Zone
- •Creating the Sector Mesh
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Load model
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the Model File
- •STAR Set-up in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice panel
- •Activating the Lagrangian model
- •Defining the ELSA scalars
- •Setting up the Lagrangian droplets
- •Defining boundary regions and boundary conditions
- •Setting up analysis controls
- •Adding extended data for the ELSA model
- •Writing the Geometry and Problem Files and Saving the Model

TWO-STROKE ENGINES |
Chapter 19 |
Meshing with the Trimming Method |
|
|
|
Figure 19-12 Two-stroke trimmed cylinder template
At this stage, you can also merge the vertices on small-scale edges to improve the cell connectivity:
•Ensure the VMerge drop-down menu is set to
Edges
•In the Trim panel, enter 0.05 in the box next to
the VMerge button and click VMerge
• Click Put to put the updated template back into the trim database
Assembling the trimmed template
The final stage in generating a trimmed template is to add an extrusion layer and then assemble the full model:
•In the Trim panel, set Extrusion to 0.3
•Click Assemble
•When the child process is complete, the trimmed template is loaded into the Template panel, as shown in Figure 19-13
19-12 |
Version 4.20 |
Chapter 19 |
TWO-STROKE ENGINES |
|
Meshing with the Trimming Method |
|
|
Figure 19-13 Two-stroke trimmed and assembled template
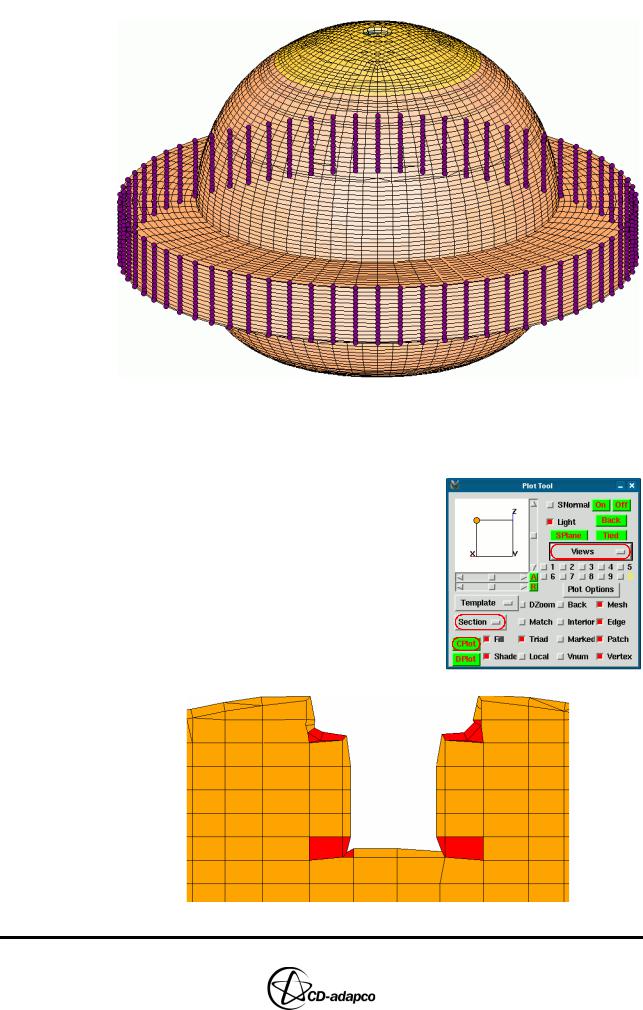
To display the extrusion layer, create a section plot through the centre of the cylinder, as shown in Figure 19-14:
•Enter the following commands to define the section, by specifying a point on the section plane and the direction of the normal to that plane:
SPoint, 0, 0, 0 SNormal, 0, 1, 0
• In the Plot Tool, change the display mode from Hidden to Section
•Set the Views option to View 0, 1, 0
Figure 19-14 Cross-section showing the extrusion layer
Version 4.20 |
19-13 |

TWO-STROKE ENGINES |
Chapter 19 |
Meshing with the Trimming Method |
|
|
|
Running Star Setup
Run Star Setup to store the geometry data obtained so far and generate the files used in pro-STAR and STAR:
•In the Select panel, click Star Setup to open the Star setup panel
•Deselect the Use unwarper toggle button
•Select the Reset smoothers toggle button
•Select pro-STAR 4.20 from the pro-STAR drop-down menu
•Click Star setup
Checking the mesh
The Create Result panel generates the computational meshes used in STAR at specified crank angles. You can then check the mesh quality and validity before starting the analysis. The following description shows how to check the computational mesh at BDC and TDC.
To create a mesh at BDC:
•In the Select panel, click Create Result
•In the Create Result panel, set Angle (deg) to 540
•Select the Interpolate toggle button
•Click Create Result to create the mesh
at 540 degrees crank angle. Note that a result.d540.0.dbs file is created in the working directory. This is a database-format file containing the mesh at the specified crank angle
19-14 |
Version 4.20 |

Chapter 19 |
TWO-STROKE ENGINES |
|
Meshing with the Trimming Method |
|
|
•When the child process is complete, click Read Result to read the mesh into the General Workspace window, as shown in Figure 19-15
•Enter command, Check, NegVolume to check that there are no cells with negative volumes
Figure 19-15 Two-stroke engine at 540 degrees crank angle
•Repeat the above process with Angle (deg) set to 720 to check the computational mesh at TDC, as shown in Figure 19-16
Figure 19-16 Two-stroke engine at 720 degrees crank angle
Version 4.20 |
19-15 |
