
- •TABLE OF CONTENTS
- •Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
- •The es-ice Environment
- •es-ice Meshing Capabilities
- •Tutorial Structure
- •Trimming Tutorial Overview
- •Required Files
- •Trimming Tutorial files
- •Automatic 2D Tutorial files
- •Wall Temperature Tutorial files
- •Mesh Replacement Tutorial files
- •Multiple Cylinder Tutorial files
- •Closed-Cycle Tutorial files
- •Sector Tutorial files
- •Two-Stroke Tutorial files
- •Mapping Tutorial files
- •ELSA Tutorial files
- •Chapter 2 SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+
- •Importing and Scaling the Geometry
- •Creating Features
- •Defining Surfaces
- •Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry
- •Chapter 3 GEOMETRY IMPORT AND VALVE WORK
- •Importing the Surfaces
- •Modelling the Valves
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 4 MESHING WITH THE TRIMMING METHOD
- •Modifying Special Cell Sets in the Geometry
- •Defining Flow Boundaries
- •Creating the 2D Base Template
- •Creating the 3D Template
- •Trimming the 3D Template to the Geometry
- •Improving cell connectivity
- •Assembling the Trimmed Template
- •Running Star Setup
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 5 CREATING AND CHECKING THE MESH
- •Chapter 6 STAR SET-UP in es-ice
- •Load Model
- •Analysis Set-up
- •Valve Lifts
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Cylinder
- •Port 1 and Port 2
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Cylinder
- •Port and Valve 1
- •Port and Valve 2
- •Global settings
- •Post Set-up
- •Cylinder
- •Port 1 and Port 2
- •Global settings
- •Time Step Control
- •Write Data
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 7 STAR SET-UP in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice Panel
- •Setting Solution and Output Controls
- •File Writing
- •Chapter 8 RUNNING THE STAR SOLVER
- •Running in Serial Mode
- •Running in Parallel Mode
- •Running in Parallel on Multiple Nodes
- •Running in Batch
- •Restarting the Analysis
- •Chapter 9 POST-PROCESSING: GENERAL TECHNIQUES
- •Creating Plots with the es-ice Graph Tool
- •Calculating Apparent Heat Release
- •Plotting an Indicator Diagram
- •Calculating Global Engine Quantities
- •Creating a Velocity Vector Display
- •Creating an Animation of Fuel Concentration
- •Creating an Animation of Temperature Isosurfaces
- •Chapter 10 USING THE AUTOMATIC 2D TEMPLATE
- •Importing the Geometry Surface
- •Defining Special Cell Sets in the Geometry
- •Modelling the Valves
- •Creating the Automatic 2D Template
- •Refining the 2D Template Around the Injector
- •Adding Features to the Automatic 2D Template
- •Using Detailed Automatic 2D Template Parameters
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Chapter 11 MULTIPLE-CYCLE ANALYSIS
- •Setting Up Multiple Cycles in es-ice
- •Setting Up Multiple Cycles in pro-STAR
- •Chapter 12 HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS
- •Resuming the es-ice Model File
- •Mapping Wall Temperature
- •Exporting Wall Heat Transfer Data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Cycle-averaging Wall Heat Transfer Data
- •Post-processing Wall Heat Transfer Data in pro-STAR
- •Plotting average wall boundary temperatures
- •Plotting average heat transfer coefficients
- •Plotting average near-wall gas temperature at Y-plus=100
- •Mapping Heat Transfer Data to an Abaqus Model via STAR-CCM+
- •Chapter 13 MESH REPLACEMENT
- •Preparing the File Structure
- •Rebuilding the Dense Mesh
- •Creating Ahead Files for the Dense Mesh
- •Defining Mesh Replacements
- •Setting Up Mesh Replacement in pro-STAR
- •Setting up the coarse model
- •Setting up the dense model
- •Chapter 14 MULTIPLE CYLINDERS
- •Resuming the es-ice Model File
- •Making, Cutting and Assembling the Template
- •Setting Up Multiple Cylinders
- •Checking the Computational Mesh
- •STAR Set-Up in es-ice
- •Analysis set-up
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Post Setup
- •Time Step Control
- •Write Data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Importing the Geometry
- •Generating the Closed-Cycle Polyhedral Mesh
- •Assigning shells to geometry cell sets
- •Specifying General, Events and Cylinder parameters
- •Creating a spray-optimised mesh zone
- •Importing a user intermediate surface
- •Checking the spray-optimised zone
- •Creating the closed-cycle polyhedral mesh
- •Running Star Setup
- •Creating and checking the computational mesh
- •Saving the Model File
- •Chapter 16 DIESEL ENGINE: SECTOR MODEL
- •Importing the Bowl Geometry
- •Defining the Bowl Shape
- •Defining the Fuel Injector
- •Creating the 2D Template
- •Creating the Sector Mesh
- •Creating and Checking the Mesh
- •Saving the Model
- •Chapter 17 DIESEL ENGINE: STAR SET-UP IN es-ice and pro-STAR
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Load model
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary conditions
- •Post setup
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the Model File
- •STAR Set-up in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice Panel
- •Selecting Lagrangian and Liquid Film Modelling
- •Setting up the Fuel Injection Model
- •Setting up the Liquid Film Model
- •Setting up Analysis Controls
- •Writing the Geometry and Problem Files and Saving the Model
- •Chapter 18 DIESEL ENGINE: POST-PROCESSING
- •Creating a Scatter Plot
- •Creating a Spray Droplet Animation
- •Chapter 19 TWO-STROKE ENGINES
- •Importing the Geometry
- •Meshing with the Trimming Method
- •Assigning shells to geometry cell sets
- •Creating the 2D template
- •Creating the 3D template
- •Trimming the 3D template to the geometry
- •Assembling the trimmed template
- •Running Star Setup
- •Checking the mesh
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary conditions
- •Post setup
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the es-ice Model File
- •Chapter 20 MESHING WITH THE MAPPING METHOD
- •Creating the Stub Surface in the Geometry
- •Creating the 2D Base Template
- •Creating the 3D Template
- •General Notes About Edges and Splines
- •Creating Edges and Splines Near the Valve Seat
- •Creating the Remaining Edges and Splines
- •Creating Patches
- •The Mapping Process
- •Chapter 21 IMPROVING THE MAPPED MESH QUALITY
- •Creating Plastered Cells
- •Chapter 22 PISTON MODELING
- •Meshing the Piston with the Shape Piston Method
- •Chapter 23 ELSA SPRAY MODELLING
- •Importing the Bowl Geometry
- •Defining the Bowl Shape
- •Setting the Events and Cylinder Parameters
- •Creating the Spray Zone
- •Creating the Sector Mesh
- •STAR Set-up in es-ice
- •Load model
- •Analysis setup
- •Assembly
- •Combustion
- •Initialization
- •Boundary Conditions
- •Time step control
- •Write data
- •Saving the Model File
- •STAR Set-up in pro-STAR
- •Using the es-ice panel
- •Activating the Lagrangian model
- •Defining the ELSA scalars
- •Setting up the Lagrangian droplets
- •Defining boundary regions and boundary conditions
- •Setting up analysis controls
- •Adding extended data for the ELSA model
- •Writing the Geometry and Problem Files and Saving the Model
SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
Chapter 2 |
Defining Surfaces |
|
|
|
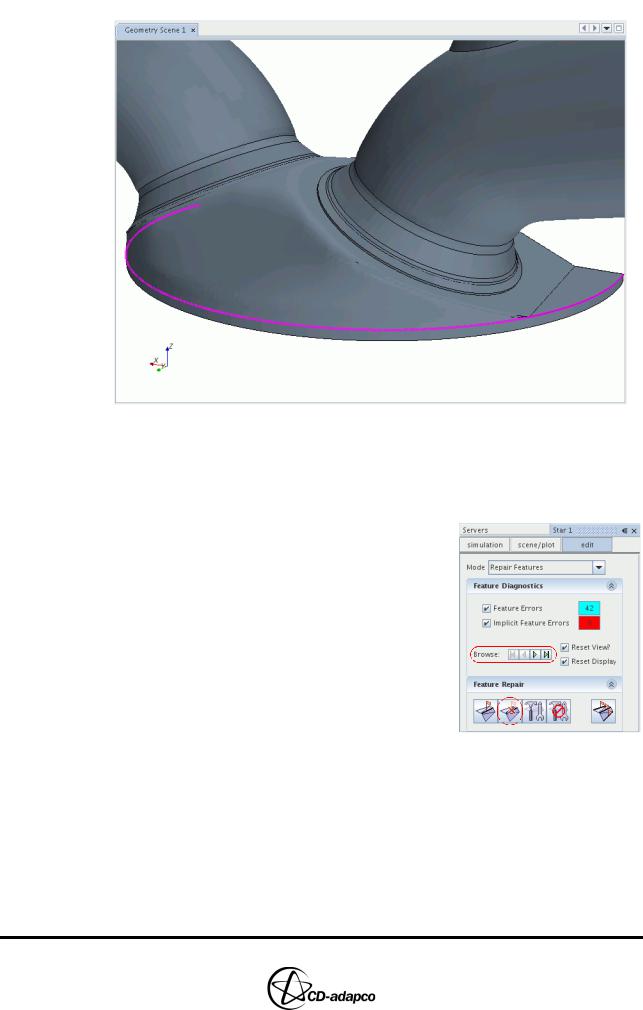
Figure 2-7 Example of missing Features between the cylinder head and liner
Next, remove unnecessary Features from the surface geometry. You can use the diagnostics tool to highlights Features that, according to the software, are likely to need removing.
•In the surface repair panel, click Start Diagnostics... Feature errors are highlighted on the surface in cyan
•Clear the checkbox next to Reset Displayed to keep displaying the entire surface
•Use the Browse buttons to cycle through the
errors and inspect them individually
• Click Unflag feature edges (or press U on the keyboard) to remove a Feature
•When complete, click Close
Defining Surfaces
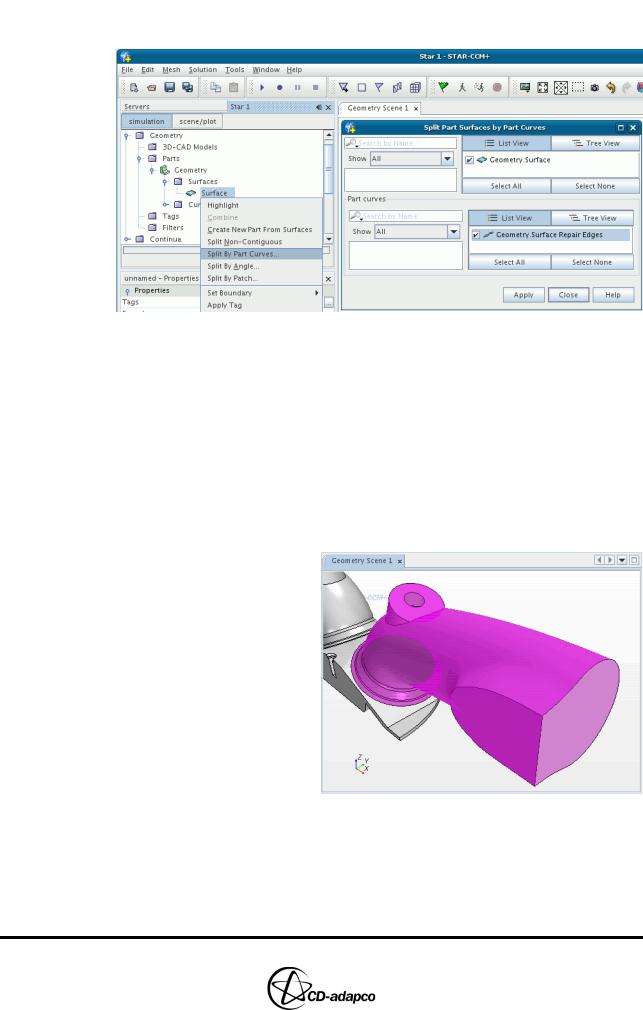
If no surface definitions were imported from the geometry, you can split the surfaces according to existing Features and then combine them to define the cylinder components.
•Expand the Geometry > Parts > Geometry > Surfaces manager, right-click the Surface node and select Split By Parts Curves...
•In the Split Part Surface by Part Curves panel, tick the part curve checkbox as shown in Figure 2-8
2-6 |
Version 4.20 |
Chapter 2 |
SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
|
Defining Surfaces |
|
|
•Click Apply and then Close
Figure 2-8 Splitting surfaces by part-curves
Next, combine the surfaces to define the engine components, that is piston, liner, cylinder head, ports, valves and spark plug. The required surfaces can be selected on either the object tree or the Graphics window. To aid grouping of the remaining surfaces, hide the combined surfaces for each component. The following steps detail the process of combining surfaces representing the intake port (Port 1) with a table summarising the surfaces for other engine components.
To combine the surfaces:
•Expand the Geometry > Parts > Geometry > Surfaces manager. Select the following nodes while holding down the <Ctrl> key:
•Surface 9
•Surface 18
•Surface 26
•Surface 27
•Surface 31
•Surface 33
•Surface 35
•Surface 40
•Surface 42
•Right-click any of the
selected surfaces in the Graphics window and select Combine
•Right-click the combined surface, select Rename... and name the surface as
Port1
•Right-click the combined surface in the Graphics window and select Hide to allow an easier selection of the intake valve
•Follow the previously described steps to continue combining surfaces. For
Version 4.20 |
2-7 |

SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
Chapter 2 |
Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry |
|
|
|
your guidance, the surfaces for each engine component are summarised in the following table:
Combined Surface |
Individual Surface |
|
|
|
Surface 2 |
|
|
|
Surface 20 |
|
|
|
Surface 21 |
|
|
Port2 |
Surface 36 |
|
|
|
Surface 37 |
|
|
|
Surface 38 |
|
|
|
Surface 39 |
|
|
|
Surface 13 |
|
|
|
Surface 14 |
|
|
Valve1 |
Surface 15 |
|
|
|
Surface 22 |
|
|
|
Surface 24 |
|
|
|
Surface |
|
|
|
Surface 10 |
|
|
Valve2 |
Surface 11 |
|
|
|
Surface 28 |
|
|
|
Surface 30 |
|
|
Combined Surface |
Individual Surface |
|
|
|
|
Intake |
Surface 19 |
|
|
|
|
Exhaust |
Surface 25 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 8 |
|
|
|
|
SparkPlug |
Surface 12 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 16 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 23 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 6 |
|
|
|
|
Head |
Surface 17 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
Surface 34 |
|
|
|
|
Liner |
Surface 29 |
|
|
||
Surface 41 |
||
|
||
|
|
|
Piston |
Surface 3 |
|
|
||
Surface 4 |
||
|
||
|
|
Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry
Typically, a valve surface mesh is of sufficiently high quality and thus more desirable than the remeshed surface. Therefore, the recommended practice is to separate the valves from the rest of the geometry.
•Press <Ctrl> key and select Geometry > Surfaces > Valve1 and Valve2
•Right-click one of the selected surfaces and select Create New Part From Surfaces (see Figure 2-9)
2-8 |
Version 4.20 |

Chapter 2 |
SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
|
Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry |
|
|
Figure 2-9 Creating a new part from the valve surfaces
•Rename Geometry > Parts > Part as Valves
The next step is to set up a Surface Remesher mesh operation and define its parameters:
•Right-click the Geometry > Operations node and select New > Automated
Mesh
•In the Create Automated Mesh Operation panel, tick the checkbox next to
Parts > Geometry
•Under Surface Meshers, select Surface Remesher and click OK
•Select the Automated Mesh > Meshers > Surface Remesher node
•In the Properties panel, set the Surface Remesher parameters as shown in Figure 2-10:
•Deselect the Perform proximity refinement checkbox
•Set Minimum face quality to 0.0
Figure 2-10 Surface Remesher properties
Version 4.20 |
2-9 |
SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
Chapter 2 |
Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry |
|
|
|
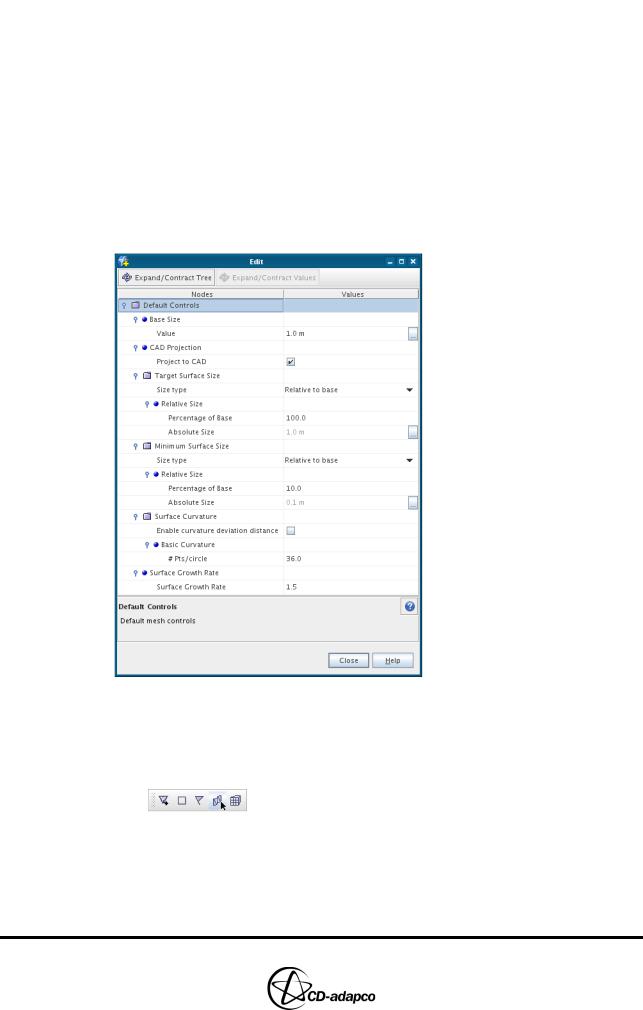
•Right-click the Operations > Automated Mesh > Default Controls node and select Edit...
•In the Edit panel, click Expand/Contract Tree to access all parameters
•Set the meshing parameters as shown in Figure 2-11:
•Set Base Size > Value to 1.0 m
•Ensure that the Project to CAD toggle button is selected
•Ensure Target Surface Size > Percentage of Base is set to 100
•Ensure Minimum Surface Size > Percentage of Base is set to 10
•Ensure that Basic Curvature > #Pts/circle is set to 36
•Set Surface Growth Rate to 1.5
•Click Close
Figure 2-11 Mesh reference values
The surface can now be meshed using the STAR-CCM+ Surface Remesher.
•In the Mesh Generation toolbar, click Generate Surface Mesh
The surface is then exported for use in are exported under two separate IDs in
es-ice. Both the Geometry and Valves parts a single database (.dbs) file.
•Right-click the Geometry > Parts > Geometry node and select Export
•In the Save panel, set Descriptions to Automated Mesh.Remesh from the drop-down menu
2-10 |
Version 4.20 |

Chapter 2 |
SURFACE PREPARATION IN STAR-CCM+ |
|
Remeshing and Exporting the Geometry |
|
|
•Set File Name to geometryRemesh, Files of Type to pro-STAR Surface mesh (*.dbs) and click Save
•In the Database Export Options panel, set Database Id to 1, Title to
Geometry and click OK
•Right-click the Geometry > Parts > Valves node and select Export
•In the Save panel, ensure that Descriptions is set to Root from the drop-down menu
•Select geometryRemesh.dbs and click Save
•In the Database Export Options panel, set Database Id to 2, Title to Valves and click OK
Version 4.20 |
2-11 |
