
- •Министерство образования и науки российской федерации
- •Английский язык.
- •Молодцова в.Е. Английский язык: Учебное пособие для студентов архитектурно-строительного факультета / Под ред. Л.А. Семашко. — Челябинск, юУрГу, 2005. — 60 с.
- •Contents
- •Unit 1. Building Construction…………………………………………... 5
- •Introduction
- •Unit 1 Building Construction
- •New words:
- •Fill in the gaps with the words given below.
- •Put the prepositions into the sentences and translate them.
- •Make up sentences out of given words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Agree or disagree with the statements.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •A) Make up the right sentences according to the model.
- •Unit 2 elements of buildings
- •New words:
- •Translate the following derived words.
- •Read the following international words. What Russian words do they associate with?
- •Find the synonyms.
- •Put the correct word into each gap.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following word combination.
- •Using the dictionary find the right translation (part b) of the word combinations (part a).
- •Put in the proper preposition (of, in, into, from, onto, to, for, between).
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to the meaning of the words ''floor'', ''stor(e)y'', ''level''.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the function and meaning of ''one'', ''ones''.
- •Find and translate the sentences in which ''one'' is used as a substitution word.
- •Compare the following pairs of sentences given in Active and Passive Voice and translate them into Russian.
- •Use the predicates of this sentences in Passive Voice and translate them.
- •Translate the following sentences. Mind the predicates in Passive Voice.
- •Read and translate the text. Elements of buildings
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Define the type of each door and window.
- •Replace the words and word combinations in italics (a) by their contextual synonyms (b).
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Give the English equivalents.
- •With your group-mates fill in the table using the text.
- •Unit 3 foundations
- •New words:
- •Mark the number of a sentence where "to be" is translated as "должен".
- •Translate the following sentences. Pay attention to different functions of the verb "to be".
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to modal verbs and their equivalents.
- •Say and write the following sentences in:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to the modal verbs.
- •Suggest the Russian equivalents.
- •Read the text and translate it in Russian. Foundations
- •There are some notes the student made after reading the text "Foundations". Did he remember everything right? Read his notes and correct them if necessary.
- •Match the beginnings of the sentences (1 – 4) to their ends (a – d) using the information from the text.
- •Caissons
- •Say the facts proving the following statements.
- •Unit 4 floors
- •New words:
- •Translate the following derived words according to the models.
- •Beams and their types
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text. Beams and their types
- •Match the definitions with the appropriate words.
- •Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •Lightweight steel beams and joists introduced
- •Unit 6 shells, trusses and space frames
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text . Shells, trusses and space frames
- •Match the definitions with the appropriate words.
- •Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •Replace the words in bold type into their contextual synonyms given below.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Identify the type of the given trusses. Explain the difference between the Pratt and the Warren truss systems.
- •With your partner, discuss the main features of trusses and space frames. Use the following words and word combinations.
- •Unit 7 Roofs
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Aluminium roofs for reservoirs and storage tanks
- •Speak directly about construction of roofs for water reservoirs using the following expressions:
- •New words:
- •Build up and translate the gerunds according to the model.
- •Translate the sentences with gerunds.
- •Translate the sentences with the Continuous Tenses.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the ing-forms.
- •Read and translate the text. Towards Industrialized Construction
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Match the beginnings of the sentences (a) with their endings (b).
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Interview your partner about the reasons of moving building construction towards industrialization. Use the following words and expressions.
- •Read and translate Text 2. From the history of building construction
- •Answer the questions to the text 2. Check your answers in accordance with the text.
- •Read the text for the second time and mark interesting facts in each part of it.
- •What is a ''rule of thumb'' technique? unit 9
- •Assembly works and time-tabling
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text. Assembly works and time-tabling
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Identify each kind of assembly works.
- •Identify the part of the building or the phase of the assembly sequence described in the sentences.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Make a list of other things that could go wrong on a building site. Say when they might occur and how they could affect the time schedule. References
New words:
attic [´ætık] чердак, мансарда
laying [´leııN] кладка
multangular [mAl´tæNgjulq] многоугольный
slope [slqVp] скат, наклон
waterproofing [´wO:tqpru:fıN] водонепроницаемый
flat roof [´flæt ru:f] плоская крыша
pitched roof [´pıtSt ru:f] скатная крыша
shed roof [Sed ru:f] односкатная крыша
gable roof [´geıbl ru:f] двускатная (щипцовая) крыша
hip roof [´hıp ru:f] четырехскатная (вальмовая) крыша
gambrel roof [´gæmbr(q)l ru:f] двускатная мансардная крыша
mansard roof [´mænsa:d ru:f] четырехскатная мансардная крыша
heat insulation теплоизоляция
atmospheric precipitates атмосферные осадки
Translate the following derived words according to the models.
Model: verb stem + ing noun
To build – строить building – здание
To cover – covering, to paint–painting
To plan – planning, to dwell – dwelling
Read the following international words and translate them into Russian.
Function, aesthetic, construction, atmospheric, solarium, park, climate, drainage, practical, triangle, material, group.
Match the words from the left column with the words in the right one.
A. heat B. precipitates
waterproofing roof
steep function
pitched appeal
atmospheric insulation
aesthetic slope
Fill in the blanks with the words given below. Translate the sentences.
New waterproof roofing materials made … more practical.
The external covering of a roof must prevent … from penetrating a building.
One type of roof coverings consists of a … film that repels water.
In the areas with dry climate … of water off the roof is of secondary importance.
… is a room or space immediately below the roof of a building.
The mansard roof have a strong … appeal.
(aesthetic, atmospheric precipitates, an attic, flat roof, waterproof, the drainage)
Read and translate the text.
ROOFS
Roof is an overhead building construction, performing carrying, waterproofing and heat insulation functions. Roofs have been constructed in a wide variety of forms as dictated by technical, economic, or aesthetic considerations.
Two main types of roofs are flat roofs and sloping ones. The flat roof has historically been widely used in the areas where the climate is dry and the drainage of water off the roof is thus of secondary importance. Flat roofs came into widespread use in Europe when new waterproof roofing materials and the use of structural steel and concrete made them more practical. Flat roofs soon became the most commonly used type to cover warehouses, office buildings, and other commercial buildings, as well as for many residential structures. Besides, the flat roof also perform other functions: it can serve as a solarium, a garden, a sport ground or even as a car park.
Sloping roofs come in many different varieties. The simplest is the shed, which has only one slope. A roof with two slopes that form an "A" or triangle is called a gable, or pitched, roof. This type of roof was used as early as the temples of ancient Greece and is still a very common form of roof. A hip, or hipped, roof is a gable roof that has slopes instead of vertical ends. It was commonly used in Italy and elsewhere in southern Europe and is now a very common form in American houses. Gable and hip roofs can also be used for homes with more complicated layouts. The gambrel roof is a type of gable roof with two slopes on each side, the upper being less steep than the lower. The mansard roof is a hipped gambrel roof, thus having two slopes on every side. It was widely used in Renaissance and Baroque French architecture. Both of the above-mentioned roof types can provide extra attic space or other room without building an entire additional floor. They can also have a strong aesthetic appeal.
The external covering of a roof must prevent rainfall or other atmospheric precipitates from penetrating a building. There are two main groups of roof coverings. One group consists of a waterproof film that repels water. The tar that is used to coat roofing felt is the prime example of this type. The other group consists of pieces of a waterproof material that are arranged in such a way as to prevent the direct passage of water through the joints between those pieces. This group includes shingles made of various materials, tiles made of clay or slate, and corrugated sheets of steel, aluminum, lead, copper or zinc.
Flat roofs are normally covered with roofing felt and tar, while sloped roofs are generally covered with shingles or sheet metal.
Match the definitions with the appropriate words.
shed a) a type of gable roof with two slopes on each side,
the upper being less steep than the lower.
gable roof b) a roof which has only one slope
hip roof c) a hipped gambrel roof having two slopes on every side.
gambrel roof d) a roof with two slopes that form an "A" or triangle
mansard roof e)a gable roof that has slopes instead of vertical ends
Find the answers to the following questions in the above text.
What are the functions of a roof?
What types are roofs divided into?
Where has flat roofs been widely used? Why?
What are the most common application of flat roofs nowadays?
What types of sloping roofs exist?
What is the aim of external roof covering?
What types of roof covering do you know?
What type of roof is usually covered with tar?
What kind of covering is used for sloping roofs?
a) Look at the picture and define the type of each roof.
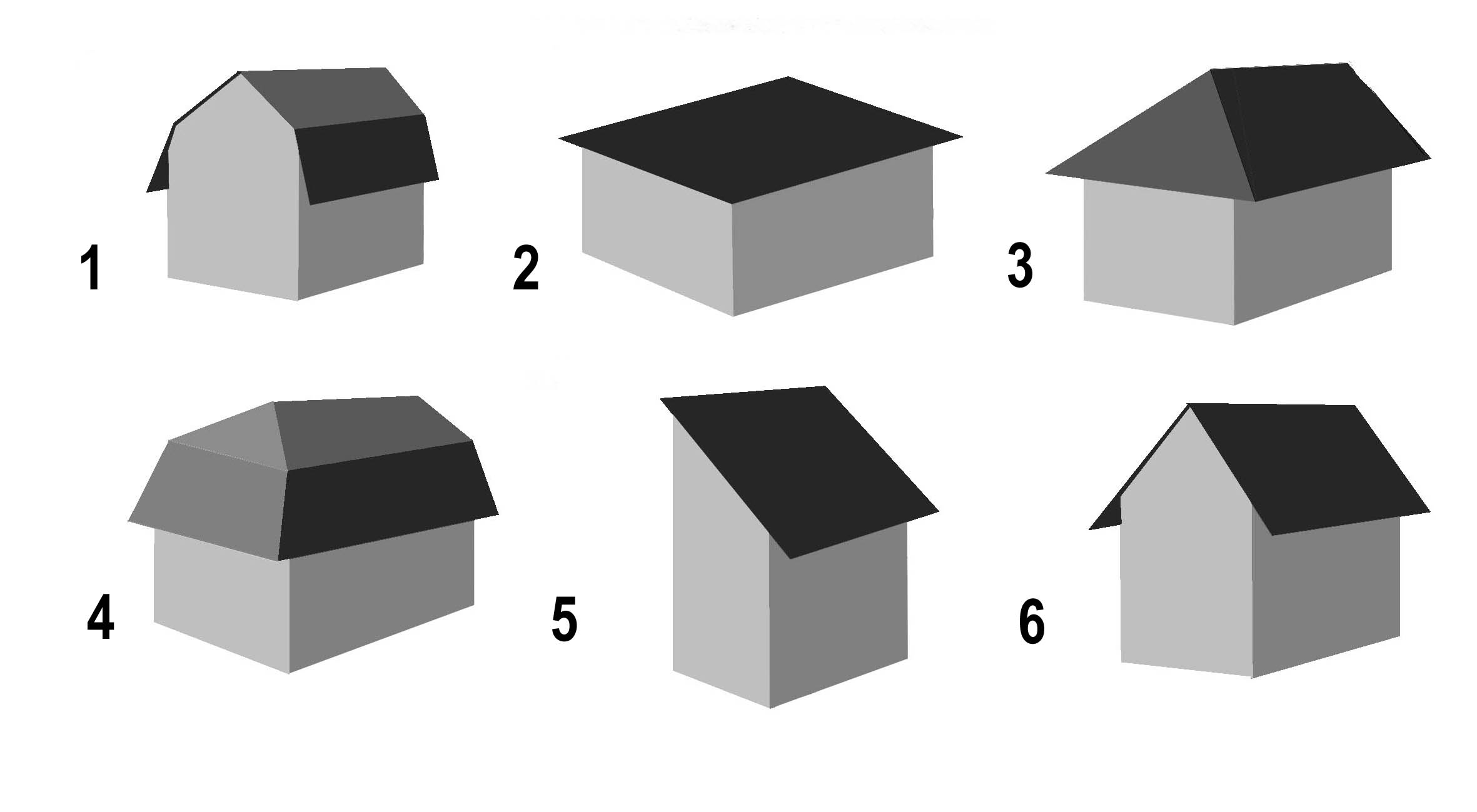
b) Think of the best type of roof for:
detached house; university building;
block of flats; bungalow;
department store; sky-scraper.
c) Explain your choice. Suggest the appropriate kind of covering.
Mark the row which contain modal verbs.
1. form, lay, locate, resist, protect, design, situate;
2. should, can, is to, need, must, may, able to;
3. span, chip, insulation, nail, moisture, material.
Fill in the blanks with a modal verb or its equivalent in the necessary form.
... I read this book? ‑ I think you ....
On Monday we ... go to the Russian Museum.
... I use a dictionary while I am translating the text? ‑ No, you ....
The lecturer ... come at 9 o´clock in the morning.
Yesterday I ... attend the parents´ meeting at school but I ... .
This worker ... train young people for work in our shop.
Professor N. ... deliver a lecture but he did not feel well and ... to come.
We ... ... ... proceed with our experiment.
They ... ... obtain better results.
They ... ... ... provide us with necessary material.
She ... ... ... ... supervise these students´ studies next week.
Answer the questions using the model.
Model: Why can´t you do it now? (to go home at once)
Because I must go home at once.
Why can´t we go away at once? (to finish my report)
Why can´t you give me both books? (to return one of them to the library)
Why can´t they use the conventional treatment of the felt deck? (the insulation layer)
Why can´t they use the both low rise roof? (the flat roof of domestic property)
Why can´t he live in his old house? (to demolish the house)
Translate the text paying attention to new words and ways of expressing the object.
