
- •Министерство образования и науки российской федерации
- •Английский язык.
- •Молодцова в.Е. Английский язык: Учебное пособие для студентов архитектурно-строительного факультета / Под ред. Л.А. Семашко. — Челябинск, юУрГу, 2005. — 60 с.
- •Contents
- •Unit 1. Building Construction…………………………………………... 5
- •Introduction
- •Unit 1 Building Construction
- •New words:
- •Fill in the gaps with the words given below.
- •Put the prepositions into the sentences and translate them.
- •Make up sentences out of given words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Agree or disagree with the statements.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •A) Make up the right sentences according to the model.
- •Unit 2 elements of buildings
- •New words:
- •Translate the following derived words.
- •Read the following international words. What Russian words do they associate with?
- •Find the synonyms.
- •Put the correct word into each gap.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following word combination.
- •Using the dictionary find the right translation (part b) of the word combinations (part a).
- •Put in the proper preposition (of, in, into, from, onto, to, for, between).
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to the meaning of the words ''floor'', ''stor(e)y'', ''level''.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the function and meaning of ''one'', ''ones''.
- •Find and translate the sentences in which ''one'' is used as a substitution word.
- •Compare the following pairs of sentences given in Active and Passive Voice and translate them into Russian.
- •Use the predicates of this sentences in Passive Voice and translate them.
- •Translate the following sentences. Mind the predicates in Passive Voice.
- •Read and translate the text. Elements of buildings
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Define the type of each door and window.
- •Replace the words and word combinations in italics (a) by their contextual synonyms (b).
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Give the English equivalents.
- •With your group-mates fill in the table using the text.
- •Unit 3 foundations
- •New words:
- •Mark the number of a sentence where "to be" is translated as "должен".
- •Translate the following sentences. Pay attention to different functions of the verb "to be".
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to modal verbs and their equivalents.
- •Say and write the following sentences in:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to the modal verbs.
- •Suggest the Russian equivalents.
- •Read the text and translate it in Russian. Foundations
- •There are some notes the student made after reading the text "Foundations". Did he remember everything right? Read his notes and correct them if necessary.
- •Match the beginnings of the sentences (1 – 4) to their ends (a – d) using the information from the text.
- •Caissons
- •Say the facts proving the following statements.
- •Unit 4 floors
- •New words:
- •Translate the following derived words according to the models.
- •Beams and their types
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text. Beams and their types
- •Match the definitions with the appropriate words.
- •Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •Lightweight steel beams and joists introduced
- •Unit 6 shells, trusses and space frames
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text . Shells, trusses and space frames
- •Match the definitions with the appropriate words.
- •Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •Replace the words in bold type into their contextual synonyms given below.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Identify the type of the given trusses. Explain the difference between the Pratt and the Warren truss systems.
- •With your partner, discuss the main features of trusses and space frames. Use the following words and word combinations.
- •Unit 7 Roofs
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Aluminium roofs for reservoirs and storage tanks
- •Speak directly about construction of roofs for water reservoirs using the following expressions:
- •New words:
- •Build up and translate the gerunds according to the model.
- •Translate the sentences with gerunds.
- •Translate the sentences with the Continuous Tenses.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the ing-forms.
- •Read and translate the text. Towards Industrialized Construction
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Match the beginnings of the sentences (a) with their endings (b).
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Interview your partner about the reasons of moving building construction towards industrialization. Use the following words and expressions.
- •Read and translate Text 2. From the history of building construction
- •Answer the questions to the text 2. Check your answers in accordance with the text.
- •Read the text for the second time and mark interesting facts in each part of it.
- •What is a ''rule of thumb'' technique? unit 9
- •Assembly works and time-tabling
- •New words:
- •Read and translate the text. Assembly works and time-tabling
- •Fill in the gaps with the appropriate words.
- •Identify each kind of assembly works.
- •Identify the part of the building or the phase of the assembly sequence described in the sentences.
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Make a list of other things that could go wrong on a building site. Say when they might occur and how they could affect the time schedule. References
There are some notes the student made after reading the text "Foundations". Did he remember everything right? Read his notes and correct them if necessary.
The loads that a structure imposes on the ground normally reach the ground through walls, piers, or columns.
Foundations are strong bases of buildings, usually lying below ground level, on which they are built up.
According to the old classification, foundations can be divided into spread (shallow) and deep.
Box footings provide foundations equal to the whole area of the substructure.
Deep excavation is necessary for piling.
For tall buildings grillages of timber beams were used.
Buoyancy principle means creating open basements below ground level of sufficient volume to displace a weight of earth.
Match the beginnings of the sentences (1 – 4) to their ends (a – d) using the information from the text.
An ideal stratum have rarely been found ... .
Shallow foundations spread the load fairly near the surface… .
These piles, hammered into the ground, acted as ... .
The heaviest reinforced-concrete piles. ... .
The new requirements for tall buildings were mainly met... .
columns, transmitting part of the load to firmer ground at the foot;
simply by providing each wall, pier, or column with a substantially wider base;
are nowadays cast in situ in prebored holes;
in the places where men have wanted to build;
by the substitution of grillages of steel beams for the less efficient earlier spread footing.
Define the type of the given foundations.
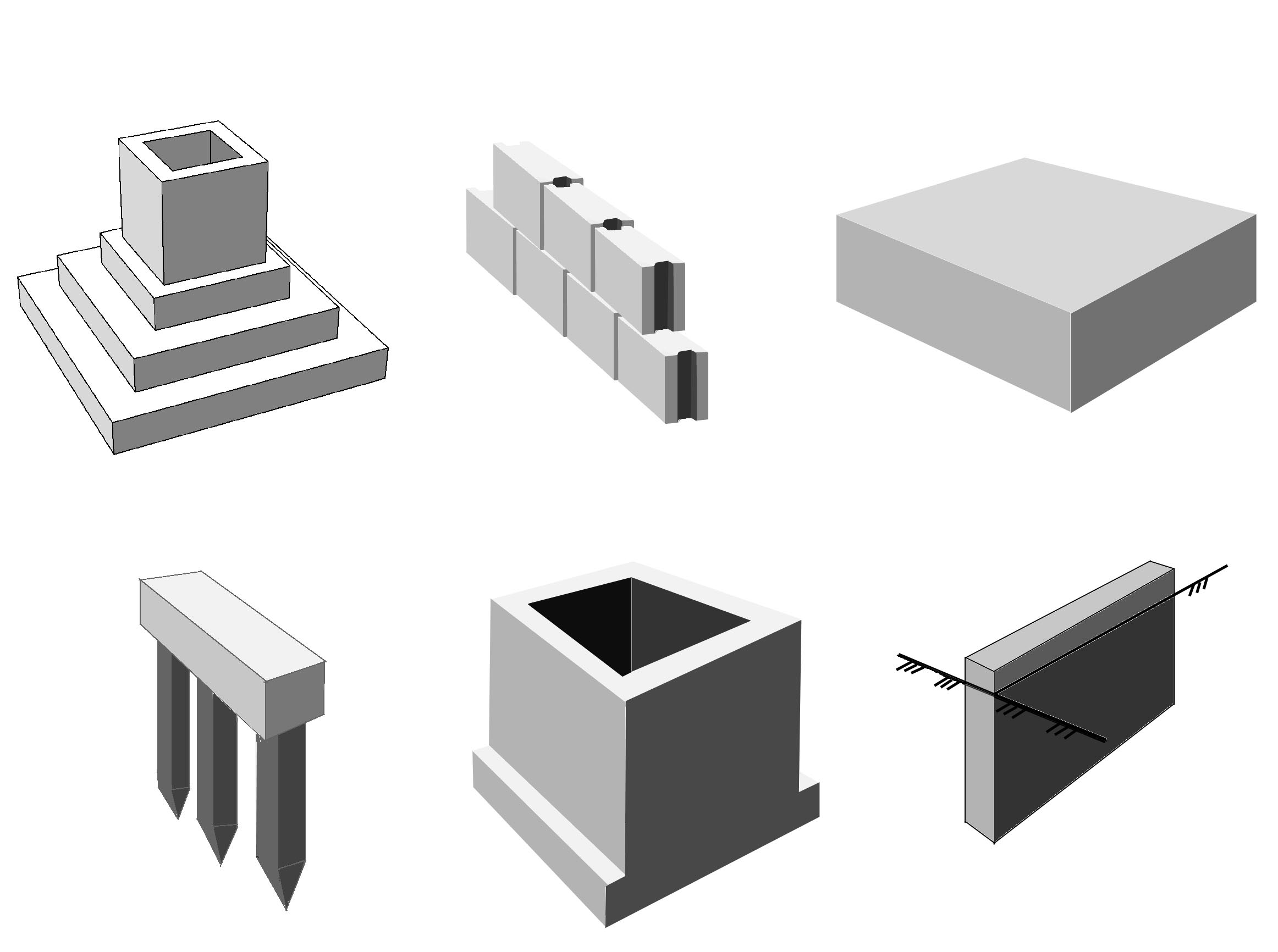
Now you have learnt some more facts about foundations. Can you answer the following questions?
1. How do the loads reach the ground?
2. What is an ideal stratum for a building?
3. What are the types of foundations according to the current classification?
4. What was used for deep underwater foundations?
5. What is used instead of spread footing?
6. How can you describe the buoyancy principle?
Your friend is revising for his examination. He asks you to help because he doesn't know the meaning of some terms. Explain these terms.
The strip footing, pile foundation, mat foundation, the buoyancy principle.
Read and translate text 2 using a dictionary if necessary.
Caissons
The word "caisson" is derived from the French word meaning "case". In civil engineering a caisson may be defined as a large watertight box used to excavations of foundations and the construction of substructures. It is an integral part of the structure. This box or caisson may be "open", without a bottom or may be excluded by air pressure, and the box becomes a pneumatic caisson. This was a development of the earlier cofferdam — a wall within which, after pumping out the water, it was possible to excavate and then build the base of the pier in the dry. The ordinary open caisson consists of a box with cross walls. Sometimes the caisson is constructed of reinforced concrete or a steel cylinder.
Say if its true or false. Use the following expressions: "That's right" or "That's true", "That's wrong" or "According to the text…".
The word "caisson" isn't of English origin.
In construction engineering a caisson is defined as a small watertight box applied to exclude water during the assembly work.
This box may be with or without a bottom.
If the box is inverted, the water may be excluded by water pump.
The common open caisson has usually a box with cross walls.
