
- •Management and Managers Менеджмент и Менеджеры
- •1.1. Words to be learned:
- •1.2. Read and translate the following international words:
- •1.3. Word-building. Translate into Russian.
- •What Is "Management"?
- •1.5. Read and render in Russian.
- •It is interesting to know that… .
- •1.6. Read the text with a dictionary and pay attention to jobs and their definitions. What is a Manager?
- •1.7. Read the text and speak about levels of management using the scheme. What are managers of all levels responsible for? Levels of Management
- •1.8. Read and learn job titles:
- •1.9. Match the jobs and their functions.
- •1.10. Here are three diagrams representing the structure of an organization. Study them and do the tasks below. Pay attention to the terms used.
- •1.11. Read the text and draw a company structure.
- •2.1. Words to be learned:
- •2.2. Read the words in (a) and find synonyms in (b).
- •2.3. Read the text with a dictionary and retell it, using the scheme. What Do Managers Do?
- •2.4. Choose the right answer:
- •2.5. Use a dictionary to complete the chart below. Mark
- •2.6. Read the text and find out:
- •2.7. Read and find out what roles a manager plays. Roles Performed by Managers
- •2.8. Read and translate with a dictionary. What role would you perform more willingly? Mintzberg's Set of Ten Roles
- •3.1. Read and translate the text. People Are the Heart of Every Business
- •Examples of Flow Charts:
- •3.2. Answer the questions:
- •3.3. Read and translate the text. Management Style
- •3.3. Answer the questions on the text.
- •4.1. Read the text and discuss in groups. Give your reasons for and against. Choose the most important items to your “hearts content” (сколько душе угодно). Leadership and Management
- •Principles of Leadership.
- •4.2. What is your opinion on the following? The Traits of an Effective Leader
- •Behaviours People Value in Leaders
- •4.4. Is your future job the right job for you? Find out by doing the quiz. What is your score? What type of personality are you? Work in pairs. Tick the statements your partner agrees with.
- •4.5. Now add up (your ticks and check your scores. Three or
- •Personality types
- •How to Effectively Manage the People?
- •5.2. Read and summarize. Add some more points if you want. How to Motivate Your Employees?
- •5.3. You're going to be a good manager, aren't you? Read the text
- •Qualities of a Good Manager
- •5.4. Choose what is most important for a true manager. Give your
- •5.5. These are the survey results. Look them through and answer the questions:
- •5.6. Read and dramatize the dialogue.
- •5.7. Answer the questions on the above dialogue:
- •5.8. Read the text and answer the questions below the text. How to Manage Managers
- •5.9. Answer the questions:
- •5.10. Study the information of the text. Can you manage time? Time Management
- •5.11. Translate the sentences using necessary words from the text "Time Management".
- •5.12. In a busy working day, it's not easy to find time to study. Discuss these questions with your classmates and plan how to manage your time.
- •6.1. Read the story below and render it in English. The Big Rocks of Time
- •6.2. Food for Thought.
- •Richard Branson's 10 secrets of success
- •6.4. Read and translate the text. Do the tasks below the text. Prestigious Business Award for Fabiola
2.5. Use a dictionary to complete the chart below. Mark
the stressed syllable in each more than one syllable word.
-
adjectives
nouns
verbs
ad′ministrator
super′visory
lead
′manager
organi′zational
employ′ee
pro′mote
pro′ductive
2.6. Read the text and find out:
a) Which skills are important at each managerial level?
b) What are the most common managers' personal characteristics?
Skills
In order to perform the functions of management and to assume
multiple roles, managers must be skilled. Robert Katz identified three managerial skills that are essential to successful management: technical, human, and conceptual. Technical skill involves process or technique knowledge and proficiency. Managers use the processes, techniques and tools of a specific area. Human skill involves the ability to cooperate and interact effectively with people. Conceptual skill involves the formulation of ideas. Managers understand abstract relationships, develop ideas, and solve problems creatively. Thus, technical skill deals with things, human skill concerns people, and conceptual skill concerns ideas.
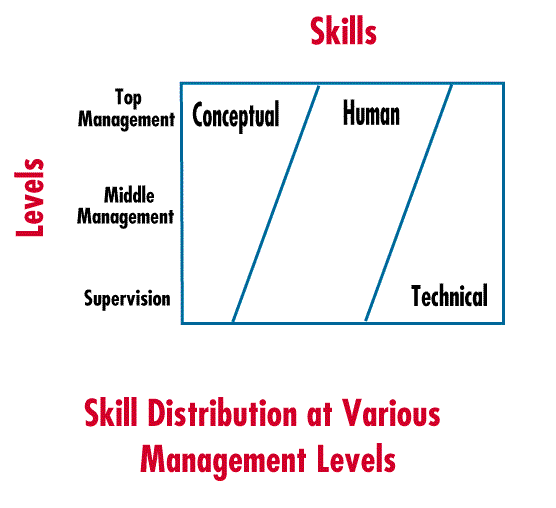
A manager's level in the organization determines the relative importance of possessing technical, human, and conceptual skills. Top level managers need conceptual skills in order to view the organization as a whole. Conceptual skills are used in planning and dealing with ideas and abstractions. Supervisors need technical skills to manage their area of specialty. All levels of management need human skills in order to interact and communicate with other people successfully.
The following are some skills and personal characteristics that are important for managers:
Leadership - ability to influence others to perform tasks
Self-objectivity - ability to evaluate yourself realistically
Analytic thinking - ability to interpret and explain information
Behavioral flexibility - ability to modify personal behavior to react objectively rather than subjectively to accomplish organizational goals
Oral communication - ability to express ideas clearly in words Written communication - ability to express clearly ideas in writing
Personal impact - ability to create a good impression and instill confidence
Resistance to stress - ability to perform under stressful condition
Tolerance for uncertainty - ability to perform in ambiguous situations.
2.7. Read and find out what roles a manager plays. Roles Performed by Managers
A manager wears many hats. Not only is a manager a team leader, but he or she is also a planner, organizer, cheerleader, coach, problem solver, and decision maker - all rolled into one. In addition, managers' schedules are usually jam-packed. Whether they're busy with employee meetings, unexpected problems, or strategy sessions, managers often find little spare time on their calendars. (And that doesn't even include responding to e-mail!)
In his classic book, The Nature of Managerial Work, Henry Mintzberg describes a set of ten roles that a manager fills. These roles fall into three categories:
Interpersonal: This role involves human interaction.
Informational: This role involves the sharing and analyzing of information.
Decisional: This role involves decision making.
