
- •Learningenglish1.Ru
- •Learningenglish1.Ru
- •Предисловие
- •Contents
- •P review
- •Look at the picture and answer the questions below.
- •Which of the following happens to you for the first time when you meet someone?
- •Can you remember when and where you met some of the following people for the first time?
- •Vocabulary 1: jobs
- •Match professions with their definitions.
- •Write down at least one job from the list that would probably be impossible for these people.
- •Look at the family tree and complete the sentences below.
- •Correct the mistakes.
- •Work with a partner. What is a phrasal verb? What makes it different from other verbs? Choose the correct alternative to complete the sentences.
- •Complete the text using the correct form of the phrasal verbs in Exercise b.
- •Who do you live with? Do other members of your family live near you, or do you have to travel to see them?
- •Read the statistics about families in the usa and the uk. How do you think the same statistics would be different in Russia?
- •Find the examples of Present tenses in the text “Modern families”.
- •Look at the verbs expressing attitude. Describe relationship between James, Louise and Richard.
- •Fill in the gaps with the most suitable words using the information from the sites:
- •Study the typical questions for Application Form.
- •You are going to visit your grandmother living abroad. You will need to fill in the application form similar to the one above. Write your answers.
- •Discuss.
- •Here are some verb phrases connected with daily routine.
- •V ocabulary 1: daily routine
- •Study the following. Sleep
- •Keeping clean
- •Evenings
- •Housework
- •Now complete some more word partnerships and expressions by matching the verbs on the left with the correct word on the right.
- •Fill in the gaps with appropriate words.
- •Read the following statements. Which do you think are true for your country? Compare your ideas in groups.
- •How we really spend our time
- •Write down four things from the text that you think are surprising or interesting. Compare with your partner.
- •Are you happy with the way you use your time? What would you like to spend more/less time doing? Discuss in groups.
- •Choose the best alternative between Past Simple or Past Progressive.
- •Read the text and open the brackets using Past Simple or Past Perfect tenses.
- •Supply the suitable form of past tenses.
- •Insert the proper words and write the questions.
- •Make up tag questions.
- •Make an embedded question or a new sentence from the question in brackets.
- •You are going to interview your partner in order to complete a similar pie-chart how he/she spends his/her time. First spend a few minutes preparing for the interview. Think about:
- •Vocabulary 2: work duties
- •Study the following. What do you do?
- •Working hours
- •Read the email and answer these questions:
- •Work in pairs. What do the people in the photos do?
- •How would you personally start job hunting? Use the phrases in the box to help you.
- •What do you remember about your first day at school or university? Describe your feelings and behavior (mind using Past Tenses).
- •Here are some “dos” and “don’ts” about how to behave in a new job. Can you tell which are which?
- •Read the article and find “dos” and “don’ts” from the list on the previous page.
- •Read the article again and find out why…
- •Vocabulary: personal traits
- •Match the descriptions in column b with the personality adjectives in column a. Use a dictionary if necessary.
- •You will hear a manager interviewing a person for a job. Listen out for these verbs, and then use them to complete sentences 1-5.
- •Listen again to the interview and complete the notes the interviewer makes.
- •Read the short extract from the interview and recognize any constructions expressing Future Actions.
- •Fill the gaps with the verb in brackets using either to be going to or will form of the future tense.
- •Put the verb into the most suitable form with future meaning, Present progressive or Present simple.
- •Put the words into the correct order paying attention to the usage of tenses denoting future actions.
- •Open the brackets paying attention to the usage of tenses denoting future actions (negative/question/affirmative forms).
- •Role-play the following situation.
- •Read Adam Hall’s Curriculum Vitae (cv).
- •What do you know about Russia? Match the above pictures 1-6 with descriptions a) – f). What information can you give about the pictures?
- •Use the dictionary to find the meaning of the following words:
- •How would you say these numbers?
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Complete the fact file about Russia.
- •Match pictures 1-4 to a)-d).
- •Look at the graph below and complete the sentences with to, at, of, by.
- •Put the parts of a sentence in the correct order and describe the graph below.
- •Read a part of a business plan and draw the graph of the rate of inflation.
- •What kind of movement do the verbs below describe? Match them to the symbols. Use some symbols more than once.
- •What do you know about Tatarstan? Do the quiz and say which of the data were surprising for you?
- •Read and translate the text. History
- •Geographical position
- •The capital
- •The government
- •Industrial regions
- •Answer questions to the text. Make up a dialogue on the basis of this information.
- •Itinerary of William Smith, trip to New York, 23-26 November
- •Tell if you agree or disagree with these quotations.
- •Match phrases 1)–8) with pictures a)-f), some of them can be used more than once:
- •We say 'on the front/on the back' of a piece of paper.
- •Study the vocabulary
- •Read and translate the dialogue.
- •What countries is English the first language? Match English-speaking countries with their national flags and capitals.
- •Do you know where English is the second official language? Rearrange the letters and read some of these countries, name their capitals.
- •Module 1 Across Britain
- •Study the vocabulary from Exercises b, e.
- •Write down the italicized phrases from the text. Match them to these uses of ‘the’.
- •With a partner study the popular activities offered to tourists in England. Choose any three you would wish to do and give arguments to support your choice. Use the language skills given above.
- •Before you read, think about main characteristics of a nation's economic system.
- •Skim-read the text and compare your answers with those offered in the text.
- •Look in the text and find the following words and phrases.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Draw the table ‘Britain’s economy over the last decades’ and complete it.
- •I. Summarize the information about Britain’s Economy. Use the headings below.
- •Make a list of all geographical names mentioned in the text. Be sure that you can read them correctly. Use dictionary if necessary.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Match the words from the text with their definitions, use vertical prompts if necessary.
- •I. What is the main point made by r. Kennedy? (4) Do you agree with him?
- •Missing word cloze quiz. Choose the correct word from 1) – 8).
- •Read Canada Profile and ask questions to the given pieces of information.
- •Verb forms change in the following way:
- •Read the text again and decide whether these statements are true or false. Correct the false ones.
- •I. Use words from each box to make word partnerships from the text:
- •Discuss the following questions in groups.
- •You will hear a radio discussion in which two students are talking about their first few weeks in higher education. First discuss these questions.
- •Listen again. For questions 1-5, choose the best answer a, b or c.
- •Vocabulary
- •Complete the sentences with the correct word. Use each word once only.
- •Match the phrasal verbs in italics in the sentences to the definitions a) – j) below.
- •Which of these would make most students happy and why?
- •Before you read, answer these questions.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Are the following statements true or false? Correct the false ones.
- •Find words in the text that mean:
- •Choose the correct answer to the following.
- •Define the paragraph that contains the following information.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Continue the following sentences using the information from the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Fill in the gaps with the necessary prepositions.
- •Find the words in the text which mean:
- •Make your sentences with the words.
- •Open the brackets by putting the adjectives and adverbs into the correct form.
- •Complete the sentences using soon, well, much, many and translate them into Russian.
- •Put the words in the right order to form a statement.
- •Complete each sentence using the information in brackets.
- •Admission
- •Business star
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Say which paragraphs contain information on:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Look through paragraphs 1, 2, 6, 7, 8, write out 6 phrasal verbs and give their Russian equivalents. Define the type each of the phrasal verbs belongs to:
- •Find in the text 9 noun chains.
- •Find in paragraphs 1, 3, 7, 8 words and word combinations with the meaning «чтобы», «чтобы не», «так, чтобы / таким образом, чтобы».
- •Say which of the following sentences presents most accurately the main idea of the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Look through paragraphs 1,2,4,7 and find 6 verbs which go with the word “business” and 4 collocations with this word. Give their Russian equivalents.
- •Say which paragraphs contain information on:
- •Say which of the following sentences presents most accurately the main idea of the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Find in the text English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Say whether the following statements are true, false or there is no information on the subject in the text.
- •Say which paragraphs contain the information on:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Find in the text words or word combinations which are equivalent in meaning to the following ones:
- •Find in the text English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Say whether the following statements are true, false or there is no information on the subject in the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following agricultural terms:
- •Find in the text English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following derivatives:
- •Find in the text 10 ed-forms of English verbs and translate them into Russian paying attention to different functions they perform in the sentences.
- •Say whether the following statements are true, false or there is no information on the subject in the text.
- •Say which paragraphs contain the information on:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Find in the text English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Say which paragraphs contain the information on:
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Find in the text English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Say whether the following statements are true, false or there is no information on the subject in the text.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Give Russian equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Find English equivalents to the following phrases:
- •Справочник по грамматике английского языка Cуществительное (The Noun)
- •Общие сведения об артиклях
- •Неопределенный артикль
- •Определенный артикль
- •Определённый артикль употребляется:
- •Артикли не употребляются:
- •Употребление определенного артикля
- •Множественное число имен существительных
- •Исключения
- •Личные местоимения
- •Притяжательные местоимения
- •Указательные местоимения
- •Вопросительные местоимения
- •Относительные местоимения
- •Возвратные местоимения
- •Неопределенные местоимения
- •Отрицательные местоимения
- •Взаимные местоимения
- •Оборот There is / There are
- •Местоимения some, any, no и их производные.
- •Имя прилагательное (The Adjective)
- •Исключения
- •Наречие (The Adverb)
- •Глагол (The Verb)
- •Основные глагольные формы
- •Инфинитив
- •Причастие I
- •Формы причастия
- •Функции причастия I
- •Причастие II
- •Функции причастия II
- •1. Определением.
- •Герундий
- •Функции герундия
- •Повелительное наклонение.
- •Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты
- •Can / could
- •To be able to
- •May / might
- •To be allowed to to be permitted to
- •To have (to)
- •Условные придаточные предложения
- •Условные предложения 0 типа
- •Условные предложения I типа
- •Союзы условных придаточных предложений.
- •Правило согласования времен
- •Косвенные вопросы
- •Косвенные команды, просьбы
- •Интернет-ресурсы, использованные при составлении учебного пособия:
- •Learningenglish1.Ru
Draw the table ‘Britain’s economy over the last decades’ and complete it.
Britain’s economy over the last decades
Period of time |
Critical activities |
over the past two decades |
|
since 1992 |
|
in the late 2008 |
|
H. Answer the following questions about the text.
How is Britain’s economy characterized in general? What is the statistic used to measure the economy? How do you understand the following – “one of the quintet of trillion dollar economies”?
The first ingredient of a nation's economic system is its natural resources. What about the UK?
What is the UK’s CB? Does the UK undertake an independent monetary policy? Is Britain a member of the euro zone?
What is the key sector of Britain’s economy? What does it cover? How much does it contribute to GDP? What industries decline? How do you understand the following – “a net importer of energy”?
I. Summarize the information about Britain’s Economy. Use the headings below.
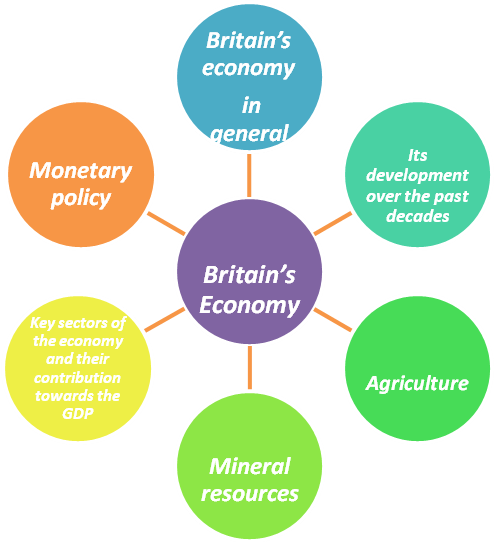
OVER TO YOU
Search the Internet and find the information on the topics below. Write a summary about Britain’s economy on one of the following topics and make a presentation to your group mates.
|
|
|
|
GRAMMAR: TWO OR MORE NOUNS TOGETHER
A. In English two or more nouns can be combined together. In the noun + noun construction, the first noun functions like an adjective and describes the second noun. Very often, the first noun answers the question What kind? Translate these noun combinations from the text:
oil resources (the resources of oil)
interest rate moves (moves of a rate of interest)
Find other noun combinations and translate them. Give examples of your own.
GRAMMAR: VERB+ing
B. What are the main forms of the verb? Study these uses of verb+ing and translate the examples from the text.
Uses of verb+ing |
Examples |
as an adjective |
The UK is a leading trading power. |
as part of continuous verb form |
Britain’s oil and natural gas reserves are declining. |
as a noun and the subject
|
Services, particularly banking, account by far for the largest proportion of GDP. |
an ‘-ing’ clause after a noun |
Agriculture producing about 60% of food needs is highly mechanized and efficient. |
after certain verbs* |
A number of new measures to stimulate the economy and stabilize the financial markets include part-nationalizing the banking system, cutting taxes etc. |
the preposition + ‘-ing’ (words commonly used in this pattern include after, before, besides, by, in, on, since, through, when, while, with, without) |
Since emerging from recession in 1992, Britain’s economy enjoyed the longest period of expansion. |
* 1. Many verbs are followed by ‘-ing’ form.
Verbs of liking and disliking
-
adore
detest
dislike
dread
enjoy
fancy
like
love
mind
resent
I don’t mind telling you.
Verbs of saying and thinking
-
admit
consider
deny
describe
imagine
mention
recall
suggest
recommend
understand
Can you imagine buying that car!
Other common verbs
-
avoid
commence
delay
finish
face
include
involve
keep
miss
postpone
practise
resist
risk
save
stop
Avoid giving any unnecessary data.
Common phrasal verbs
-
burst out
carry on
end up
give up
go round
keep on
put off
set about
look forward to
leave off
They kept on working for a while.
Some common phrases
-
can’t help can’t stand feel like
I can’t help worrying.
NB With the verbs underlined we can also put an object before the ‘–ing’ form.
Can you imagine Helen buying that car!
2. Sometimes we need to decide whether to use a verb in its ‘-ing’ form (doing, working) or infinitive (to do, to work).
The –ing form focuses on:
a) an action or state before the action of the first verb.
He finished doing her accounts yesterday.
b) the activity itself. The second verb functions like a noun.
He recommends selling shares now.
The to-infinitive form focuses on:
a) a purpose
She wishes to ask you a favour.
b) a future situation
They are planning to launch a new project.
3. Some verbs can be followed by either ‘–ing’ form or an infinitive.
-
attempt
begin
bother
can’t bear
can’t stand
cease
continue
deserve
fear
forget
go on
hate
intend
like (=enjoy)
love
mean
prefer
regret
remember
start
stop
try
I love meeting people. = I love to meet new people.
NB The underlined verbs can be followed by either ‘–ing’ form or an infinitive but the meanings are very different!!!
They stopped making fax machines. (finish an action)
We stopped to get petrol. (finish one action in order to do another one)
C. Look at the italicized words in the sentences below and say what the ways of using “verb+ing” are? Translate these sentences.
1) The UK is steadily moving towards the formation of a knowledge-based economy focusing on high technology, flexible workforce and innovative work solutions. 2) More than 25 percent of entrepreneurs established financial companies, dealing in public shares and bonds. 3) The business and financial services include the trading, investment and real estate sector. 5) This business offers more freedom in making company policies. 6) Processing raw materials is the field of the manufacturing sector.7) Revenues have stopped coming in.8) The English dislike people asking them what they earn.
D. Make up ‘-ing’ clauses.
The UK is steadily moving towards the formation of a knowledge-based economy that focuses on high technology, flexible workforce and innovative work solutions.
A business plan is a communication tool for entrepreneurs who start a new company or establish a new line of business in an existing company.
Statistics indicate that the UK health industry which includes the pharmaceutical industry accounts for more than 48 percent of the gross domestic product.
While he testified to the Senate Finance Committee, US trade representative said about broader institutional reforms at the WTO.
When people consume goods and services, they provide a basis for further production.
Most people who own a house have a mortgage.
E. Open the brackets using an ‘-ing’ form or infinitive.
I’m still looking for a job but I hope (find) something soon.
They risk (lose) business to their competitors.
Please don’t forget (send) the samples.
He denies (pass on) any trade secrets.
They are planning (launch) a new line of clothes.
Does your job involve (meet) a lot of people?
They agreed (lend) me some money.
We should start (build) partnerships today.
Study some other ways of using Verb+ing. Translate the examples.
Uses of verb+ing |
Examples |
in contrast clauses after despite, in spite of, although, though |
Although accounting for only about 1 per cent of the world’s population, Britain is the fourth largest trading nation in the world. |
after fixed phrases There’s no point (in)… It’s a waste of time/money… It’s (not) worth … It’s no use … |
It is worth remembering that the Union Jack is more popular in England than in Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
|
G. Translate the sentences and say what the ways of translation of
‘-ing’ form in Russian are.
1) It’s a waste of money buying things you don’t need. 2) It’s no use arguing any more. 3) Britain is a leading member of both the EU and the Commonwealth. 4) In the fields of arts, broadcasting and sport Britain continues to lead the world. 5) Despite having only 1 % of the world’s population, Britain is the fourth largest trading nation in the world. 6) British agriculture is noted for its efficiency and productivity and at the same time comprehensive planning and control have steadily reduced air and water pollution. 7) Tax policy in a developing country constitutes an essential part of development policy. 8) Banks put much of their funds in a variety of bonds and other lower-yielding financial instruments. 9) Resulting profit or loss will cause a change in the proprietor’s capital. 10) An accounting period may follow the calendar, in which case it begins on January 1 and ends on December 31 of the same year. The business is then said to have a calendar-year accounting period. Any business that has an accounting period consisting of 12 months other than a calendar year is generally known as a fiscal-year accounting period. 11) The financial statements present the accounting information in formal reports that tell managers, creditors, prospective investors, how the business is doing. 12) The National Bureau of Economic Research determines the amount of the business activity in the economy by looking at things like employment, industrial production, real income and wholesale-retail sales. 13) Banks prefer to make loans instead of simply putting their money into bonds and other safer investments. 14) All businesses exist for the purpose of earning a profit. 15) Consumer loans are used mainly for financing major purchases. 16) A good rule of thumb for determining the difference between a recession and a depression is to look at the changes in GNP. 17) A bank’s principal activities revolve around gathering deposits and placing this money in either loans or investments of various kinds. 18) The most obvious way in which additional assets can be obtained for the business is by borrowing. 19) Investments may be either short- or long-term assets depending on the nature of the investments. 20) The Bank’s report on aid effectiveness identified a number of policies, ranging from micro-economic stability, through micro-economic efficiency, to the policies oriented towards the poor. 21) The EU imposes strict quotas and high tariffs on products from efficient producers in Latin America, while allowing free access to those from a handful of small African, Caribbean and Pacific countries. It claims it is providing aid by giving producers from poor countries preferential access and good prices. 22) WTO members’ common goal is rising standards of living in developing countries. Achieving that goal will require difficult decisions.

Do you know these famous Britons? Do these puzzles and read three more noted Britons.
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 One of Britain’s greatest leaders, who was the Prime Minister of the country during World War II
2 He discovered the law of gravity when an apple fell on his head
3 He tried to prove that our remote granddads and grannies were monkeys
4 This man invented the telephone
5 This Queen ruled for the longest period in British history
6 A member of the Beatles who was murdered in the US
7 The author of Jungle Book
|
|
|
1 Scotland’s national poet
2 The author of Treasure Land
3 The author of Ivanhoe
4 A famous explorer who discovered Australia and Hawaii
5 A comic actor with a small black moustache, a bowler hat, and a funny way of walking
6 The author of Alice in Wonderland
7 A very famous singer, once a member of the Beatles
GRAMMAR: PARTICIPLE 2/PAST PARTICIPLE/V-ed form/V3
Uses of V3 |
Examples |
as a part of a perfect verb form
|
Britain has become self-sufficient in energy It had imported over 99 percent of petroleum before oil and gas reserves were found in the North Sea |
as a part of a passive verb form |
The United Kingdom is headed by the Queen. |
as an adjective before or after a noun |
The closed door The improved variant The work done The cars produced |
A. Open the brackets putting the verb in the form of Past Participle and explain the case of using a Past Participle form.
The Museum of Madame Tussaud (visit) by a group of students was a big success.
The score (receive) on an exam was not enough to enter Cambridge University.
The plant introduced a new wage piece system to increase the number of cars (produce).
Taxes (levy) on the population in Britain are a relatively small proportion.
World War II (follow) by the Civil War caused great damage to the economy of the country.
This has (be) an excellent year so far, and we have (reach) most of our sales targets.
I was looking forward to my business trip to England because I had never (be) to England before.
The Channel Tunnel was (build) in 1961.
Enterprises (own) by the state constitute the greater part.
The Russian word “оффшорный” (borrow) from English means unregulated or out of control.
B. Translate the sentences into Russian paying attention to the function of Past Participle form.
Training should combine theory and practice in the field chosen.
The amount of electricity generated was not enough.
The results obtained were thoroughly analyzed.
The workers freed in one place are transferred to other shops.
More than 25% of all exported machinery are intended for building projects carried out with our technical assistance.
Attempts made to find a suitable approach only led to internal contradictions.
There hadn’t been any significant improvement before the new production methods were introduced.
This redistribution of funds guaranteed accelerated rates of economic growth.
Products made at our plant are quite competitive in the local market.
The cost of your purchases and of the services rendered is put on the account indicated on the card.
WORD FILE
Unit 3 Module 1 |
||
island isle peninsula mainland coast off the coast latitude rainfall spell n shower gale mountain range pasture sheets of water plains (for farming) lowland upland valley settlement rural economy agriculture dairy farming changeable constant |
uninhabitable innumerable mild temperate/moderate severe flat densely populated commercial extreme n, adj consequently rarely mostly due to to consist of to be made up of to rank to tend to persist to extend to contain to trace of to be fond of to take up to reduce to decline in importance |
to account for to outpace to push back into recession to implement a number of measures to cut taxes to remain to oppose doing smth trading power decade public ownership growth social welfare programmes needs labour force banking insurance services GDP economic slowdown expansion interest rate opinion polls majority
|
Module 2 The USA
PREIVIEW
Match pictures 1 – 7 with their descriptions 1) – 6).
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
5
4
|
|||||
 A
A6
lthough New York City and Philadelphia each served briefly as the capital of the United States, in 1790, Congress chose it as the permanent seat of government. George Washington helped select the site for the city.Nicknamed «the Golden State», it is the third largest state in area after Alaska and Texas. Today it is the land of the giant redwoods; it has the highest population of any state in the nation and is America's principal agricultural state. It is also the home of Hollywood, the center of America's movie and television industry.
One of the original 13 states it is known as the «Empire State». The state includes everything from skyscrapers in Manhattan to rivers, mountains, and lakes. Today, it has the third largest population in the US, and remains the financial center of the country.
The United States Capitol is the meeting place of the United States Congress, the legislature of the Federal government of the United States. Located in Washington, D.C., it sits atop Capitol Hill.
A

7
rticle III, §1, of the Constitution provides that “the judicial Power of the United States, shall be vested in one supreme Court, and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish.”The power of the Executive Branch is vested in the President of the United States, who also acts as head of state and Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces. The White House is the official residence of the President of the United States.
|













