- •Таврійська державна агротехнічна академія
- •Англійська мова Посібник з позааудиторного читання для студентів 2 курсу за спеціальністю "Інформаційні технології проектування"
- •Contents
- •Передмова
- •Unit 1 What is a Computer?
- •Some Beginning Terms
- •Computer Types
- •Personal or micro
- •Minicomputer
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Making classifying.
- •3. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations.
- •4. Complete the diagram of a computer system.
- •5. Discussion.
- •Unit 2 What is Input?
- •Types of Input
- •Pointing devices
- •Terminals
- •Multimedia input
- •Voice Input
- •Video Input
- •Data automation
- •General Devices
- •Ocr software
- •Data accuracy
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Discussion.
- •Unit 3 What is Processing?
- •Digital Data
- •Digital Codes
- •Input/Output Storage
- •Machine Cycle
- •Memory Addresses
- •Processor Speed
- •Motherboard
- •Isa slots
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Fill in the scheme of basic organization of a computer with the following:
- •Input unit, output unit, control unit, alu, memory
- •Unit 4 What is Output?
- •Types of Output
- •Categories of Output
- •Printers Printer Features
- •What paper type used?
- •What print quality?
- •What will it print?
- •What kind of cable connection?
- •Printer Types
- •Types of Impact Printers
- •Thus, Things to Consider When Choosing a Printer:
- •Screens
- •Making Colored Pictures c rt screen:
- •Lcd screen
- •Scan Pattern
- •Light vs. Ink
- •Screen Features
- •Type of Screens
- •Other Output Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Complete the scheme of main printer types.
- •Unit 5 What is Storage?
- •Magnetic discs
- •Types of Magnetic Disks
- •Sectors
- •Clusters
- •Cylinders
- •What happens when a disk is formatted?
- •Capacity of a Disk depends on:
- •Capacity of Disks
- •Accessing Data
- •Caring for Data
- •Optical Discs
- •How optical disks are similar
- •How It Works (a simple version)
- •Materials
- •Read Only:
- •Write Once:
- •Rewrite:
- •Advantages of Optical Disks
- •Disadvantages of Optical Disks
- •Other Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Match the disk area names with the pictures below.
- •3. Give some instructions of caring for discs. Care of Floppy Disks
- •Unit 6 System Software
- •Operating systems
- •What can a computer do without an operating system?
- •Functions of Operation Systems
- •Allocating system resources
- •Monitoring system activities
- •File and Disk Management
- •Types of Operating Systems
- •Common Operating Systems
- •Changes
- •Which is most popular?
- •Utilities
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Match the names of the operating systems with their logos:
- •Bibliography
Types of Magnetic Disks
Diskette / Floppy Disk Sizes:
|
Both sizes are made of mylar with an oxide coating. The oxide provides the magnetic quality for the disk. The "floppy" part is what is inside the diskette covers - a very floppy[15] piece of plastic (i.e. the mylar)
Other Removable Media[16]
Several other kinds of removable magnetic media are in use, such as the popular Zip disk. All of these have a much higher capacity than floppy disks. Some kinds of new computers come without a floppy disk drive at all.
Each type of media requires its own drive. The drives and disks are much more expensive than floppy drives and disks, but then, you are getting much larger capacities.
Hard Disks
T hese
consist of 1 or more metal platters which are sealed inside a case.
The metal is one which is magnetic. The hard disk is usually
installed inside the computer's case, though there are removable and
cartridge types, also.
Technically the hard
drive
is what controls the motion of the hard disks which contain the data.
But most people use "hard disk" and "hard drive"
interchangeably. They don't make that mistake for floppy disks and
floppy drives. It is clearer with floppies that the drive and the
disk are separate things.
hese
consist of 1 or more metal platters which are sealed inside a case.
The metal is one which is magnetic. The hard disk is usually
installed inside the computer's case, though there are removable and
cartridge types, also.
Technically the hard
drive
is what controls the motion of the hard disks which contain the data.
But most people use "hard disk" and "hard drive"
interchangeably. They don't make that mistake for floppy disks and
floppy drives. It is clearer with floppies that the drive and the
disk are separate things.
Disc Format
All magnetic disks are similarly formatted, or divided into areas, called
tracks
sectors
cylinders
The formatting process sets up a method of assigning addresses to the different areas. It also sets up an area for keeping the list of addresses. Without formatting there would be no way to know what data went with what. It would be like a library where the pages were not in books, but were scattered[17] around on the shelves[18] and tables and floors. You'd have a hard time getting a book together. A formatting method allows you to efficiently use the space while still being able to find things.
Tracks
A track is a circular ring on one side of the disk. Each track has a number. The diagram shows 3 tracks. |
|
Sectors
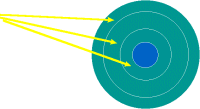
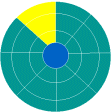
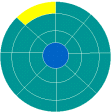
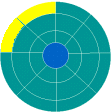
A disk sector is a wedge-shape [19]piece of the disk, shown in yellow. Each sector is numbered. On a 5ј" disk there are 40 tracks with 9 sectors each. On a 3Ѕ" disk there are 80 tracks with 9 sectors each. So a 3Ѕ" disk has twice as many named places on it as a 5ј" disk. |
|
A track sector is the area of intersection[20] of a track and a sector, shown in yellow. |
|
Clusters
A cluster is a set of track sectors, ranging from 2 to 32 or more, depending on the formatting scheme in use. The most common formatting scheme for PCs sets the number of track sectors in a cluster based on the capacity of the disk. A 1.2 gig hard drive will have clusters twice as large as a 500 MB hard drive. |
|
1 cluster is the minimum space used by any read or write. So there is often a lot of slack space[21], unused space, in the cluster beyond[22] the data stored there.
There are some new schemes out that reduce this problem, but it will never go away entirely.
The only way to reduce the amount of slack space is to reduce[23] the size of a cluster by changing the method of formatting. You could have more tracks on the disk, or else more sectors on a track, or you could reduce the number of track sectors in a cluster.