- •Таврійська державна агротехнічна академія
- •Англійська мова Посібник з позааудиторного читання для студентів 2 курсу за спеціальністю "Інформаційні технології проектування"
- •Contents
- •Передмова
- •Unit 1 What is a Computer?
- •Some Beginning Terms
- •Computer Types
- •Personal or micro
- •Minicomputer
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Making classifying.
- •3. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations.
- •4. Complete the diagram of a computer system.
- •5. Discussion.
- •Unit 2 What is Input?
- •Types of Input
- •Pointing devices
- •Terminals
- •Multimedia input
- •Voice Input
- •Video Input
- •Data automation
- •General Devices
- •Ocr software
- •Data accuracy
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Discussion.
- •Unit 3 What is Processing?
- •Digital Data
- •Digital Codes
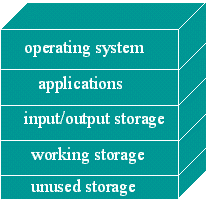
- •Input/Output Storage
- •Machine Cycle
- •Memory Addresses
- •Processor Speed
- •Motherboard
- •Isa slots
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Fill in the scheme of basic organization of a computer with the following:
- •Input unit, output unit, control unit, alu, memory
- •Unit 4 What is Output?
- •Types of Output
- •Categories of Output
- •Printers Printer Features
- •What paper type used?
- •What print quality?
- •What will it print?
- •What kind of cable connection?
- •Printer Types
- •Types of Impact Printers
- •Thus, Things to Consider When Choosing a Printer:
- •Screens
- •Making Colored Pictures c rt screen:
- •Lcd screen
- •Scan Pattern
- •Light vs. Ink
- •Screen Features
- •Type of Screens
- •Other Output Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Complete the scheme of main printer types.
- •Unit 5 What is Storage?
- •Magnetic discs
- •Types of Magnetic Disks
- •Sectors
- •Clusters
- •Cylinders
- •What happens when a disk is formatted?
- •Capacity of a Disk depends on:
- •Capacity of Disks
- •Accessing Data
- •Caring for Data
- •Optical Discs
- •How optical disks are similar
- •How It Works (a simple version)
- •Materials
- •Read Only:
- •Write Once:
- •Rewrite:
- •Advantages of Optical Disks
- •Disadvantages of Optical Disks
- •Other Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Match the disk area names with the pictures below.
- •3. Give some instructions of caring for discs. Care of Floppy Disks
- •Unit 6 System Software
- •Operating systems
- •What can a computer do without an operating system?
- •Functions of Operation Systems
- •Allocating system resources
- •Monitoring system activities
- •File and Disk Management
- •Types of Operating Systems
- •Common Operating Systems
- •Changes
- •Which is most popular?
- •Utilities
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Match the names of the operating systems with their logos:
- •Bibliography
2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
cps, lpm, ppm, dpi, pt, USB, CRT, LCD, VDT, VDU, RGB, CMYK, TV, CGA, EGA, VGA, SVGA, COM.
3. Complete the scheme of main printer types.
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
… |
|
|
|
… |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Dot-Matrix |
|
… |
|
… |
|
|
Ink Jet |
|
… |
|
… |
|||||
Unit 5 What is Storage?
After reading this unit you should aim to achieve these targets by answering the questions at the end of the unit. You should be able to: - outline main storage devices and terms; - define different disk types, their applications, advantages and disadvantages; - propose your own instructions of caring for computer discs. |
Storage refers to the media and methods used to keep information available for later use. Some things will be needed right away while other won't be needed for extended periods of time. So different methods are appropriate[1] for different uses[2].
Remember from previously all the kinds of things that are stored in Main Memory[3]. Thus [6], Primary Storage is Main Memory This keeps track[4] of what is currently being processed. It's volatile[5]. (power off erases all data)
|
Main Memory
|
For Main Memory, computers use RAM, or Random Access Memory. This uses memory chips and is the fastest but most expensive type of storage.
Secondary Storage is called Auxiliary Storage[7] |
|
This is what is not currently being processed. This is the stuff "filed away"[8], but ready to be pulled out[9] when needed. It is nonvolatile. (power off does not erase)
Auxiliary Storage is used for:
Input |
- data & programs |
Output |
- saving results of processing |
So, Auxiliary Storage is where you put last year's tax info[10], addresses for old customers[11], programs you may or may not ever use, data you entered yesterday - everything that is not being used right now.
Magnetic discs
Of the various types of Auxiliary Storage, the types used most often involve[12] some type of magnetic disk. These come in various sizes and materials, as we shall see. This method uses magnetism to store the data on a magnetic surface.
Advantages: high storage capacity, reliable[13], gives direct access to data[14].
A drive spins the disk very quickly underneath a read/write head, which does what its name says. It reads data from a disk and writes data to a disk. (A name that actually makes sense!)

 rinters
rinters