- •Таврійська державна агротехнічна академія
- •Англійська мова Посібник з позааудиторного читання для студентів 2 курсу за спеціальністю "Інформаційні технології проектування"
- •Contents
- •Передмова
- •Unit 1 What is a Computer?
- •Some Beginning Terms
- •Computer Types
- •Personal or micro
- •Minicomputer
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Making classifying.
- •3. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations.
- •4. Complete the diagram of a computer system.
- •5. Discussion.
- •Unit 2 What is Input?
- •Types of Input
- •Pointing devices
- •Terminals
- •Multimedia input
- •Voice Input
- •Video Input
- •Data automation
- •General Devices
- •Ocr software
- •Data accuracy
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Discussion.
- •Unit 3 What is Processing?
- •Digital Data
- •Digital Codes
- •Input/Output Storage
- •Machine Cycle
- •Memory Addresses
- •Processor Speed
- •Motherboard
- •Isa slots
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Fill in the scheme of basic organization of a computer with the following:
- •Input unit, output unit, control unit, alu, memory
- •Unit 4 What is Output?
- •Types of Output
- •Categories of Output
- •Printers Printer Features
- •What paper type used?
- •What print quality?
- •What will it print?
- •What kind of cable connection?
- •Printer Types
- •Types of Impact Printers
- •Thus, Things to Consider When Choosing a Printer:
- •Screens
- •Making Colored Pictures c rt screen:
- •Lcd screen
- •Scan Pattern
- •Light vs. Ink
- •Screen Features
- •Type of Screens
- •Other Output Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Complete the scheme of main printer types.
- •Unit 5 What is Storage?
- •Magnetic discs
- •Types of Magnetic Disks
- •Sectors
- •Clusters
- •Cylinders
- •What happens when a disk is formatted?
- •Capacity of a Disk depends on:
- •Capacity of Disks
- •Accessing Data
- •Caring for Data
- •Optical Discs
- •How optical disks are similar
- •How It Works (a simple version)
- •Materials
- •Read Only:
- •Write Once:
- •Rewrite:
- •Advantages of Optical Disks
- •Disadvantages of Optical Disks
- •Other Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Match the disk area names with the pictures below.
- •3. Give some instructions of caring for discs. Care of Floppy Disks
- •Unit 6 System Software
- •Operating systems
- •What can a computer do without an operating system?
- •Functions of Operation Systems
- •Allocating system resources
- •Monitoring system activities
- •File and Disk Management
- •Types of Operating Systems
- •Common Operating Systems
- •Changes
- •Which is most popular?
- •Utilities
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Match the names of the operating systems with their logos:
- •Bibliography
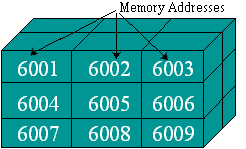
Memory Addresses
We need a method of naming the places where Main Memory stores data. Each location needs a unique name, just like houses in a town need a unique street address.
|
|
Rather than a street name and house number, memory addresses are just numbers.
A memory address holds 1 byte of data where
1 bit = |
0 or 1, on or off |
1 byte = |
8 bits |
1 kilobyte (K or KB) = |
1024 bytes |
1 megabyte (MB) = |
1024 kilobytes |
You might wonder why 1024 instead of 1000 bytes per kilobyte. That is because computers don't count by tens like people. Computers count by twos and powers of 2. 1024 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2, that is 2 times itself ten times. It's a rather convenient size number (for computers!).
Update: Things are changing faster than I can type! The explanation above is no longer entirely true (July 2000). Different scientific and technical areas are using the words differently. For data storage devices and telecommunications a megabyte is 1 000 000 bytes. For data transmission in LANs a megabyte is 1 048 576 bytes as described above. But for data storage on a floppy disk a megabyte is 1 024 000 bytes!
Processor Speed
We all are impatient and want our computer to work as fast as possible, and certainly faster than the guy's at the next desk! Many different factors determine how fast your computer gets things done. Processor speed is one factor. But what determines the processor's speed?
System clock rate = rate of an electronic pulse used to synchronize processing. (Only one action can take place between pulses.) Measured in megahertz (MHz) where 1 MHz = 1 million cycles per second. This is what they are talking about if they say a computer is a 700 MHz machine. It's clock rate is 700 million cycles per second. Bigger number = faster processing
Bus width = the amount of data the CPU can transmit at a time to main memory and to input and output devices. (Any path bits travel is a bus.) An 8-bit bus moves 8 bits of data at a time.
Bus width can be 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 so far. Think of it as "How many passengers (bits) can fit on the bus at once to go from one part of the computer to another." Bigger number = faster transfer of data.
Word size = a word is the amount of data the CPU can process at one time. An 8-bit processor can manipulate 8 bits at a time. Processors can be 8-, 16-, 32-, or 64-bit so far.
Bigger the number = faster processing
You want a nice match between the word size and the bus size and the clock. It wouldn't do any good to have a bus that can deliver data 128 bits at a time, if the CPU can only use 8 bits at a time and has a slow clock speed. A huge line of data would form, waiting to get off the bus! When computers gets clogged like that, bad things can happen to your data. It's like people waiting to get in the theater. After a while, some of them may leave!!
Physical Components
There are several physical components of a computer that are directly involved in processing. The processor chip itself, the memory devices, and the motherboard are the main ones.
Microprocessor- |
a single silicon chip containing CPU, ALU, and some memory. The ROM (Read Only Memory) cannot be changed by the user and contains the minimum instructions the computer needs to get started, called booting. There may also be another chip dedicated to calculations. The microprocessor chip is located on a large circuit board called the main board or motherboard. The physical size of a computer chip is very small, as the ant below illustrates.
|
Memory Devices:
Vacuum tube - |
oldest type. Didn't hold up long and generated a lot of heat. |
Core - |
small metal rings. Magnets tip a ring to left or right, which represents on and off. Relatively slow. |
Semiconductor - |
integrated circuit on a chip. This is what modern computers use for memory. Pictured below is a 72-pin SIMM. |
Speed
Memory speed measures the time it takes to move data in or out of memory. It is measured differently for different kinds of memory chips:
in nanoseconds (ns) for EDO and FPM (smaller is faster) 1 ns = 1 billionth of a second.
in MHz (higher is faster) for SDR SDRAM, DDR, SDRAM, and RDRAM.
The capacity of a memory chip is measured in megabytes. Sizes are measured in megabytes and come in powers of 2: 1, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 MB on one memory board. Several such boards can be installed in the computer to increase the amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) available as Main Memory. Motherboards have only so many slots for memory so there are limits. Some motherboards require that all slots be filled and that all slots contain the same size memory board. It can get frustrating as there are no warning labels about this!