
- •Таврійська державна агротехнічна академія
- •Англійська мова Посібник з позааудиторного читання для студентів 2 курсу за спеціальністю "Інформаційні технології проектування"
- •Contents
- •Передмова
- •Unit 1 What is a Computer?
- •Some Beginning Terms
- •Computer Types
- •Personal or micro
- •Minicomputer
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Making classifying.
- •3. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations.
- •4. Complete the diagram of a computer system.
- •5. Discussion.
- •Unit 2 What is Input?
- •Types of Input
- •Pointing devices
- •Terminals
- •Multimedia input
- •Voice Input
- •Video Input
- •Data automation
- •General Devices
- •Ocr software
- •Data accuracy
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Discussion.
- •Unit 3 What is Processing?
- •Digital Data
- •Digital Codes
- •Input/Output Storage
- •Machine Cycle
- •Memory Addresses
- •Processor Speed
- •Motherboard
- •Isa slots
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •3. Fill in the scheme of basic organization of a computer with the following:
- •Input unit, output unit, control unit, alu, memory
- •Unit 4 What is Output?
- •Types of Output
- •Categories of Output
- •Printers Printer Features
- •What paper type used?
- •What print quality?
- •What will it print?
- •What kind of cable connection?
- •Printer Types
- •Types of Impact Printers
- •Thus, Things to Consider When Choosing a Printer:
- •Screens
- •Making Colored Pictures c rt screen:
- •Lcd screen
- •Scan Pattern
- •Light vs. Ink
- •Screen Features
- •Type of Screens
- •Other Output Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Complete the scheme of main printer types.
- •Unit 5 What is Storage?
- •Magnetic discs
- •Types of Magnetic Disks
- •Sectors
- •Clusters
- •Cylinders
- •What happens when a disk is formatted?
- •Capacity of a Disk depends on:
- •Capacity of Disks
- •Accessing Data
- •Caring for Data
- •Optical Discs
- •How optical disks are similar
- •How It Works (a simple version)
- •Materials
- •Read Only:
- •Write Once:
- •Rewrite:
- •Advantages of Optical Disks
- •Disadvantages of Optical Disks
- •Other Devices
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Match the disk area names with the pictures below.
- •3. Give some instructions of caring for discs. Care of Floppy Disks
- •Unit 6 System Software
- •Operating systems
- •What can a computer do without an operating system?
- •Functions of Operation Systems
- •Allocating system resources
- •Monitoring system activities
- •File and Disk Management
- •Types of Operating Systems
- •Common Operating Systems
- •Changes
- •Which is most popular?
- •Utilities
- •Comprehension Tasks
- •1. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
- •2. Give the main meanings of the following abbreviations:
- •3. Match the names of the operating systems with their logos:
- •Bibliography
Motherboard
Here we see a diagram and a photo of a motherboard (or main circuit board). This one is suitable for a Pentium CPU. Nothing has been plugged in or attached yet.
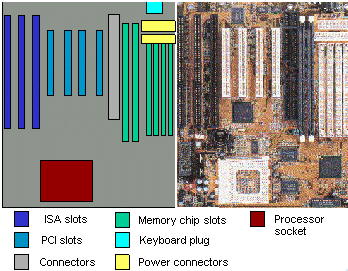
Connectors
Here is where cables connect to the motherboard for things like hard drives, floppy drives, and CD-ROM drives.
Isa slots
This board has 3 slots for the older ISA/VESA boards for things like video cards, sound cards, internal modems, etc.
Keyboard plug
This is where the keyboard attaches, thru the back of the computer.
Memory slots
There are 4 short slots for SIMM memory. This board has two long slots for a new kind of memory called DIMM DRAM. This board can handle a maximum of 256 MB of memory.
From the manufacturer's description:
Two 168 pin DIMM DRAM slots (8/16/32/64 MB module)
Four 72 pin SIMM memory slots (4/8/16/32/64 MB module)
Supports maximum 256 MB with Fast Page/EDO/SDRAM DRAM
That's pretty scary stuff. Just keep such information handy for when someone who understands these things asks you about them.
PCI slots
This board has 4 slots for the newer PCI boards for peripherals like video cards, sound cards, internal modems, etc.
Power Connections
This is where the power supply connects to the motherboard.
Processor socket
What is visible here is the place where the processor plugs into the motherboard. When the processor is installed, you still can't see it because on top of it is a heat sink and fan to keep the processor cool. Hot processors make mistakes or even melt important parts on the chip.
Different processors are different sizes. So the socket on the motherboard has to match the processor. Also, the circuits in the motherboard itself must be different for different processors.
Comprehension Tasks
1. Match the computer terms with their definitions:
1) processor 2) connector 3) vacuum tube 4) central processing unit 5) memory 6) bus width 7) booting 8) binary numbers 9) semiconductor 10) microprocessor |
a) a cable that connects to the motherboard for things like hard drives, floppy drives, and other devices b) a place to store information (also RAM and ROM) c) a chip designed with a specific set of usable instructions d) the principal part of any digital computer system, generally composed of the main memory, control unit, and arithmetic-logic unit e) the oldest type of memory devices f) any of a type of miniature electronic device that contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry necessary to perform the functions of a digital computer's central processing unit g) the amount of data the CPU can transmit at a time to main memory and to input and output devices h) numbers written with just 0 and 1 i) a process of starting computer j) integrated circuit on a chip |
2. Complete the sentences with the word from the list below.
1. The information processing cycle includes the following processes:
a) input, processing, output, storage
b) input, output, manipulation, arithmetic
c) data, processing, printing, editing
d) storage, display, data, information
2. The computer's processor consists of the following parts:
a) CPU and Main Memory
b) Control Unit and ALU
c) Main Memory and storage
d) Operating system and Applications
3. CPU stands for______.
a) Core packet unit
b) Clock picket unit
c) Central processing unit
d) Central product unit
4. The arithmetic/logic unit performs the following actions:
a) checks data for accuracy
b)does calculations using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
c) does logical comparisons, such as equal to, greater than, less than
d) both calculations and logical comparisons
5. The main memory of a computer must be large enough to contain _____.
a) the operating system
b) the applications
c) input/output storage & working storage
d) all of the above
6. The name of the location of a particular piece of data is its _____.
a) address
b) memory name
c) storage site
d) data location
7. A megabyte is actually equal to ____ kilobytes.
a) 100
b)1000
c) 1024
d) 1024 x 1024
8. The clock rate of a processor is measured in ____.
a) milliseconds
b) megahertz
c) megabytes
d) nanoseconds
9. If the bus width of a processor is 16 bits, that means that the processor can _____ 16 bits of data at a time.
a) add
b) transfer
c) count
d) think with
10. If a processor has a word size of 32 bits, compared to a processor with a word size of 16 bits, it can process _____ at a time.
a) twice as much
b) half as much
c) a fourth as much
d) the same amount
