
- •Практикум по грамматике английского языка для подготовки к итоговой аттестации
- •Е. Ю. Воякина, н. А. Гунина, л. Ю. Королева Практикум по грамматике английского языка для подготовки к итоговой аттестации
- •How to use Present Simple and Present Continuous
- •1 Read the paragraph and answer the questions:
- •2 Some people complain about complexities of normal life. They think that their life isn’t exciting enough. Talk about your daily routine. Do you live an action-packed life?
- •3 Complete the sentences with the present simple or present continuous form of the verbs in brackets.
- •4 Make questions to the answers about alan.
- •6. Put the verb in brackets in the correct form (present simple or present continuous).
- •7. Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verb (present simple or present continuous).
- •8 Complete the dialogue:
- •9 Role-play the conversation in 7.
- •10 Talk to as many people in the class to find a person who shares similar interests with you.
- •1. Present Continuous
- •2. Present Simple
- •I apologise I insist I promise I recommend I suggest
- •3. Mixed Present Simple and Present Continuous
- •Unit 2. Present Perfect vs. Present Perfect Continuous
- •Have been to / have been in / have gone to
- •1 Write positive sentences in present perfect simple
- •2 Write negative sentences in present perfect simple.
- •4 Read the text about Loch Ness and complete the sentences.
- •6 Which form is correct: Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous?
- •7 Put the verbs into the correct tense: Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous
- •8 Complete the conversation with the appropriate tenses: Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous
- •9 Act out a similar conversation.
- •10 Complete the conversation with the appropriate tenses: Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous
- •11 Role play. Job interview. Work in groups of 4.
- •1 You are writing a letter to a friend. In the letter you give news about yourself and other people. Use the words given to make sentences. Use the present perfect.
- •2 Read the situations and write sentences. Choose one of the following:
- •4 Read the situations and write sentences with just, already or yet.
- •5 Put in been or gone.
- •6 You are asking somebody questions about things he or she has done. Make questions from the words in brackets.
- •7 Complete b’s answers. Some sentences are positive and some negative. Use a verb from this list:
- •8 Complete these sentences using today/this year/this term etc.
- •9 Read the situations and write sentences as shown in the examples.
- •1 Write a question for each situation.
- •2 Read the situations and complete the sentences.
- •3 Mixed Present Perfect Continuous Present Perfect Simple
- •4 For each situation, ask a question using the words in brackets.
- •5 Put the verb into the more suitable form, present perfect simple (I have done etc.) or continuous (I have been doing etc.).
- •6 Are the underlined verbs right or wrong? Correct them if they are wrong.
- •7 Read the situations and write questions from the words in brackets.
- •8 Complete b’s answers to a's questions.
- •Habit in the Past
- •Past Facts and Generalizations
- •Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- •1. Make past simple ‘wh’ questions:
- •2. Put the verbs into the correct form (simple past or present perfect).
- •3. Write the verbs in the correct tense (Simple Past or Present Perfect).
- •4 Choose the past simple or the present perfect:
- •5 Work in pairs. In turns talk about the suggested topic for about 1 minute. Use Present Perfect and Past Simple.
- •6 Match the beginning of the sentence to its ending.
- •7 Fill in the blanks with used to or a form of be used to.
- •1 Read what Sharon says about a typical working day.
- •2 Put one of these verbs in each sentence.
- •3 A friend has just come back from holiday. You ask him about it. Write your questions.
- •4 Complete the sentences, Put the verb into the correct form, positive or negative.
- •2 Brian changed his lifestyle. He stopped doing some things and started doing other things.
- •3 Compare what Carol said five years ago and what she says today.
- •1 Put the verbs in brackets in the correct form, present perfect or past simple.
- •2 Are the underlined parts of these sentences right or wrong? Correct the ones that are wrong.
- •3 Are the underlined parts of these sentences right or wrong? Correct the ones that are wrong.
- •4 Make sentences from the words in brackets. Use the present perfect or past simple.
- •5 Put the verb into the correct form, present perfect or past simple.
- •6 Write sentences about yourself using the ideas in brackets.
- •7 Put the verb into the most suitable form, present perfect or past simple.
- •Past Continuous
- •Past Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous
- •1 Use Past Continuous to describe actions happening at a specific time in the past.
- •2 Choose the correct time expression used with the past continuous tense.
- •3 My memorable event. The sentences are mixed. Put them in the correct order to make a story
- •4 Describe your memorable event. Use Past Simple and Past Continuous.
- •6 Choose the past perfect, or the past simple:
- •7 Choose the past perfect, or the past perfect continuous
- •1 What were you doing at the following times? Write one sentence as in the examples. The past continuous is not always necessary (see the second example).
- •1 Read the situations and write sentences from the words in brackets.
- •2 Read the situations and write sentences ending with before. Use the verb given in brackets.
- •4 Put the verb into the correct form, past perfect (I had done etc.) or past simple (I did etc.).
- •1 Read the situations and make sentences from the words in brackets.
- •2 Read the situations and complete the sentences.
- •3 Put the verb into the most suitable form, past continuous (I was doing), past perfect (I had done) or past perfect continuous (I had been doing).
- •Unit 5 Future forms
- •1 Present Simple vs Present Continuous
- •2 Going to vs. Future Simple
- •3 Future Continuous / Future Perfect / Future Perfect Continuous
- •4 No Future in Time Clauses
- •1 Complete the sentences using will ('ll) or going to.
- •2 Read the situations and complete the sentences using will ('ll) or going to.
- •3 Holiday Plans. Ask and answer questions about travel plans
- •5 Future Perfect or Future Perfect Continuous
- •6 Future Simple or Present Simple
- •1 A friend of yours is planning to go on holiday soon. You ask her about her plans. Use the words in brackets to make your questions.
- •2 Tom wants you to visit him but you are very busy. Look at your diary for the next few days and explain to him why you can't come.
- •3 Have you arranged to do anything at these times? Write (true) sentences about yourself.
- •4 Put the verb into the more suitable form, present continuous or present simple.
- •1 Answer the questions. You are going to do all these things but you haven't done them yet. Use going to and the word(s) in brackets.
- •2 Write a question with going to for each situation.
- •3 Read the situations and complete the dialogues. Use going to.
- •4 What is going to happen in these situations? Use the words in brackets.
- •2 Read the situations and write sentences with I think I'll ... Or I don't think I'll ...
- •3 Which is correct?
- •4 What do you say in these situations? Write sentences with shall I ...? or shall we ...?
- •1 Read about Colin. Then you have to tick (V) the sentences which are true. In each group of sentences at least one is true.
- •2 Put the verb into the correct form, will be (doing) or will have (done).
- •1 Complete these sentences using the verbs in brackets. All the sentences are about the future. Use will/won't or the present simple (I see/he plays/it is etc.).
- •2 Make one sentence from two.
- •3 Read the situations and complete the sentences.
- •1 Read the text and put the verbs in brackets into present simple passive.
- •2 Put the verbs in brackets into past simple passive.
- •3 Choose the best option.
- •4 Using the passive, ask questions to which the bold type words are answers.
- •5 Fill in the passive in the appropriate tense.
- •6 Complete the text with the correct form of the verbs in brackets. Use Active or Passive voice.
- •7 Change the sentences from Active to Passive and vice versa.
- •8 Put the verb in bracket in the correct Active/Passive voice and tense.
- •9 Say if the sentences are Right or Wrong. Correct the mistakes.
- •10 Look at the Hotel Information table and write sentences as in the example.
- •11 Role-play the conversation in 10. Student a – a hotel guest, Student b – a receptionist.
- •12 Passive Pair work Activity. Read the situation below and make a role-play. Use Present Perfect, Past Simple, Future Passive.
- •1 Complete the sentences using one of these verbs in the correct form.
- •2 Write questions using the passive. Some are present and some are past.
- •3 Put the verb into the correct form, Present simple or Past simple, Active or Passive.
- •4 Rewrite these sentences. Instead of using 'somebody/they/people' etc. Write a Passive sentence.
- •5 Write sentences in the passive. Use these phrases.
- •6 Rewrite these sentences. Instead of using 'somebody' or 'they', write a Passive sentence using the correct tense.
- •7 Make sentences from the words in brackets. Sometimes the verb is Active, sometimes Passive. Mind the tenses.
- •8 Put the verbs in brackets together with the adverbs into the Active or Passive in the correct tense.
- •9 Turn from active into passive.
- •10 Rewrite the following passages in the passive.
- •It is said that... He is said to... (be) supposed to...:
- •1 Rephrase the sentences using Passive voice in two ways. Omit unimportant agents.
- •2 Write these sentences in another way, beginning in the way shown.
- •3 Paraphrase the sentences using Passive voice. Pay attention to prepositions.
- •4 Read each sentence. Then make two new sentences in the passive.
- •5 Read each sentence. Then make two new sentences in the passive.
- •6 Report these rumors.
- •10 Tick (V) the correct sentence, (a) or (b), for each picture.
- •11 Why did you do these things? Answer using 'have something done'. Use one of these verbs:
- •12 Now you have to use 'have something done' with its second meaning.
- •13 Discuss the questions with your partner.
- •1 Rewrite the sentences in the Passive. Do it in two ways when possible.
- •2 Put the following sentences into the passive voice. Sometimes several variants of Passive are possible.
- •1 Fill in the blanks with can or can’t.
- •3 Complete the answers to the questions with was/were able to.
- •4 Answer the questions with a suggestion. Use could.
- •5 Write these sentences in a different way using may or might.
- •6 Write sentences with may or might.
- •7 Complete the sentences with can / can't /could / couldn't and one of these verbs. (ability)
- •8 Look at the following phrases and write in which write you think it is. Then use one of the modal verbs in brackets to fill the gaps.
- •9 Imagine it is the year 3012. Describe how things are then.
- •1 Complete the sentences using can or (be) able to. Use can if possible; otherwise use (be) able to.
- •2 Complete the sentences using could, couldn't or was/were able to.
- •3 Put in can or could. Sometimes either word is possible.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of can.
- •5 Complete the sentences with a verb in the correct form.
- •6 Read the situations and make sentences from the words in brackets. Use may or might.
- •7 Complete the sentences using might not or couldn't.
- •9 May or Might: choose the correct answer.
- •10 Write a second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first. Use the words in brackets.
- •1 Fill in must or mustn’t.
- •2 Fill in the blanks with can / can’t or must / mustn’t.
- •3 Fill in the blanks using proper Have To structure and match the examples with the pictures.
- •4 Use must / mustn’t / have to or (not) have to.
- •5 Fill in the blanks using (not) have to / must (not) / can / could:
- •1 Put in must or can't.
- •2 Complete the sentences with a verb in the correct form.
- •3 Complete these sentences with must or have to (in the correct form). Sometimes it is possible to use either; sometimes only have to is possible.
- •4 Make questions with have to.
- •6 Complete these sentences with mustn't or don't/doesn't have to.
- •8 Complete the sentences with must, mustn't or needn't.
- •9 Complete the sentences with must / mustn’t or needn’t:
- •11 Write a sentence (beginning in the way shown) that means the same as the first sentence.
- •12 Complete the sentences using modals listed below. Use capital letters when necessary and you may have to change “have” to “had.” Some gaps may have more than one correct answer.
- •13 Use a suitable present or past modal verb.
- •14 A mysterious letter has arrived for Tom by special delivery. He is nervous about opening it. Add suitable modal verbs to complete the dialogue. He is with Jill, his wife.
- •Unit 10. Conditionals
- •Real condition
- •How to form Zero Conditionals
- •How to form First Conditionals
- •Unreal condition (present and future situation)
- •How to form Second Conditionals
- •Unreal condition (past situation)
- •How to form Third Conditionals
- •1. Choose the correct form of the verb:
- •2. Match the two halves of the sentences:
- •4. Complete the sentences with these phrases:
- •5. Complete the sentences. Use the correct form of the verbs in brackets:
- •6. What would you do in each situation? These are unreal present situations:
- •9. Write sentences with “ wish…”:
- •10. You don’t like your new house. Write what you wish:
- •11. Using the bold type in the sentences, write wishes as in the example:
- •1. Put the verbs into the correct form.
- •2. You ask a friend questions. Use What would you do if ...?
- •3. Answer the questions in the way shown.
- •4. Use your own ideas to complete these sentences.
- •5. Put the verb into the correct form.
- •6. Write a sentence with If ... For each situation.
- •7. Write sentences beginning I wish ...
- •8. Write your own sentences beginning I wish ...
- •9. Put the verb into the correct form.
- •10. Write a sentence with if for each situation.
- •11. Imagine that you are in these situations. For each situation, write a sentence with I wish ...
- •12. What do you say in these situations? Write sentences with I wish ... Would ...
- •13. Are these sentences right or wrong? Correct the ones that are wrong.
- •2. Report the following. Begin each sentence with ‘She said...’:
- •1. Yesterday you met a friend of yours, Charlie. Here are some of the things Charlie said to you:
- •2. Somebody says something to you which is the opposite of what they said before. Write a suitable answer beginning I thought you said ....
- •3. Here are some things that Ann said to you:
- •4. The following sentences are direct speech:
- •5. Change into reported speech:
- •6. Change into reported speech:
- •11. Some of the blank spaces below need articles, others do not. Fill in the articles where needed:
- •1. Some of these sentences need a/an. Correct the sentences which are wrong. If the sentence is already correct, put 'right':
- •2. Complete the sentences using one of the following words. Use a/an where necessary:
- •3. Complete the sentences using one of the following words. Sometimes the word needs to be plural (-s):
- •4. Which of the underlined parts of these sentences is correct?
- •5. Complete the sentences using these words. Sometimes you need the plural (-s):
- •6. What do you say in these situations? Complete the sentences using one of the words from exercise 5:
- •9. Put in a/an or the in these sentences where necessary:
- •10. Put in the or a/an where necessary. If no word is necessary, leave the space empty(-):
- •11. Put in the or a/an where necessary. If the sentence is already correct, put 'right':
- •12. Complete the sentences using one of the following. Use the where necessary:
- •13. Put in the where necessary. Leave a space (-) if the sentence is already complete:
- •14. Some of these sentences are correct, but some need the (perhaps more than once). Correct the sentences where necessary. Put 'right' if the sentence is already correct:
- •Adjectives
- •Degrees of comparison of adjectives
- •Adverb or adjective
- •1. Write what the underlined word is: adjective or adverb:
- •2. Use one of the words from the box to complete each sentence below:
- •3. Underline the correct item:
- •3 Complete the sentences using one of the following words:
- •5. Put in the right word:
- •6. Complete each sentence using a word from the list. Sometimes you need the adjective (careful etc.) and sometimes the adverb (carefully etc.):
- •7. Choose two words (one from each box) to complete each sentence:
- •10. Complete the sentences. Each time use the comparative form of one of the words in the list. Use than where necessary:
- •13. Complete the sentences using as ... As:
- •Conclusion
- •References
2 Put the following sentences into the passive voice. Sometimes several variants of Passive are possible.
Someone has already paid the electrician for his work.
………………………………………………………………………………..
They taught him French and gave him a dictionary.
………………………………………………………………………………..
When we first met, they had already offered me a job at the bank.
………………………………………………………………………………..
A man requested the stranger to leave the meeting.
…………………………………………………………………………………
A young woman asked the rest of us to be there at eight o’clock.
…………………………………………………………………………………
They had eaten all the dinner before they finished the conversation.
…………………………………………………………………………………
Who wrote it?
…………………………………………………………………………………
The author has written a special edition for children.
…………………………………………………………………………………
Did the idea interest you?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Why didn’t they mend the roof before it fell in?
…………………………………………………………………………………
The burglars had cut a huge hole in the steel door.
…………………………………………………………………………………
The organizers will exhibit the paintings till the end of the month.
…………………………………………………………………………………
When did they ring the church bells?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Does listening to music disturb you?
…………………………………………………………………………………
3 Put the following sentences into the PASSIVE VOICE.
Someone has already paid the electrician for his work.
………………………………………………………………………………..
They taught him French and gave him a dictionary.
………………………………………………………………………………..
When we first met, they had already offered me a job at the bank.
………………………………………………………………………………..
A man requested the stranger to leave the meeting.
…………………………………………………………………………………
A young woman asked the rest of us to be there at eight o’clock.
…………………………………………………………………………………
They had eaten all the dinner before they finished the conversation.
…………………………………………………………………………………
Who wrote it?
…………………………………………………………………………………
The author has written a special edition for children.
…………………………………………………………………………………
Did the idea interest you?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Why didn’t they mend the roof before it fell in?
…………………………………………………………………………………
The burglars had cut a huge hole in the steel door.
…………………………………………………………………………………
The organizers will exhibit the paintings till the end of the month.
…………………………………………………………………………………
When did they ring the church bells?
…………………………………………………………………………………
Does listening to music disturb you?
…………………………………………………………………………………
4 Read the following sentences and write another one with the same meaning.
It is believed that the wanted man is living in New York.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is said that many people are homeless after the floods.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is expected that the government will lose this election.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is known that the Prime Minister is in favour of the new law.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is believed that the thieves got in through the kitchen window.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is thought that the prisoner escaped by climbing over the wall.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is claimed that he drove through the town at 90 miles an hour.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is reported that two people were seriously injured in the accident.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is said that three men were arrested after the explosion.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is believed that Maria will not win the prize.
…………………………………………………………………………………
It is considered that the 2008 Olimpic Games will be held in Turkey.
………………………………………………………………………………….
It is said that our teacher is 55 years old.
………………………………………………………………………………….
It is thought that Tom didn’t steal their rings.
………………………………………………………………………………….
It is claimed that this examination will be the most difficult one.
………………………………………………………………………………….
It is believed that John will marry Ann at the end of this month.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
It is expected that people will live in Mars in 2050.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
5 Change these sentences into PASSIVE FORM.
People believe that the strike will end soon.
………………………………………………………………………………….
People believe that the thieves got through the kitchen window.
………………………………………………………………………………….
People say that the company is loosing a lot of money.
………………………………………………………………………………….
When is he going to pay the taxes?
………………………………………………………………………………….
Who has designed these buildings?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
How much do they spend on these activities?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
They broke a lot of plates while they were dancing?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Who invented the electric bulb?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
People believe that they are secret agents.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
People think that he takes harmful drugs.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Did they give you a great reception?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Nobody sends her a card at Christmas.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Did anyone call an ambulance after the accident?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
Will you pay the fine?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
6 Write the correct tense or voice.
 Hospitals
are places where people …………………………. (examine) and
……………………………… (bring) back to good health. I’m
lucky because I ……………………………………(never /
take) to hospital when she …………………………… (hit) by
a car last month. Luckily no bones …………………………..
(break) but she …………………………
Hospitals
are places where people …………………………. (examine) and
……………………………… (bring) back to good health. I’m
lucky because I ……………………………………(never /
take) to hospital when she …………………………… (hit) by
a car last month. Luckily no bones …………………………..
(break) but she …………………………
(examine) carefully and x-rays ………………………………… (take). She …………………….. (keep) there for a night and she ………………………………….. (give) permission to leave the next day.
Ambulance services are also important. Patients …………………………… (must / take) to hospital as quickly as possible. A lot of people ………………………………… (kill) in road accidents and a lot more …………………………………. (injure) but if more ambulances………………………………. (put) into service, more lives ………………………………..
(can / save).
7 Rewrite the following passage changing the suitable sentences into PASSIVE VOICE.

Jane Johnson has been worried all last week. Last Monday, she received a letter from the police. In the letter they asked her to call the police station. Jane wondered why the police wanted her, and nothing worried her any more. There, they told her that they had found her bike. They picked it up in a small village a week ago. Somebody stole it 10 years ago, when she was a girl of fifteen. Now, they are sending it to her.
8 Fill in the blanks with the correct preposition and than rewrite the sentence in PASSIVE.
1. People always complaint …………………… the electricity bill.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
2. The candidate made a good impression …………the Managing Director.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
3. Sarah doesn’t look …………… your child well. He always gets into trouble.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
4. Someone has already sent ..................... Mr Jones.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
5. Robbers broke ..................... the shop and stole all the money.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
6. The police gave no comments ..................... this case.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
7. They insist ..................... my participation in the contest.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
8. He can’t put up ..................... his noisy neighbours.
…………………………………………………………………………………..
9 Write sentences in the way shown.
1. Jill didn't repair the roof herself. She _had it repaired._
2. I didn't cut my hair myself. I ______________________________________________
3. They didn't paint the house themselves. They ________________________________
4. Sue didn't make the curtains herself. _______________________________________
10 Use the words in brackets to complete the sentences. Use the structure 'have something done'.
1. We _are having the house painted_ (the house/paint) at the moment.
2. I lost my key. I'll have to ………………………………….. (another key/make).
3. When was the last time you ………………………………….. (your hair/cut)?
4. You look different ………………………………….. (you/your hair/cut)?
5. ………………………………….. (you/a newspaper/deliver) to your house or do you go to the shop to buy one?
6. A: What are those workmen doing in your garden?
B: Oh, we ………………………………….. (a swimming pool/build).
7. A: Can I see the photographs you took when you were on holiday?
B: I'm afraid I ………………………………….. (not/the film/develop) yet.
8. This coat is dirty. I must ………………………………….. (it/clean).
9. If you want to wear earrings, why don't you ………………………………….. (your ears/pierce)?
11 Make up sentences using 'have something done'.
He/repair/roof/yesterday
__________________________________________________________________
I’d like to/pierce/my ears/when I’m 16
__________________________________________________________________
I usually/cut/my hair/in the hairdressing saloon
__________________________________________________________________
Jack/service/his car/never
__________________________________________________________________
They will/install/windows/tomorrow
__________________________________________________________________
The hotel needs to/fix/the elevator
__________________________________________________________________
Lord Vincent/decorate/his castle/now/for a party
__________________________________________________________________
She/steal/her purse/on holiday
__________________________________________________________________
When/you/paint/your house?
__________________________________________________________________
I’m going to/test/my eyes/next week
__________________________________________________________________

Unit 8. Modals: can, could and (be) able to, may, might
MODAL VERBS are a small group of verbs that are used with other verbs to change their meaning in the sentence in various ways.
MODAL VERBS are used with other verbs (in front of a verb) to express the speaker’s opinion at the time of speaking. They express the speaker’s attitude towards an event, a situation or the person they are speaking to.
We use MODAL VERBS, not for situations / things that have definitely happened, BUT to talk about things we expect, which are possible, which we think are necessary, which we are not sure about, etc…
Differences from other English verbs:
They have no infinitive form or participles.
They do not need auxiliary DO = questions and negatives are made without do, does, did:
Question - Can we go now?
Negative - I can’t ride a bike.
They have no - s in the 3rd person singular:
Mary can swim very well and Mary should learn it before her trip to Brazil.
They do not normally stand alone. They are nearly always used in front of a verb. The main verb is always an Infinitive without to:
Jane might arrive before dinner, but I doubt it.
A few modals are followed by to:
Perhaps you ought to see a doctor.
Can


He can swim. He can’t swim.
1. Can is used to express the ability to do something.
I can swim very well.
Can he speak English fluently? - No, he can't.
We cannot sing at all!
2. It expresses the possibility to do something.
We can go to the seaside at last. Our holidays start next week.
3. We use it to say that something is probable.
It can be John. He has blond hair and he is wearing glasses.
4. It expresses the permission to do something.
Why not? You can marry her. She is a nice girl.
We use can + infinitive (can do/can see etc.):
We can see the lake from our bedroom window.
Can you speak any foreign languages?
I can come and see you tomorrow if you like.
The negative is can't (= cannot):
I'm afraid I can't come to the party on Friday.
(Be) able to ... is possible instead of can, but can is more usual:
Are you able to speak any foreign languages?
But can has only two forms, can (present) and could (past). So sometimes it is necessary to use (be) able to...
Compare:
I can't sleep.
BUT: I haven't been able to sleep recently. (can has no present perfect)
Tom can come tomorrow.
BUT: Tom might be able to come tomorrow. (can has no infinitive)
Could and was able to...
Sometimes could is the past of can. We use could especially with:
see hear smell taste feel remember understand
When we went into the house, we could smell burning.
She spoke in a very low voice, but I could understand what she said.
We also use could to say that somebody had the general ability or permission to do something:
My grandfather could speak five languages.
We were completely free. We could do what we wanted. (= we were allowed to do ...)
We use could for general ability. But if we are talking about what happened in a particular situation, we use was/were able to... or managed to... (not could):
The fire spread through the building quickly but everybody was able to escape.
or ... everybody managed to escape. (but not 'could escape').
Compare:
Jack was an excellent tennis player. He could beat anybody. (he had the general ability to beat anybody)
BUT:
Jack and Alf had a game of tennis yesterday. Alf played very well but in the end Jack managed to beat him. or ... was able to beat him. (= he managed to beat him in this particular game)
The negative couldn't (could not) is possible in all situations:
My grandfather couldn't (could not) is possible in all situations
We tried hard but we couldn't persuade them to come with us.
Alf played well but he couldn't beat Jack.
Could is also used in the future (especially to make a suggestion):
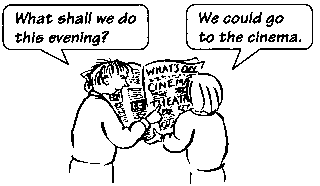
Can is also possible in these sentences ('We can go for a walk,' etc.). Could is less sure than can. You must use could (not 'can') when you don't really mean what you say:
I'm so angry with him. I could kill him! (not 'I can kill him').
We also use could to say that something is possible now or in the future:
The phone is ringing. It could be Tim.
I don't know when they'll be here. They could arrive at any time.
Can is not possible in these examples (not 'It can be Tim').
Sometimes could means 'would be able to...':
We could go away if we had enough money. (= we would be able to go away)
I don't know how you work so hard. I couldn't do it.
May and might
1. May is used for permissions.
You may borrow my car. I won't need it.
May I smoke here? – No, you can't, I'm sorry.
2. May is used to express probability or prediction.
They may call tomorrow. I hope so.
The main difference between may and can is in style. May is more formal than can. Can is typical of spoken English.
3. The opposite of may is must not or may not.
May I smoke here?
- You mustn't smoke here. (strong prohibition)
- You may not smoke here. (more polite, very formal)
- You can't smoke here. (informal spoken English)
Study this example situation:
 You
are looking for Bob. Nobody is sure where he is but you get some
suggestions.
You
are looking for Bob. Nobody is sure where he is but you get some
suggestions.
You: Where's Bob?
He may be in his office. (= perhaps he is in the house)
He might be playing in the yard. (= perhaps he is playing in the yard)
Ask Ann. She might know. (= perhaps she knows)
We use may or might to say that something is a possibility. Usually you can use may or might you can say:
It may be true. or It might be true. (= perhaps it is true)
She mightn’t know. or She may not know.
Sometimes could has a similar meaning to may and might:
The phone's ringing. It could be Tim. (= it may/might be Tim).
You could have left your bag in the shop. (= you may/might have left it...).
But couldn't (negative) is different from may not and might not.
Compare:
She was too far away, so she couldn't have seen you. (= it is not possible that she saw you).
A: I wonder why she didn't say hello.
B: She might not have seen you. (= perhaps she didn't see you; perhaps she did).
We use may and might to talk about possible actions or happenings in the future:
I haven't decided yet where to spend my holidays. I may go to Ireland. (= perhaps I will go to Ireland)
Take an umbrella with you when you go out. It might rain later. (= perhaps it will rain)
Usually it doesn't matter whether you use may or might. So you can say:
I may go to Ireland. or I might go to Ireland.
But we use only might (not may) when the situation is not real:
If I knew them better, I might invite them to dinner. (The situation here is not real because I don't know them very well, so I'm not going to invite them. 'May' is not possible in this example.)
Let’s Practice
