
- •Part I money
- •How much do you know about money?
- •It is interesting to know
- •What is barter?
- •Fill in the words from the box . Look up the following words in the dictionary and compose your own sentences with them.
- •In to on from
- •Exercise 2
- •Money Matters
- •It is interesting to know
- •Money: where to get it and to spend it?
- •Who wants to be a millionaire?
- •Eh si hypap ohw ahs on noeym btu sknwo woh ot teg ti thlyoens
- •It is interesting to know
- •Part II clothes Topical Vocabulary
- •Indoor and Outdoor Wear
- •Example: velvet ribbon
- •Father and son
- •It is interesting to know
- •It is interesting to know
- •If The Shoe Fits
- •It is interesting to know
- •Fashion
- •Feelings for fashion
- •Audrey Hepburn
- •It is interesting to know
- •Part IV shopping
- •It is interesting to know
- •Three thousand years of world trade
- •In the beginning
- •The ancient world - bc
- •The ancient world - ad
- •The middle ages
- •Comprehension check
- •It is interesting to know
- •What kinds of shops cater for people’s needs?
- •It is interesting to know
- •When Shopping is a Problem
- •What are your shopping habits?
- •Street Markets
- •It is interesting to know
- •Overchoice
- •Advertising
- •It is interesting to know
- •It costs a pretty packet!
- •Choosing Clothes
- •It is interesting to know
- •It is interesting to know
- •It is interesting to know
- •Know Your Rights!
- •If things go wrong...
- •If I had money…
It is interesting to know
Reading
Read the text and answer the questions that follow.
What is barter?
You give me a ton of bananas. I give you six computers. This is called barter. We exchange goods, but not money. It's a simple principle. Many people think barter is used in primitive societies, or perhaps in countries with a very weak currency. They don't think barter companies can be successful businesses.
But here are some surprising facts and figures. In the US there are more than 400 barter companies. Many were set up more than 30 years ago. Barter is a $6 million industry in the US. In the UK, barter companies are doing extremely good business. One of them, the Barter Company, began trading only three years ago. It now has eleven offices in the UK and Europe and manages barter business for 595 companies.
Why is barter increasing? Who needs barter, when you've got cash, at least not enough cash, and not at the right times. But they may have goods and services that they can't sell. They put these into a barter pool. The barter pool gives them exchange credit. With this credit they can 'buy' other goods and services from the pool.
So barter today is not the simple cross-trade of bananas for computers that we began with. In fact, you 'sell' your bananas to the pool, which contains office furniture, office equipment, clothing, printing, technology and so on. You can 'buy' from the pool what you need. Perhaps it's not surprising that the most traded items are accommodation and travel. Successful barter companies offer a big choice and are global and international. They are a safe investment for the twenty-first century.
Answer the questions:
Barter is used
only in countries with weak currency
only in primitive societies
in any business environment
Barter today is
a direct exchange of goods
buying and selling from a pool of goods
buying and selling for cash
Barter trade in the UK is
increasing
decreasing
staying at the same level
Who organizes barter trade today?
individual companies
specialized companies
governments.
![]() Listening
Listening
Listen to a short story of the uses of, and alternatives to money. Decide which of the pictures of alternatives to money that are given below are mentioned. Answer the following questions:
When and where did they begin to use coins?
What were the first coins made of?
Has money been used only as a method of payment?
When did the use of paper money begin?
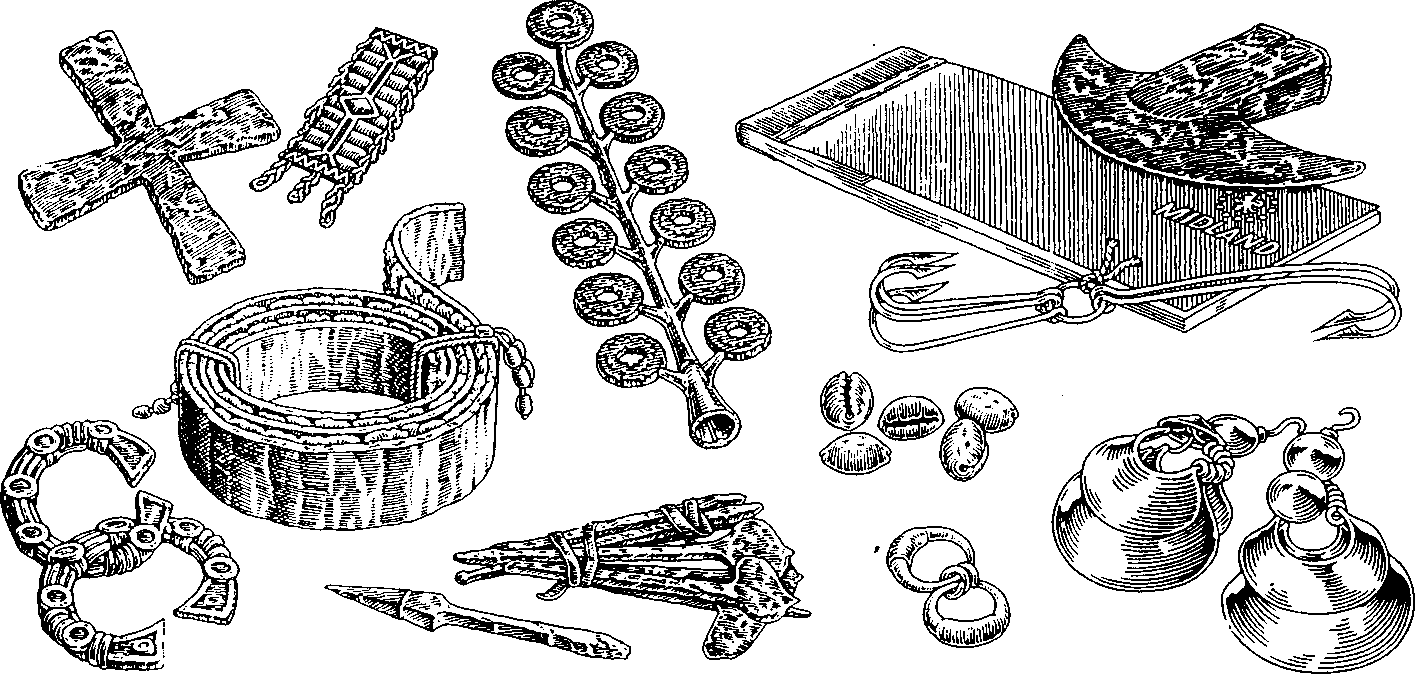
Speaking
Discuss the following questions in your group:
1.What are the advantages and disadvantages of some of the alternatives to our idea of money mentioned in the listening exercise and of those shown in the pictures above?
2. What would be the consequence of a world without money? Would there be no poverty?
3. What are the advantages of using a bartering system?
Exercise 1
Translate the following sentences into English.
Який сенс накопичувати багатство, адже краще жити в своє задоволення.
Не могли б ви розміняти цю банкноту?
В усі часи гроші були засобом вимірювання цінності.
Бартер – це система безпосереднього обміну, яка використовувалася ще в первісному суспільстві.
Я не знаю, навіть приблизно, скільки коштує щоденна газета або два десятки яєць.
Гроші – це засіб купівлі та продажу товарів, вимірювання цінності та накопичення багатства.
На кожній монеті є напис та цифри, що свідчать про її цінність.
Гроші керують світом. Саме вони є причиною всіх негараздів.
Економіка будь-якого суспільства базується на грошах, які випускаються у вигляді монет та банкнот.
Монети виготовляються з таких цінних металів, як золото та срібло, а також із міді, свинцю та алюмінію.
Зараз номінальна вартість монет не залежить від вмісту металу в них.
Хоча паперові гроші зручні у користуванні, майбутнє за кредитними картками.
Topical vocabulary and speech patterns combined:
Reading
Read the text and jot down the unknown words and phrases in your vocabularies.
Personal finance
Sometimes in a shop they ask you: ‘How do you want to pay?’ You can answer: ‘Cash / By cheque / By credit card’.
In a bank you usually have a current account, which is one where you pay in your salary and then withdraw money to pay your everyday bills. The bank sends you a regular bank statement telling you how much money is in your account. You may also have a savings account where you deposit any extra money that you have and only take money out when you want to spend it on something special. You usually try to avoid having an overdraft or you end up paying a lot of interest. If your account is overdrawn, you can be said to be in the red (as opposed to to be in the black or in credit).
Sometimes the bank may lend you money - this is called a bank loan. If the bank (or building society) lends you money to buy a house, that money is called a mortgage.
When you buy (or, more formally, purchase) something in a shop, you usually pay for it outright but sometimes you buy on credit. Sometimes you may be offered a discount or a reduction on something you buy at a shop. This means that you get, say, £10 off perhaps because you are a student. You are often offered a discount if you buy in bulk. It is not usual to haggle about prices in a British shop, as it is in, say, a Turkish market. If you want to return something which you have bought to a shop, you may be given a refund, i.e. your money will be returned, provided you have a receipt.
The money that you pay for services, e.g. to a school or a lawyer, is usually called a fee or fees; the money paid for a journey is a fare.
If you buy something that you feel was very good value, it's a bargain. If you feel that it is definitely not worth what you paid for it, then you call it a rip-off (very colloquial).
Public finance
The government collects money from citizens through taxes. Income tax is the tax collected on wages and salaries. Inheritance tax is collected on what people inherit from others. Customs or excise duties have to be paid on goods imported from other countries. VAT or value added tax is a tax paid on most goods and services when they are bought or purchased. Companies pay corporation tax on their profits. If you pay too much tax, you should be given some money back, a tax rebate.
The government also sometimes pays out money to people in need, e.g. unemployment benefit (also known informally as the dole) disability allowances and student grants (to help pay for studying). Recipients draw a pension / unemployment benefit or are on the dole or on social security.
Every country has its own special currency. Every day the rates of exchange are published and you can discover, for example, how many dollars there are currently to the pound sterling or hryvnya.
A company may sell shares to members of the public who are then said to have invested in that company. They should be paid a regular dividend on their investment, depending on the profit or loss made by the company.
Exercise 1
Give the English equivalents to the words and phrases given. Be ready to use them in the sentences of your own.
Отримати відшкодування, банківська позика, депозитний рахунок, капіталовкладення, поточний рахунок, платити відразу, знімати гроші, вносити гроші на поточний рахунок, торгуватися, перевищення кредиту, мито, акцизний збір, здирництво, податок на спадщину, плата за проїзд, одержувати пенсію, курс обміну валюти, купувати оптом, купувати у кредит, сплачувати відсотки, мати гроші на банківському рахунку, прибутковий податок, податок на додану вартість, акції, допомога по безробіттю, плата за послуги, дивіденд, повернення податку, соціальне забезпеченння, збиток, грошова допомога по інвалідності, прибуток, корпоративний податок, вигідна покупка, сплачувати рахунки, знижка, касовий чек.
Exercise 2
Fill in the gaps with the given verbs. Mind the tense.
|
buy spend lose pay cost sell win waste find give |
My car was five years old, so I……………… it and ……………… a new one.
I was very sad when I …………… my watch in the street. It was a present from my wife and it …………… her a lot of money. Fortunately, somebody ………… it the next day and took it to a Police Station.
I ………… over $2.000 for my computer, but it isn't worth very much now.
My father………… me $50 last week but I ………… most of it on a ticket for a concert on Friday.
Last week somebody ………… $1m in a game on television. It was incredibly exciting.
I'm afraid I ………… my money on those CDs because I never play them.
Exercise 3
Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right.
|
day-to-day use
|
Exercise 4
Choose the right answer.
When you retire at the age of sixty-five, you receive a(n) …. from the government.
a) allowance b) fine c) grant d) pension
If production in the factory exceeds the target, the workers get a ……..
a) bonus b) donation c) gratuity d) premium
Income tax is related to one’s annual ………
a) allowance b) wages c)income d) bonus
The kidnappers demanded a ….. of $1,000,000.
a) aid b) allowance c) ransom d) reward
A salesman is paid …… on the goods he sells.
a) commission b) percentage c) provision d) salary
The President admitted taking ……. and had to resign.
a) bribes b) fees c) fines d) premiums
Mr Rich earns $8,000 a month…… and $5,000 a month net.
a) bulk b) gross c) mass d) wholesale
You can only ……. this postal order at a post office.
a) alter b) cash c) exchange d) pay
Mrs Unemployed is finding it difficult to pay the …… on her insurance policy.
a) bonuses b) fees c) fines d) premiums
Our company made a record …… last year.
a) benefit b) earn c) profit d) winning
While you are away from the office on business trips, you will be given a daily …… of $50 towards meals and accommodation.
a) allowance b) fine c) permit d) reward
I hate the beginning of each year when all the ……. start coming in and I have to find the money to pay them all.
a) accounts b) bills c) receipts d) fines
For some jobless people, joining the …….queue is a humiliating experience.
a) benefit b) dole c) grant d) ration
Every Friday Fred ….. money out of the bank.
a) cashed b) drew c) robbed d) stole
It’s a good school, but the ……. are rather high.
a) fares b) cost c) fees d) pay
Exercise 5
Is the ordinary 'person-in-the-street' pleased to see these newspaper headlines or not?
Mortgage rate goes up Wages to be frozen Pension age raised
Interest rates down VAT to be reduced NUMBER ON DOLE RISES
Exercise 6
Complete the sentences with the suitable words.
Money which has to be paid on what you inherit is known as ……………………
If the bank lends you money, you have a bank …………………………………...
If you have some money in your account you are in the …………………………
I paid too much tax last year so I should get a …………………………… soon.
If it's no good, take it back to the shop and ask for a ………………………….
A fixed amount which is paid, usually monthly, to workers of higher rank is known as a ………………………………………………………
A sum of money which is owed to someone is a …………………………………
Money which in the form of coins and notes, not cheques is ……………………
Money paid as a punishment for breaking the law is a……………………………
An amount of money you receive, usually weekly, in return for labour or service is known as …………………………………
Money paid while travelling, especially on public transport, buses, trains, etc. is a ………………………
A tax on imported articles paid to the Customs is ……………………………….
Money paid by a divorced father to his former wife for the upkeep of his children is …………………….
Money paid at a restaurant after eating is a ……….………………………
Money paid to the government for services that the state provides is called ……
Extra percentage paid on the loan is ………………………………………….
Money paid for professional services, e.g. to a doctor is called a ……………….
Money returned to you after you pay too much is …………….
Money paid for a place to live is …………
Exercise 7
Put each of the following words or phrases into its place in the text below.
banks beads buy coins change
currency depositing earn exchange rate
goods investments money paper bills
savings accounts sell shells value
Money
Money is what people use to……….. things. People spend money on ……… and services. Many people save part of their money by………… it in a bank. People ………. money by performing services. They also earn money from ………, including government bonds, and from ……… .
………… can be anything people agree to accept in exchange for the things they ……… or the work they do. Ancient peoples used such varied things as………, ……….., and cattle as money. Today, most nations use metal coins and ………. . Different countries’ ……….. and bills look different and have different names.
A person can ……. his money for the money of any country according to the ………… . Usually, such rates are set by the central…….. of a country. The ……. of a country’s ………. may change, depending on the economic and political conditions in that country.
Exercise 8
Translate into English.
Наступного року уряд планує додати до держбюджету 49 млрд грн завдяки основним податкам: податку на додану вартість, прибутковому податку, акцизному збору.
Якщо я віддам всі свої борги, у мене зовсім не залишиться грошей.
Найбільше грошей наша сім’я витрачає на продукти.
Коли постає вибір – що купувати і як, я завжди намагаюсь купувати речі оптом, а не в роздріб, а коли і купую якусь одну дорогу річ, то шукаю магазини, де можна придбати товари в розстрочку й під низькі відсотки.
Люди неохоче сплачують податки, але заплативши, скажімо, податок на спадщину чи прибутковий податок, ви можете бути певні, що хтось отримає допомогу по безробіттю, допомогу по непрацездатності або пенсію.
Вона зараз не працює, бо доглядає за дитиною і отримує допомогу по догляду за дитиною.
Купівля на виплат дуже зручна для тих, хто не хоче брати позику в банку, а потім сплачувати її та відсотки.
Люди віддають перевагу “твердій валюті”, тому міняють гривні на долари та євро.
У банку ви можете відкрити поточний рахунок, депозитний рахунок, отримати готівку по чеку, або ж обміняти валюту по курсу, встановленому НБУ.
Я віддаю перевагу поточному рахунку, а не депозитному, так як я ділова людина, і мені часто доводиться знімати гроші.
Коли ви сплачуєте за покупку готівкою, ви можете попросити надати вам знижку.
Купуючи коштовну річ у Великобританії обов’язково візміть у власника крамниці касовий чек, і коли ви пред’явите його на митниці вам повернуть ПДВ.
Заплати за проїзд, будь ласка, я залишила свій гаманець вдома.
Він зізнався в тому, що брав хабарі.
Викрадачі людей вимагали викуп у сумі $50 000.
Exercise 9
Match the statements below with a word(s) from the box.
|
building society cash cheque credit card currency deposit fee grant wages income tax in credit interest loan mortgage overdrawn pension receipt rate of exchange salary unemployment benefit (VAT) value added tax withdrawal |
A word for a document you receive when you buy something.
A word for an organisation which lends you money to buy a house or a flat.
A word for money you earn from a larger amount of money or pay on money you borrow.
Two words for money which is lent to you.
Two words for the action of taking out or putting money into a bank account.
Three words for methods of paying for things you buy.
Two words to describe the status of your account.
Two words for money the government takes away from you.
Three words to describe the payment you receive for work you do.
Two words to do with money from a foreign country.
Three words or expressions to describe money which the government may pay you.
Exercise 10
Fill in the table bellow for this or any other country.
|
Rate of inflation __________ Exchange rate (against the US dollar) __________ Interest rate __________ Basic level of income tax __________ Rate of VAT __________ Monthly state pension __________ |
Exercise 11
Complete the following sentences. Each (-) represents one letter.
I spend about $ 1.5 a week on bus f_ _ _ _ .
I had to pay d _ _ _ on the Turkish carpet I brought in through the Customs yesterday.
Now that Mr Old has retired, he lives partly on his p_ _ _ _ _ _ and partly on the
i _ _ _ _ _ _ _ from his savings account.
In spite of its size his family was quite w _ _ _ -off, because he brought in a good
s_ _ _ _ _.
Gold would be a good i _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ ; it’s bound to increase in value.
Due to inflation the s_ _ _ _ _ _ _ of living went down by fifteen p_ _ _ _ _ _ .
I couldn’t buy the house because the bank refused to let me have a m_ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
You must stop wasting your money on silly things and start s_ _ _ _ _ . This is the only solution to your f_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ troubles.
One dollar is e_ _ _ _ to over 5.37 hryvnyas.
The v_ _ _ _ of the pound has fallen recently.
I want $500-worth of Euro. What is the e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ rate, please?
All the workers in our firm get a Christmas b_ _ _ _ of $ 100.
Exercise 12
