
- •Изучаем основы бизнеса down to business
- •Часть 1 Хабаровск
- •Введение
- •I. TextWhat is Business?
- •Input – transformation – output
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •Sale of goods
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •Sam. – Look, many people would like to start a business. It involves
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar a. Grammar Review Exercises
- •I. Text types of economic systems
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •Key word – combinations
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •A. Grammar Folio
- •The Passive Voice
- •Страдательный (пассивный) залог
- •B. Exercises
- •I. Text economic entity assumption
- •Sole Proprietorships
- •Partnerships
- •Advantages and Disadvantages of a Partnership
- •Corporations
- •Advantages and disadvantages of a corporation
- •Vocabulary
- •Exhibit 3.1. Prevalence and Profits of the Three Forms of Business Ownership
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar a. Grammar Folio The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- •B. Exercises
- •I. Text labour market
- •Exhibit 4.1. Sector of the us Economy
- •Exhibit 4.2. Shift in Employment by Industry Sector
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech and writing practice exercises
- •Curriculum Vitae
- •C.S.E.* Maths, English, Geography, History, Chemistry 1987
- •Interests:
- •Commentaries
- •Interests: __________________________________________________
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar a. Grammar Folio The Past Perfect Tense
- •B. Exercises
- •I. Text nature of accounting
- •A Typical Finance Department
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •B. Exercises
- •I. Text financial statements
- •Balance Sheet
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •Income Statement
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •Statement of Cash Flows
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary exercises
- •III. Speech and writing practice exercises
- •Exhibit 6.1. Balance Sheet for Computer Discount Warehouse
- •Exhibit 6.2. Income Statement for Computer Discount Warehouse
- •Exhibit 6.3. Statement of Cash Flows for Computer Discount Warehouse
- •Prepare the financial statements at May31 for David Palmer, Attorney at Law.
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •A. Grammar Folio
- •The Modals and Their Equivalents
- •To have to
- •B. Exercises
- •Supplementary texts for translation text 1 people who made a fortune
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 2 upbeat on russia
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 3 mergers and acquisitions
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 4 shareholders
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 5 starting up business in russia
- •I. Professional Overview of the Russian Recruiting Market
- •II. Professionals Most Demanded by Western Companies in Russia
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 6 along scientific lines
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 7 auditing
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Text 8 the changing accounting profession
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Список литературы
- •Содержание
I. Text nature of accounting
Business is an increasingly important activity throughout the world today. Consequently, the opportunities for a business career have grown in variety and number. There are now five broad fields or areas of business that offer exciting careers: accounting, finance, management, marketing, and data processing. An effective accounting system is a cornerstone of any economic entity.
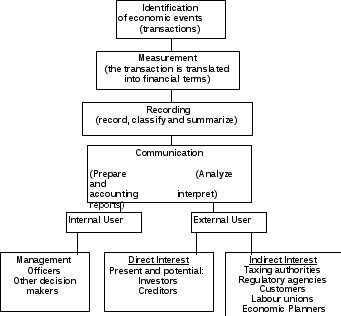
Accounting is the system business uses to measure its financial performance. Accounting is frequently called “the language of business” because of its ability to communicate financial information about an organization. Various interested parties such as managers, potential investors, creditors and the government depend on a company’s accounting system to help them make informed financial decisions. An effective accounting system, therefore, must include accurate collecting, recording, classifying, summarizing, interpreting and reporting of information on the financial status of an organization.
During the accounting process, sales, purchases, and other transactions are recorded and classified into individual accounts. These accounts are later summarized in statements that make it possible to evaluate a company’s past performance, present condition, and future prospects.
Accounting is important to business for two reasons: it helps managers plan and control a company’s operations, and it helps outsiders evaluate the business. Area of accounting concerned with preparing financial information for users outside the organization is called financial accounting. Since users of such information must compare it to similar data from other sources, financial accounting statements are prepared according to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), basic standards and procedures that have been agreed on by the accounting profession. Area of accounting concerned with preparing data for use by managers within the organization is known as management accounting. The job of management accounting includes the preparation of budgets (a financial plan for a given time period) and the analysis of production costs.
The major users of accounting are:
A) Management uses accounting information in planning, controlling and evaluating business operations Armed with accounting information, managers are better equipped to make business decisions.
B) Investors and shareholders are concerned with a company’s profit potential. They judge the wisdom of buying, holding or selling their financial interests on the basis of accounting data.
C) Creditors (suppliers and bankers) want to know whether a business is credit worthy on the basis of the accounting information obtained about this business.
Other groups with an indirect interest are taxing authorities, regulatory agencies, customers, labor unions and economists. These users need information that is accurate, objective, consistent over time, and comparable to information supplied by other companies.
The accounting process may be diagrammed as follows:
Bookkeeping and accounting are often considered to be one and the same. This confusion is understandable because the accounting process includes the bookkeeping but it also includes much more.
Bookkeeping usually involves only the recording of the economic events and therefore is just one part of the accounting process. Bookkeepers deal in taxes, cash flow, which includes cash receipts and cash disbursements, sales, purchases and different business transactions of the company. Bookkeepers first record all the appropriate figures in the books of original entry, or journals. At the end of a period, usually a month, the totals of each book of original entry are posted into the proper page of the ledger. The ledger shows all the expenditures and all the earnings of the company. On the basis of all the totals of each account in the ledger, the bookkeeper prepares a trial balance. Trial balances are usually drawn up every quarter.
Accounting, on the other hand, involves the entire accounting process, including identification, measurement, recording and communication. The accountant’s responsibility is to analyze and interpret the data in the ledger and the trial balance. The accountant is to determine the ways in which the business may grow in the future. No expansion or reorganization is planned without the help of the accountant. The work of accountants is rather complicated.
In the United States, accountants are usually classified as public, private, or governmental.
Public accountants are independent of the businesses, organizations, and individuals they serve. These accountants prepare financial statements, compute taxes, provide consultation for individuals and organizations. They provide such accounting service as auditing – formal evaluation of the fairness and reliability of a company’s financial statements. Public accountants may earn the title of CPA (Certified Public Accountant) by fulfilling rigorous requirements. Private accountants work solely for private companies or corporations that hire them to maintain financial records. Private accountants specialize in different areas of accounting, such as cost accounting (computing and analyzing production costs), tax accounting (preparing tax returns and tax planning) or financial analysis (evaluating a company’s performance and the financial implications of strategic decisions).
Governmental accountants work for governmental agencies or bureaus. Both private and governmental accountants are paid on a salary basis, whereas public accountants receive fees for their services.
Most company accountants work together as a team under the supervision of the controller who reports to the vice-president of finance. In smaller companies the controller may be in charge of the company’s entire finance operation and report directly to the president. Controllers are responsible for measuring the company’s performance. They interpret the results of the operations, plan and recommend future actions. This position is very close to the top executives of the company. The controller of a medium to large corporation monitors and cross-checks all financial data, usually with the help of a computer, in order to evaluate the company’s financial health at any given point. The controller also works with other members of top management to make certain that the company uses all its assets to best advantage.
