
- •Изучаем основы бизнеса down to business
- •Часть 2
- •Введение
- •I. Text managing financial resources
- •Exhibit 1. 1. The Flow of a Company’s Funds
- •Exhibit 1. 2. Debt versus Equity
- •Vocabulary
- •Comprehension questions
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •II. Vocabulary practice exercises
- •III speech practice exercises
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •II. Vocabulary practiceexercises
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •If – constructions.
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •II. Vocabulary exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •Vocabulary Notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •I. Text
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •II vocabulary practice exercises
- •III. Speech practice exercises
- •IV. Brush up your grammar
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •International banking services
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabularly notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Vocabulary notes
- •Изучаем основы бизнеса
- •680021, Г. Хабаровск, ул. Серышева, 47.
Vocabulary notes
home equity installment loan – ссуда с погашением в рассрочку под залог
домашнего имущества
auto lease – кредит на аренду автомобиля с возможностью его
дальнейшего выкупа
subsidized student loan – ссуда на образование, субсидированная госу-
дарством
variable rate – колеблющаяся процентная ставка
fixed rate – твёрдая процентная ставка
qualify for a loan – получать право на ссуду
repayment terms – условия погашения ссуды
credit terms – условия кредита
fixed expenses – (зд.) выплаты по кредиту
breakthrough technology – передовая технология
interactive – взаимодействующий
commercial – реклама (по радио, телевидению)
with 20% down ( down payment) – с уплаченными вперёд двадцатью
процентами (первоначальный взнос)
4. Be ready to work on the projects offered below:
1. The Evolving Banking Environment.
2. Financial Institutions and Their Traditional Services.
3. Commercial Bank Assets and Liabilities.
4. Interest Rates.
5. Banking in the New Cyberworld.
IV. Brush up your grammar
A. Grammar Folio:
The Sequence of Tenses
Reported Speech
Структурно, косвенная речь (Reported Speech) представляет собой сложное предложение, состоящее из главного и придаточного предложений. Если глагол-сказуемое главного предложения (вводящий глагол) стоит в настоящем времени (e.g. I say, he says, she asks etc.), то глагол-сказуемое придаточного предложения может стоять в любом, нужном по смыслу времени.
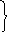 he works in the
bank
he works in the
bank
He says that he worked in the bank
he will work in the bank
Если вводящий косвенную речь глагол стоит в прошедшем времени
(e.g. I said, he asked, etc.), то в придаточном предложении происходит замена временных форм по сравнению с временными формами в прямой речи.
Таблица изменений временных форм в соответствии
с правилом согласования времён
DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH
|
The Present Indefinite |
The Past Indefinite |
|
The Present Continuous |
The Past Continuous |
|
The Present Perfect |
The Past Perfect |
|
The Present Perfect Continuous |
The Past Perfect Continuous |
|
The Past Indefinite |
The Past Perfect |
|
The Past Continuous |
The Past Perfect Continuous |
|
The Future Indefinite |
The Future Indefinite In The Past |
|
The Future Continuous |
The Future Continuous In The Past |
direct David: ”I want to get a loan”.
reported David said that he wanted to get a loan.
direct Susan: “My friends left for Europe”.
reported Susan said that her friends had left for Europe.
direct Mr. Torn: “The bank was founded in 1950.”
reported Mr. Torn told Norma that the bank had been founded in 1950.
Для выражения действия в будущем, вместо вспомогательных глаголов shall / will употребляем вспомогательный глагол would (Future-in-the-Past).
direct Lora:” I will come back soon”.
reported Lora said that she would come back soon.
В вопросительных предложениях, переведённых в косвенную речь, порядок слов остаётся таким же, как и в утвердительных предложениях, вспомогательные глаголы (do, does,did) не употребляются.
direct Sam: “Where does your father work?’
reported Sam asked me where my father worked.
При переводе в косвенную речь общего вопроса, вводим союзы whether или if.
direct Mary: “Did you have any problems?”
reported Mary asked me if I had any problems.
Повелительное наклонение (приказы, просьбы, советы, приглашения) передаётся в косвенной речи структурой verb + object + to infinitive. В отрицательных повелительных предложениях используем структуру not to + infinitive.
direct Ted: “Fill in the blank, please.”
reported Ted asked the customer to fill in the blank.
direct Mr. Clark: “Don’t touch any documents.”
reported Mr. Clark told his secretary not to touch any documents.
При переходе прямой речи в косвенную могут происходить следующие
замены:
I / we he (she) / they
my / our his (her) / their
this / these that / those
here there
now then
today that day
tonight that night
tomorrow the next day
yesterday the day before / the previous day
last the previous
ago before
next following
B. Exercises
1. Change the following sentences into Reported Speech:
1. Nick said, “I want to close my checking account.”
2. Mr. Torn said, “At Westfirst we have a wide variety of credit choices.”
3. “We are constantly looking for ways to make banking easier,” added Mr. Torn.
4. The secretary told me, “I have just seen Mr. Snow in a foreign exchange department.
5. A young lady asked John, “Where is the nearest bank?”
6. The teacher asked the students, “What banks do you know in the USA?”
7. The Chairman said, “The statement will be sent to all the stockholders tomorrow.”
8. My friend said, “I received a notice that my loan is due.”
9. We asked him, “How much interest will you pay on the loan?”
10. I asked him, “Does the bank have a branch in Geneva?”
11. The manager told me, “You can’t make a withdrawal without your passbook.”
12. Ann asked Bob, “Have you heard the news?”
13. The manager asked the secretary, “How did they get this information?”
14. Nora said, “I’ve been working in this bank since last June.”
15. The customer asked the bank officer, “Is the interest higher on a time deposit?”
16. “Am I speaking to a Westfirst representative?” asked a voice over the telephone.
17. The bank officer said to me, “Please, indicate how much money you want to borrow.”
18. “I shall miss you when you leave for London,” said Alice to Meg.
19. Mr. Brown said to his secretary, “Send this letter immediately.”
20. “Yesterday I was interested in making a long-term investment, but today I want to make a short-term one,” said Mike to Elisa.
21. The Chairman of the bank informed the customers, ”The funds you deposit with Westfirst are insured to $1,000,000 by FDIC, an agency of the federal government.”
22. “We’ve made a pretty good profit for the last three years running,” said the Chairman to the board of directors.
2. Change the following dialogues into Reported Speech. Use such
reporting verbs as to ask, to answer,to add, to tell,to wonder, to
inform, to want to know,etc.
A)
Norma - Mr. Torn, say a few words about home loans, please.
Mr. Torn - At Westfirst we offer home mortgage loans through our parent
company, Bank of America. Our customers may choose between
fixed rate home loans and advantage plus home loans.
Norma - What is the difference between these types of loans?
Mr. Torn - With fixed rate home loan customers are guaranteed that the
interest rates and payments will never change over the life of the
loan.
Norma - What advantages do plus home loans have?
Mr Torn - The main advantage is an attractive initial interest rate.
Norma - Does it mean a low initial interest rate?
Mr. Torn -Yes, and the customers may be able to buy a more expensive
home because they will have lower initial monthly payments.
B)
Linda Hunt,
investor - I have some funds on hand, and I’m wondering whether I can put
it in a savings account.
Mr. Lee,
banker - It’s a good idea, if you want to keep your investment fairly liquid.
You can make withdrawals from your savings account at any time.
Linda - What about the rate of interest?
Mr. Lee – Last year we paid 3% per annum, but this year interest on a
savings account accrues at the rate of 4%.
Linda - Is this type of account transferable?
Mr. Lee – Only time deposits are transferable, Madame.
Linda - Are these deposits insured?
Mr. Lee – Yes, we are a member of the Federal Deposit Insurance
Corporation.
3. Translate the sentences into English using Reported Speech:
1. Профессор рассказал студентам, что первый итальянский банк был
учреждён в Венеции в 1587 г.
2. Преподаватель спросил меня, какие депозитные финансовые учреж-
дения я знаю.
3. Мистер Торн сказал, что в прошлом году активы банка составили 400
миллионов долларов.
4. Норма спросила мистера Торна, какие виды кредита предлагает их банк.
5. Миссис Пристли, домохозяйка из Сиэтла, позвонила на студию и спро-
сила, может ли она обратиться за банковской ссудой по телефону.
6. Служащий банка проинформировал клиента, что его процентная
ставка и выплаты никогда не изменятся в течение срока займа.
7. Он спросил меня, сколько лет я работаю в этом банке.
8. Управляющий сказал, что когда он был банковским клерком, он рабо- тал значительно больше, чем мы. Вот поэтому-то он и управляющий!
9. Я спросил секретаря, отправила ли она вчера все необходимые документы в банк.
10. Финансовый менеджер сообщил директору, что ему удалось продлить кредит в банке.
11. Кассир объяснил мне, как пользоваться кассовым автоматом. Он попросил меня вставить пластиковую карточку в специальную щель (aperture) и ввести свой персональный код доступа.
12. Управляющего спросили, имеет ли банк филиалы в других странах мира.
13. Финансовый директор заявил, что его компания сотрудничает с банком уже более десяти лет и является его надёжным клиентом. Представитель банка, в свою очередь, сообщил, что банк готов предоставить компании «прайм-рейт». Он добавил, что компания получит двухлетний заём в пять миллионов долларов под три процента годовых.
14. Контролёр попросил секретаря никому не сообщать о принятом решении.
UNIT 3
I. TEXT
MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS
“Management is an activity or art where
those who have not yet succeeded and
those who have proved unsuccessful are
led by those who have not yet failed.”
Paulsson Frenckner
Microsoft’s Bill Gates would be the first to admit that management is needed in every type of organization. An auto plant, a baseball team, an army, and a church committee all require management. So, what’s management?
A. What is Management?
Management is the process of coordinating resources to meet organizational goals. It entails planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources (land, labour, capital, and information) to efficiently reach those goals. Planning is the primary management function, the one on which all others depend. It involves establishing objectives and goals for an organization and determining the best ways to accomplish them. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, a goal is a broad, long-range target of the organization, and an objective is a specific, short-range target or aim. A key planning activity is forecasting – making educated assumptions about future trends and events that will have an impact on the organization. Organizing, the second management function, is the process of putting the plan into action. This involves allocating resources, especially human resources, so that the overall objectives can be attained. The third is leading – the day-to-day direction and supervision of employees. In leading, managers guide, teach, and motivate workers so that they reach their potential abilities and at the same time achieve the company goals that were established in the planning process. In the last management function, controlling, managers evaluate how well company objectives are being met. Controlling is the process of measuring progress against goals and objectives and correcting deviations if results are not as expected.
One way that managers are able to perform these four basic functions necessary for the organization’s success is through total quality management. Total quality management (TQM) is both a management philosophy and a strategic management process that focuses on delivering the optimal level of quality to customers by building quality into every organizational activity. Although it has only recently been adopted by many companies, TQM has been popular in Japan since the 1950s, when Japanese businesses turned to the quality teachings of W. Edwards Deming and J.M. Juran to rebuild their industrial strength. TQM redirects management to focus on four key elements: employee involvement, customer focus, benchmarking, and continuous improvement. Employee involvement includes team building and sharing of information at all levels of organization. Focusing on the customer simply means finding out what customers really want and providing them with it. Benchmarking is comparing your company’s processes and products to the standards of the world’s best companies and then working to match or exceed those standards. Continuous improvement requires an ongoing effort to reduce defects, cut costs, slash production and delivery times, and offer customers innovative products.
Management plays a vital role in any business or organized activity. It has eight major areas of concern: market standing, innovation, human resources, financial resources, physical resources, productivity, social responsibility, and financial performance. Management is composed of a team of managers who perform the management functions and have charge of the organization at all levels. Most achievements and failures in business are the achievements or failures of individual managers. As Gates has demonstrated, when managers possess the right combination of vision, skill, experience, and determination, they can lead an organization to success.
