
- •Odessa national medical university
- •Foreign language department
- •English for medical students посібник з англійської мови
- •I Am a Student
- •Grammar in use Personal Pronouns
- •The Verb “To Be”
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Higher Medical Education in Ukraine
- •Grammar in use Numerals. (cardinal, ordinal, fractions, percentage). Dates. Time.
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Higher Medical Education in Great Britain
- •Grammar in use Simple Tenses Active Voice
- •11.A) Put the verbs in brackets into the correct forms of Present, Past or Future Simple.
- •11.B) Complete the questions with suitable auxiliary verbs and answer them:
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Odessa national medical university
- •Grammar
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Mykola ivanovich pirogov
- •Irregular Verb V-2
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студента (срс)
- •Health care in Ukraine
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студента (срс)
- •Health service in great britain and the usa Great Britain
- •Grammar in use
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •The World Health Organization
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar revision
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Emergency medical service
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use Adverbs
- •Degrees of comparison of adverbs
- •Place of adverbs in a sentence
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Polyclinics
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use Present instead of Future Теперішній час у підрядних речення часу та умови
- •Приклади
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Examination of the Patient
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use Participle I & II
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Hospital
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use Types of questions Різні види питання
- •Part II
- •Part III
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •At the Chemist’s
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use Simple Active and Passive Tenses (revision)
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Microbiology
- •Microscopy
- •Grammar in use Modal verbs
- •History of Medical Microbiology
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Microorganisms
- •Grammar in use Modal verbs and their equivalents
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Virology
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Alexander Fleming
- •Grammar in use Continuous Active Tenses
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Human body
- •Grammar in use
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Systems of the body
- •Grammar in use Simple vs Progressive
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use Degrees of Comparison of Adjectives
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Text: Andreas Vesalius (1514-1563)
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use
- •Vesalius believed the skeletal system to be the framework of the human body.
- •Vesalius' work on the vascular and circulatory systems is his greatest contribution to the complex and modern medicine.
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •I. Form adjectives from the verbs using the suffix -able (-ible).Translate them.
- •II. Form verbs with the help of the suffix -ate. Translate them.
- •Work of the Human Heart
- •Post-text assignments
- •Grammar in use the present perfect tense, active voice
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use emphatic construction
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use emphatic construction
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Post-text assignments:
- •About Respiratory Disorders
- •Grammar in Use
- •Impersonal Sentences – Безособові речення
- •Indefinite Personal Sentences – Невизначено особові речення
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Grammar in use
- •Infinitive, its forms and functions
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •I.M. Sechenov і.М. Сеченов
- •I.M. Sechenov
- •Indefinite to write be written
- •Anatomy of the nervous system Анатомія нервової системи
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студента (срс)
- •Physiology of the nervous system
- •I.P. Pavlov and his investigation
- •Grammar in use Sequence of tenses
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Reflexes
- •Grammar in Use Sequence of Tenses (revision) Послідовність часів (повторення)
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •The Anatomy of Alimentary Tract
- •Grammar in use participle I
- •Functions in the sentence
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Physiology of the alimentary tract
- •Grammar in Use the gerund
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •The liver
- •Grammar in use Gerund and its noun and verb characteristics
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Endocrine glands
- •Grammar in use
- •Verbal Noun
- •(Sing./pl.)
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Hormones
- •Grammar in Use gerund. Revision.
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Anatomy of the urinary system
- •Grammar in Use participle I
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Physiology of the urinary system
- •Grammar in use Absolute Participle Construction (revision)
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •The anatomy of reproductive system.
- •Grammar revise: Conditional sentences.
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Physiology of Reproductive System
- •Post-text assignments
- •Development of embryo and fetus
- •Grammar in Use Conditional Sentences
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Vitamins
- •Grammar in use
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Minerals
- •Grammar in use English Tenses (revision)
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Health effects of smoking cigarettes
- •Grammar in use Present Simple vs Present Continuous
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Hygiene and Prevention
- •Post-text assignments
- •Types of Prophylaxis
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •I. Form new words with the prefix over meaning “понад, вверх”.Translate them.
- •II. Form new words with the prefix under meaning „під, нижче".Translate them.
- •III. Form new terms with the meaning „поганий". Translate them.
- •IV. Form nouns indicating “процес, дію або результат дії” using the suffix ing:
- •Post-text assignments
- •Special Diets
- •Grammar revision
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
- •Table of Foodstuffs, showing their Uses.
- •Post-text assignments:
- •Grammar revision
- •9. Put questions to the following words.
- •Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (срс)
|
1. Перекладіть та вивчіть наступні словосполучення
2. Дайте відповіді на наступні питання
3. Поясніть наступні терміни у 5ти реченнях анатом
|
|
Anatomy of the Heart Анатомія серця |
Text: Anatomy of the Heart
Grammar: The Comparative and Superlative Degree of the Adjectives
Pre-text assignments
Exercise 1. Learn the new words:
-
1.
Continuously
[
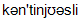 ]
]безперервно
2.
rhythmically
[‘rıðmıkƏlı],
ритмічно
3.
nutrient
[
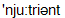 ]
]поживна речовина
4.
surface
[
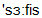 ]
]поверхня
5.
endocardium
[‘endəu’ka:dıəm]
ендокард
6.
membranous
[
 ]
]
мембранний
7.
pericardium
[
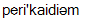 ]
]перикард
8.
septum
[
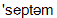 ]
]перетинка
9.
ventricle
[
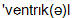 ].
]. шлуночок
10.
atrium
[
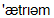 ]
]передсердя
11.
deoxygenated
[dioksidzi’neitid]
позбавлений кисню
12.
to contract
[kən’trækt]
скорочуватись
13.
sinoatrial
[sinoa´treal]
синусно-передсердний
14.
costal cartilages
[kos′təl]
реберний хрящ
Exercise 2. Read and translate the word combinations into your native language:
Muscular pump in the centre of the chest; to contract rhythmically; to send blood to the lungs; to consist of two atria and two ventricles; to be enclosed in a tough, membranous bag; a thick central muscular wall; to receive deoxygenated blood; via 2 large veins; to lose carbon dioxide; to be transferred to the left ventricle; via the pulmonary vein; one-way valves; to contract more forcibly; greater muscular bulk
Exercise 3. Read and translate the sentences paying attention to the Adjectives:
1. The resistance to blood flow through the general circulation is much greater than resistance through the lungs.
2. The left side of the heart must contract more forcibly than the right so it has greater muscular bulk.
3. If she changes her job to a less stressful one, she won’t complain of her heart so often.
4. The right atrium of the heart is larger than the left one.
5. The walls of the left atrium are thicker than those of the right one.
6. The left ventricle is longer than the right ventricle.
7. The left ventricle is more conical in form than the right one.
8. The smallest veins in the body are called venules.
9. The venules branch into larger veins which eventually carry the blood to the largest veins in the body, the vena cava.
10. The liver is the largest gland and the largest internal organ in the human body.
Exercise 4. Read and translate the text.
Anatomy of the Heart
The heart is the muscular pump in the centre of the chest that beats continuously and rhythmically to send blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. It is located on the diaphragm between the lower borders of the lungs, occupying the middle of the mediastinum. It is covered ventrally by the sternum and the adjoining parts from the third to the sixth costal cartilages. The organ is about 12 cm long, 8 cm wide at its broadest part, and 6 cm thick. The weight of the heart in men averages between 280 and 340 g and in women, between 230 and 280 g. Much of the heart consists of myocardium, a special type of muscle. The heart muscle is supplied with oxygen and nutrients by 2 coronary arteries.
The internal surface of the heart is lined with a smooth membrane, called endocardium, and the entire heart is enclosed in a tough, membranous bag, the pericardium. A thick central muscular wall, the septum, divides the heart cavity into right and left halves. Each half consists of an upper chamber, called an atrium, and a larger lower chamber, called a ventricle. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the entire body via 2 large veins called the venae cavae. This blood is transferred to the right ventricle and pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated and to lose carbon dioxide. The left atrium of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs (via the pulmonary veins); this blood is transferred to the left ventricle and then pumped to all tissues in the body.
The valves of the heart include the tricuspid valve, the bicuspid (mitral) valve, the semilunar aortic valve, and the semilunar pulmonary valve. The sinoatrial node in the right atrium of the heart initiates the cardiac impulse, causing the atria to contract. These one-way valves at the exits from each chamber ensure that blood flows in only 1 direction. As resistance to blood flow through the general circulation is much greater than resistance through the lungs, the left side of the heart must contract more forcibly than the right one that’s why it has greater muscular bulk.
POST-TEXT ASSIGNMENTS:
Exercise 5. Answer the questions.
What is heart?
Where does the heart rest?
What supplies the heart with oxygen and nutrients?
What is the heart enclosed in?
What does septum serve for?
What does each half of the heart consist of?
What are the valves of the heart?
What is the function of the right atrium?
What is the function of the left atrium?
What do one-way valves at the exits from each chamber ensure?
Why does the left side of the heart have greater muscular bulk?
Exercise 6. Match the two columns.
-
1.
to pump
a.
to deprive of oxygen
2.
to contract
b.
to separate into parts
3.
to oxygenate
c.
to acquire or get something
4.
to deoxygenate
d.
to surround on all sides; close in
5.
to receive
e.
to enrich with oxygen
6.
to transfer
f.
to raise or cause to flow by means of a pump
7.
to enclose
g.
to make available for use; provide
8.
to divide into
h.
to reduce in size by drawing together; shrink
9.
to supply
i.
to convey or remove something from one place to another
Exercise 7. Fill in the gaps using the verbs from the previous exercise.
A thick central muscular wall, the septum, … the heart cavity into right and left halves.
Two coronary arteries … the heart muscle is with oxygen and nutrients.
The pulmonary veins are large blood vessels that … oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of then heart.
Blood is … in the lungs
The heart is … in the pericardium
The right atrium … deoxygenated blood from the entire body via 2 large veins called the venae cavae.
Both atria … simultaneously, followed quickly by the simultaneous contraction of the ventricles.
The heart is a chambered muscular organ in vertebrates that … blood received from the veins into the arteries, thereby maintaining the flow of blood through the entire circulatory system.
This blood is transferred to the right ventricle and pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary artery to be ….
Exercise 8. Find the corresponding equivalents in the text:
М’язовий насос, складатися з 2-х передсердь та двох шлуночків, через дві великі вени, скорочуватись з більшою силою, через легеневі вени, вивільняти вуглекислий газ, скорочуватись безперервно та ритмічно, велике коло кровообігу, внутрішня та зовнішня оболонки серця, більша м’язова маса, верхня та нижня камери, скорочуватися з більшою силою.
Exercise 9. Make questions to the underlined words.
1. The heart beats continuously and rhythmically to send blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
2. Much of the heart consists of myocardium.
3. The heart muscle is supplied with oxygen and nutrients by 2 coronary arteries.
4. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the entire body.
5. The left atrium of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
6. One-way valves at the exits from each chamber ensure that blood flows in only 1 direction.
7. As resistance to blood flow through the general circulation is much greater than resistance through the lungs, the left side of the heart must contract more forcibly than the right.
8. Tricuspid valve lies between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
9. Descending aorta is the body’s main artery, which supplies oxygenated blood to all other parts.
10. The aorta has a large diameter in order to cope with the high pressure and large volume of blood passing through it.
Exercise 10. Translate the words in brackets.
The human heart provides a (тривалий) blood circulation through the cardiac cycle and is one of the most vital organs in the human body. It is (розділений) four (камер): the two (верхні камери) are called the left and right (передсердя) and two (нижні камери) are called the right and left (шлуночки). Normally the right ventricle (качає) the same blood amount into the lungs with each bit that the left ventricle pumps out. Physicians commonly refer to the right atrium and right ventricle together as the right heart and to the left atrium and ventricle as the left heart.
The electric energy that stimulates the heart occurs in the (синусно-передсердний) node, which produces a definite potential and then (відправляє), sending an impulse across the atria. The Purkinje fibers transmit the electric charge to the myocardium while the (клітини) of the atrial walls (передають) it from cell to cell, making the atrial syncytium.
