
Урология - Hydronephrosis
.pdf
Lesson 5

Hydronephrosis
A distention (dilation) of the kidney with urine, caused by backward pressure on the kidney when the flow of urine is obstructed.

Hydronephrosis
Primarily – or inborn develop due to some anomalia in urinary tract causing impairment of urine outflow
Secondary – or acquired develops as complication of some disease.
Aseptic
Infected

Causes
Hydronephrosis commonly results from an obstruction located at the junction of the ureter and renal pelvis (ureteropelvic junction). Causes of this type of obstruction include the following:
Structural abnormalities—for example, a birth defect in which the insertion of the ureter into the renal pelvis is too high or there is inadequate development of the ureteral muscles (congenital ureteropelvic junction obstruction)
Kinking at the ureteropelvic junction resulting from a kidney shifting downward (ptosis of the kidney)
Stones (calculi) or a blood clot in the renal pelvis
Compression of the ureter by bands of fibrous tissue, an abnormally located artery or vein, or a tumor

Obstruction below the ureteropelvic junction or from backflow (reflux) of urine from the bladder. Causes of this type of obstruction include the following:
Stones in the ureter
Blood clot in the ureter
Tumors in or near the ureter
Narrowing of the ureter resulting from a birth defect, an injury, an infection, radiation therapy, or surgery
Disorders of the muscles or nerves in the ureter or bladder
Formation of fibrous tissue in or around the ureter resulting from surgery, radiation therapy, or drugs (Bulging of the lower end of the ureter into the bladder (ureterocele)
Cancers of the bladder, cervix, uterus, prostate, or other pelvic organs
Obstruction that prevents urine flow from the bladder to the urethra, resulting from prostate enlargement (most often caused by a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia— or rectal impaction with feces
Abnormal contractions of the bladder resulting from a birth defect or a spinal cord or nerve injury
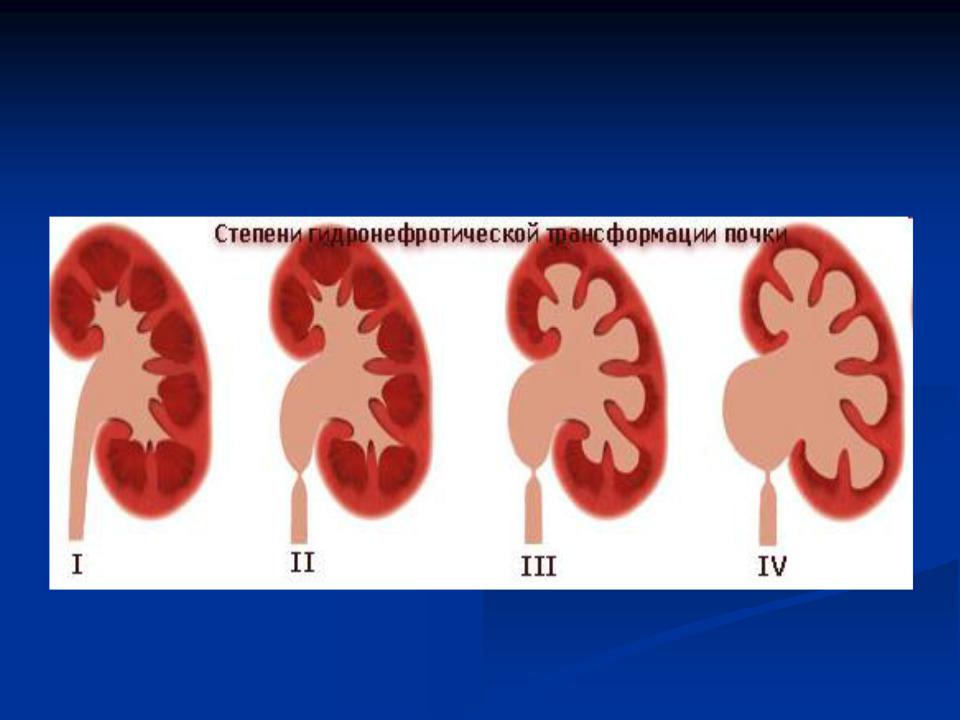
Stages
I stage – isolated dilation of pelvis with little impairment of kidney function
II stage – dilation of pelvis and calices with thinning of parenchyma and significant function impairment
III stage – atrophy of renal parenchyma. Kidney look like a a thin-walled suc.

Symptoms
When the obstruction begins quickly (acute hydronephrosis), it usually produces renal colic—an excruciating, intermittent pain in the
flank (the area between the ribs and hip) on the affected side, heamaturia.

Symptoms
People who have slowly progressive (chronic) hydronephrosis may have no symptoms, or they may have attacks of dull, aching discomfort in the flank on the affected side. A tumor like formation can be palpated at subcostal area. Sometimes a kidney stone temporarily blocks the ureter and produces painful hydronephrosis that occurs intermittently.

Hydronephrosis may cause vague intestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
People who have urinary tract infections may have pus in the urine, fever, and discomfort in the area of the bladder or kidneys.
