
Урология - Pyelonephritis
.pdf
Lesson 2
Pyelonephritis

Pyelonephritis
A non-specific inflammation of kidney interstitial tissue and renal tubules affecting both renal parenchyma and renal pelvis.

Epidemiology
Most common kidney disease in all age groups
3-5% of pregnant women suffer from acute pyelonephritis
Those children whose mothers suffered from pyelonephritis during pregnancy are more prone to suffer from this disease.
Acute pyelonephritis in children takes second place after infections of respiratory tract
Among adults it can be observed at 100 persons from 100000
60-75% of patients are 30-40 years old

Pathogenesis
Most cases are due to ascending infections from urine flow abnormalities
Urinary outflow obstruction results in urine stasis providing an environment for bacterial proliferation ( in secondary pyelonephrtis)
Seeding of the kidney by circulating bacteria or septic emboli from valvular vegetations in edocarditis (hematogenous).

ASCENDING INFECTION -In majority of cases acute pyelonephritis develops from infection in the bladder through mechanism of vesicoureteral reflux.
HAEMATOGENOUS INFECTION –
Pyogenic cocci are more often seen in haematogenous infection, though E coli. Is the commonest infecting organism in all cases of pyelonephritis.

Aetiology
Escherichia coli 75%
Proteus mirabilis 10%
Staphylococcus saprophiticus 10%
Enterococcus, Enterobacter
Klebsiella
Candida albicans

Predisposing factors
General: low immunological reactivity, diabetes mellitus, complocated pre-natal period in children
Local factors: outflow abnormalities (BPH, pregnancy, calculi, vesicouretral reflux, vesicouretral reflux, neurogenic bladder etc); invasieve diagnostical methods (cystoscopy, uretrography, retrograde ureteropyelography)

Clinical features
SYMOTOMS
1.Constant ache over one o both kidneys is the most frequent complain (this is mainly caused by distention of the renal capsule due to oedema). The pain may radiate to the lower abdomen or to the groin mimicking ureteric colic.
2.Increased frequency of micturition, urgency, nocturia and burning sensation of urination are the complaints due to cystitis which is often accompanied with.

3.Prodromal symptoms – headache, lassitude, nausea, vomiting and prostraition.
4.Rigor alongwith high temperature is quite common.
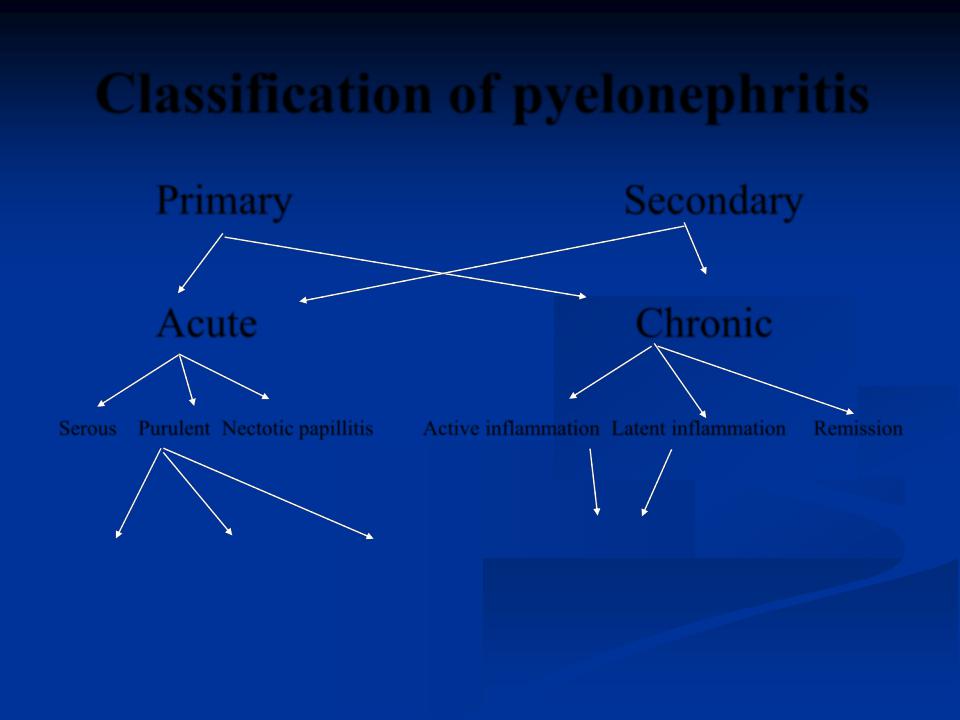
Classification of pyelonephritis
Primary |
Secondary |
Acute |
Chronic |
Serous Purulent Nectotic papillitis |
Active inflammation Latent inflammation Remission |
Apostematous Renal carbuncle Absess |
Nephrosclerosis |
|
or pyonephrosis |
