
Ermolaeva_L_D_Ekonomika_i_biznes_1
.pdf
Н.: К сожалению, на современной российской бирже торгуют всеми видами товаров. Это не запрещается делать. На мировых же биржах торгуют только биржевым товаром, включающим 30-50 наименований, именно эти товары являются ценообразующими для всех остальных товаров. Я надеюсь, что в будущем наши биржи придут к биржевому товару.
XIV. Solve problems through group discussion.
1.Discuss in pairs or small groups how true it is to say that changes in the supply of, and the demand for industrial and commercial shares and also government securities, are a reliable indicator of the strength of the British economy.
2.Describe the procedures involved in the buying and selling of shares and securities on the London Stock Exchange.
3.Explain what privatization of companies means and how the ownership and control of the company will change now that it is no longer owned and controlled by the government.
TEXT В
I. Decide which of the three main ideas from the excerpt each expression is related to. Write down the appropriate number(s) after each one. Main ideas from the text.
1.Market for shares and securities.
2.Company‟s floatation.
3.Reasons of creation of two markets on the floor of the British Stock Exchange.
Key vocabulary |
Main idea |
to issue company‟s prospectus |
2 |
second-hand shares |
|
share transactions |
|
unable to meet requirements for “full-listing” |
|
to convert shares into cash |
|
good, growth prospectus |
|
the Unlisted Securities Market |
|
floating day |
|
the company‟s launch |
|
61
THE STOCK EXCHANGE OPERATION AND ORGANIZATION
The Stock Exchange acts аs a market for both new and. second-hand shares and securities. About 80 per cent of its business is actually in Government securities. The Stock Exchange is responsible for supervising new issues of shares when firms become public limited companies, but most of its share transactions (30000 a day at the end of 1987) are in the existing securities. By providing a market for second-hand shares, the Stock Exchange makes it possible for investors to convert their shares into cash. Without this facility it would be more difficult for companies to persuade people to invest their money in new issues.
Organization. The Stock Exchange is an independent organization. It is overseen by one central agency – the Securities and Investment Board. The Council of the Stock Exchange, elected by its members, is the governing body which sets the rules and enforces standards.
Operation. Raising finance for business by „going public‟ that is by selling shares to public, can be an effective means of raising capital without incurring interest charges or by having to lose control in a business. There is a number of stages involved in a company floatation:
(a)The company has to obtain advice, usually from a merchant bank, and obtain the services of a stockbroker to sponsor it;
(b)the Stock Exchange will examine the company‟s trading history, profit and loss account, management record, and prospects;
(c)the number and types of shares to be issued has to be decided and, if such as pension funds or insurance companies;
(d)the companies‟ PROSPECTUS will be issued, giving details of the company and details and price of the shares it is offering for sale;
(e)applications for shares are made by the public and allocated;
(f)finally, on „floating day‟ shares are traded on the Stock Exchange, and the
success of the company‟s launch is measured by how many of the shares will have been bought and by how much they rise in price.
Before a company‟s shares can be traded on the Stock Exchange it has to be „listed‟, that is, its financial affairs have to be approved by the controlling body
– the Council. For many years there was only one market (the listed market for well-established companies) on the floor of the Stock Exchange. In 1980, however, a second market was created, within the Stock Exchange – the Unlisted Securities Market (USM) intended to cater for the capital needs of companies unable to meet the requirements to „full listing‟ on the Exchange. In 1987 a further development in this direction saw the establishment of the Market for shares in companies which are very young and have good prospects.
62
II. Select the correct phrase to finish the following statements about the British Stock Exchange.
1.The Stock Exchange can be characterized as: a) central agency
b) a market for shares c) the Council
2.The governing body of the Stock Exchange is a) the Securities and Investment Board
b) the meeting of its members c) the Council
3.A company may raise capital for business by: a) obtaining the services of a stockbroker
b) “going public”
c) issuing its Prospectus
4.The success of the company’s launch is measured by: a) number of shares to be issued
b) types of shares to be issued
c) number of shares that will have been bought
III. Working in small groups (or pairs) each person should take a turn talking about one of the following topics:
1.The Stock Exchange as a market for new and second-hand shares and securities.
2.How the Stock Exchange is organized.
3.What stages are involved in a company floatation.
4.Creation of other markets on the floor of the British Stock Exchange.
UNIT VII
Grammar: Gerund, Forms and Functions.
I. Read and memorize the following words and word combinations.
allowance |
- годовое (месячное содержание) |
|
to anticipate |
- предвидеть, ожидать |
|
to assess |
1) |
определять размер налога |
|
2) |
оценивать имущество для обложения налогом; |
|
3) |
оценивать |
to add up |
- складывать, находить сумму |
|
to collect |
- взимать (налоги, пошлины, проценты, |
|
|
|
63 |
|
арендную плату) |
a charge |
- налог, сбор, начисление |
community |
общественный; общество |
Customs and Excise |
- таможенно-акцизное управление |
duty |
- налог, пошлина |
customs duties |
- таможенные пошлины |
excise duties |
- акцизный сбор |
export(import) duties |
- вывозная (ввозная) пошлина |
to deduct |
- вычесть |
expenses |
- расходы |
to levy |
- взимать, собирать |
to levy duties on smth |
- обложить налогом |
licence |
- лицензия, удостоверение, официальное |
|
разрешение |
driving licence |
- водительские права |
luxury goods |
- предметы роскоши |
particular |
- особый, частный, отдельный |
rateable value |
- оценочная стоимость, облагаемая стоимость |
to recognize |
- признавать |
(to) rate |
- местный (коммунальный, муниципальный) на- |
|
лог; сбор на местные нужды; ставка, размер |
|
(таможенной пошлины, налога); |
|
- облагать местным налогом; оценивать, произ- |
|
водить оценку имущества для обложения на- |
|
логом; определять, устанавливать |
recreational facilities |
- сооружения для отдыха |
to be related to |
- относиться к, быть связанным |
(to) rent |
- арендная плата, доход с недвижимости, квар- |
|
тирная плата; сдавать в аренду, облагать |
|
арендной платой |
rent-earning capacity |
- арендная способность |
to attract rent |
- приносить доход в виде арендной платы |
revenue |
- доход, доход от налогов |
Inland Revenue |
1) департамент налогов и сборов |
|
2) финансовое управление |
(to) tax |
- налог; облагать налогом |
capital gains tax |
- налог на прибыль от капитала |
corporation tax |
- корпоративный налог |
direct tax |
- прямой налог |
indirect tax |
- косвенный налог |
inheritance tax |
- налог на наследство |
|
64 |
income tax |
- подоходный налог |
value added tax (V.A.T.) |
- налог на добавленную стоимость |
motor vehicle tax |
- налог на транспорт |
rates and taxes |
- местные сборы и государственные налоги |
tax concession |
- налоговая льгота |
waste collection and dis- |
- сбор и вывоз мусора |
posal |
|
II. The Latin prefix in - is used to make negatives. It becomes ir- before “r” and il- bеforе “l”. Make negatives of the adjectives listed below. Translate the pairs of the words:
1)direct, equal, able, active, attentive, convenient, correct, dependent, formal; convertible;
2)regular, rational, relevant, responsible, recognizable;
3)legal, literate, logical, limitable.
III. Translate the following pairs of words paying attention to the prefix re-, meaning “back”, “again”:
to produce – to reproduce, to distribute – to redistribute, to invest – to reinvest, to construct – to reconstruct, to count – to recount, to pay – to repay, to organize – to reorganize.
IV. Give the verbs from which these nouns are formed:
allowance, assessment, distribution, earner, collection, recognition, anticipation, inheritance.
V. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the meanings of the word “rate”.
1.The rate of change in births, deaths, and migration determine the total population.
2.Economic growth in Europe is expected to remain slow and the British economy is expected to have its lowest growth rate.
3.The higher the rate of interest, the greater the supply of loanable funds.
4.Local property rates paid by businesses and households are used to finance local services.
5.Rate-of-return regulation is commonly used in the USA to control the pricing policies of privately owned public utilities.
6.The travelling rate on this motor way is not limited.
7.First-rate means excellent, second-rate – fairly good and third-rate – rather poor.
8.At this rate we‟ll have to delay deliveries.
9.My property was rated at £ 20 per annum.
65
VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the forms and functions of the Gerund.
1.Investing shares in unit trusts may bе safer than buying shares in a single company.
2.He hated the idea of being interfered in his business.
3.After having informed the client about the deal the broker sent him a contract note.
4.After having been informed about the amount of commission charged for the deal the client decided to refuse it.
5.There are many ways of making reasonable profits.
6.Don‟t you mind his having changed the content of the advertisement?
7.The proper tax system can‟t be designed without taking into account public policy objectives.
8.They object to his participating in negotiations.
9.I insist on the date and time of the deal being changed.
VII. Choose the proper form of the Gerund.
1.He likes (asking/being asked) people about their incomes.
2.He doesn‟t like (asking/being asked) about his income.
3.They deny (participating/having participated) in recent illegal deal.
4.I have an opportunity of (investing/being invested) my money in the successful company.
5.I am sorry for (doing/having done) it yesterday.
6.The company succeeded in (retaining/having retained) its share of the market.
7.After (preparing/having prepared) the market research servey the chief marketing adviser presented it for the Board.
8.The Board insists on the analysis (making/being made) by an economic expert.
VIII. While translating the sentences distinguish participle, gerund and gerundial constructions.
1.They had a hope of his making a good impression on his collegues
2.Using the allowances and tax rates the taxable income may be calculated.
3.Government avoids sudden changes being made in tax structures.
4.Have you finished calculating rates?
5.Excise duty is a tax payable on some goods being exported from the country.
6.Making reasonable profits depends on setting the proper prices.
7.Setting proper prices the companies may receive reasonable profits.
8.They were surprised at the advantages having been gained from the reconstructing of the corporation.
9.I am sorry for not having prepared the financial statement in time.
66
TEXT A
TAXES
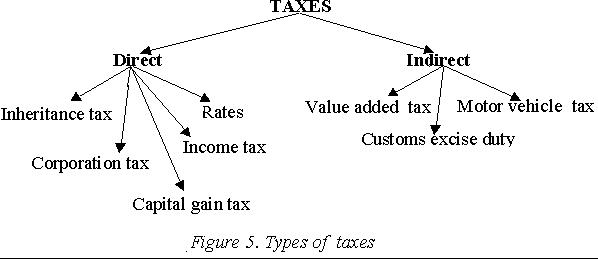
Taxes are payments made by people and business organizations to either the central government or the local government. Some taxes are described, as direct taxes and some are called indirect taxes (fig. 5).
Direct taxes
Direct taxes are normally collected by the Inland Revenue. Examples are income tax, corporation tax, capital gain tax, inheritance tax and others. Most direct taxes are progressive (the more you earn, the more you pay).
Indirect taxes
Indirect taxes are normally collected by the Customs and Excise. Indirect taxes such as value added tax (V.A.T.) are included in the price of the product and are sent by the seller of the product to the government. Most indirect taxes are „regressive‟, because it is more difficult for low paid workers to pay them.
Income tax
This is a tax payable to central government. It is assessed on the income of the individual wage earner. Before the person pays income tax to the government he is allowed to deduct allowances for expenses that he has had to pay during the year. Examples, amongst others, are an allowance as a married man and an allowance on the interest on a person's mortgage payments on his house.
Corporation tax
Corporation tax is a direct tax paid to the government on the profits of a business organization.
67
Capital gain tax
Capital gain tax is the tax levied by the government on capital profits that have not been deducted as соrрогаtion tax.
Inheritance tax
This is a direct tax levied by the government on the assets of a deceased person.
Indirect taxes
Examples are value added tax, customs and excise duty, motor vehicle tax, and television tax.
Value added tax
The tax is charged on a product at each stage of the manufacturing and distribution process. Some goods such as food and all exports are zero rated and the tax does not have to be paid.
Customs and excise duty
Customs duty is payable on some goods entering the country. Examples are electrical goods, luxury goods and tobacco.
Excise duty is a tax payable on some goods being exported from the country. Examples are whisky, matches, certain electronic goods and motor vehicles.
Motor vehicle tax
Road fund license and driving license revenue is collected by the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Centre (D.V.L.С.) in Swansea and then sent to the government. This tax is paid by all road users of motor vehicles.
Other indirect taxes
Television license revenue and revenue from various other licenses are collected by the Post Office and sent to the government.
Rates
Rates are a local direct tax levied by the local government. The revenue collected by the local government each year is used for such services as:
1)education;
2)personal social services, such as Meals on Wheels and home help;
3)school meal subsidies;
4)police;
5)housing;
6)fire service;
7)waste collection and disposal;
8)parks and other recreational facilities;
9)libraries and museums.
Rates are related to the rent-earning capacity of a particular building or piece of land. A small house, for example, which could attract only a low rent would have only a low rates charge levied on it, but the owner of a large house capable of attracting a large rent would have to pay a high rates tax. The calculations of rate
68
are done in the following way. Firstly the local council decides what their expenses will bе for the following financial year. They then add up the rateable value of all the properties in the district. For example, the anticipated expenses may be £4 million and the expected revenue from the rateable values of the properties may be say £2 million. The council would then declare a rate of £2 in the pound, and a £500 rated house would have to pay £1000 in rates (rates payable) etc.
During 1988 the rating system was being reorganized. It was proposed that the new local taxation system would levy the same community charge on each individual person in the community.
IX. Express in one word the meaning of each of the following phrases. You are given the first letter of each word and the number of letters in it.
1.A formal permission to do something (l ...).
2.A sum of money which must be paid to local authorities for local purposes (r...).
3.The levying of compulsory charges on certain items by government (t…).
4.Money paid at regular times to the owner for the use of land, a house, machinery, etc (r...).
5.An amount of money that is allowed or given to smb for spending monthly, weekly or yearly (a…).
6.Money that comes in from any source (r…).
7.A payment made to the government when goods are brought into or sent out of a country (d…).
X. Find in the text words and word combinations which can be replaced by
the items listed below: to be connected with the dead person
to collect taxes able
for the reason that
to make known;
to fix the amount of tax; expected expenses;
to take away. to make known;
XI. Put in the missing words.
1.Taxes may be classified as dir... and in… .
2.A d... tax is collected directly either by cent... gov… or 1… gov… .
3.An in… tax is part of the retail pr... of some g… and some ser… .
4.The direct t… which is paid bу most people who have incomes is called … tax.
5.Other examples of direct taxes are cor… tax, capital g… tax, inher… tax, tax and ra... .
6.Examples of indirect taxes are cust... duty, ex.... duty, and value ad... tax.
69
7.All taxes except rates are used bу central government to provide ess...... services for the people of the nat... .
8.R… are paid to the l… government.
9.Rates are used to pay for such services as ed…, pol…, fi…service, ambulance and waste collection and dis… .
XII. Choose the answer on the basis of the information you derived from the text.
1. What is corporation tax?
a)a tax which every corporation pays to the local council;
b)a proportion of income tax due to the Inland Revenue;
c)an indirect tax paid to the government on the profits of a business;
d)a direct tax paid to the government on the profits of a business;
e)a proportional tax paid annually.
2.Which of the following is an indirect tax? a) income tax;
b) capital gain tax; c) corporation tax; d) excise duty.
3.Which of the following services is not a responsibility of a local authority? a) education;
b) libraries;
c) parks and recreation activities; d) the Health Service;
e) the collection and disposal of waste.
4.What do we call a system in which the more income we receive the more
tax we pay?
a)a direct system;
b)a proportional system;
c)a regressive system;
d)a progressive system.
5. Because value added tax has to bе paid by the poor as well as the rich, it may bе said to bе unfair to the poor and what do we call this kind of tax?
a)a regressive tax;
b)a progressive tax;
c)a proportional tax;
d)a low income tax.
XIII. Answer the questions using the information of text A.
1. What are the two main classifications of taxation?
70
