
Ermolaeva_L_D_Ekonomika_i_biznes_1
.pdf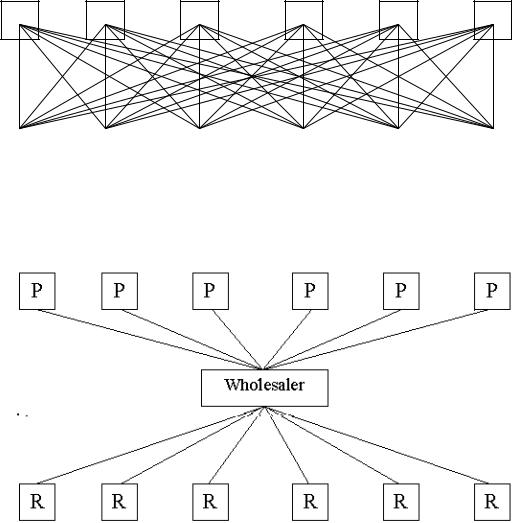
functions – buying, grading, storing, transporting, financing, risk taking, and gathering market information (fig. 2).
A.Without a Wholesaler
Producers
P |
P |
P |
P |
P |
P |
R |
|
R |
|
R |
|
R |
|
R |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retailers
B. With a Wholesaler
Producers
Retailers
Figure 2. Centralization of transactions
A wholesaler might perform functions for customer:
1.Regroup products – provide the quantity and assortment wanted by customers, at the lowest possible cost.
2.Anticipate needs – forecast customer‟s demand and buy accordingly.
3.Carry stocks – carry inventory so customers don‟t have to store a large inventory.
4.Deliver products – provide prompt delivery at low cost.
11
5.Grant credit – give credit to customers, perhaps supplying their working capital. Note: this financing function may be very important to small customers
– and is sometimes the main reason why they use wholesalers – rather than buying directly from producers.
6.Provide information and advisory service – supply price and technical information as well as suggestions on how to install and sell products (fig. 2).
7.Provide part of the buying function – offer products to potential customers so they don‟t hunt for supply sources.
8.Own and transfer title to products – help by completing a sale without the
need for other middlemen – speeding the whole buying and selling process. A wholesaler might perform the following functions for the producer-supplier:
1.Provide part of a producer‟s selling function – by going to producer – suppliers instead of waiting for their sales reps1 to call.
2.Supply capital – reduce a producer‟s need for working capital by buying his output and carrying it in inventory until it‟s sold.
3.Store inventory – reduce a producer‟s need to carry large stocks – and so cut his warehousing expenses.
4.Provide market information – as an informed buyer and seller closer to the market, the wholesaler reduces the producer‟s need for marketing research.
II. The most important service wholesalers provide is that of centralizing transactions. Figure two shows how centralization works in the case of six retailers, each of which deals with six producers. Look at the diagrams in figure two and decide on:
1.How many transactions would be needed without the wholesaler?
2.To what number does the wholesaler reduce the number of transactions?
UNIT II
Grammar: The Passive Voice; Indefinite, Continuous, Perfect Tenses
I. Read and memorize the following words and word combinations:
accumulative |
- накапливающий(ся); кумулятивный |
arrangement |
- соглашение |
assets |
- имущество, недвижимость |
available |
- имеющийся в наличии |
to borrow |
- занимать |
butcher |
- мясник |
|
|
1. reps - representatives |
|
12
debenture |
- облигация, долговое обязательство |
mortgage debenture |
- долговое обязательство, обеспеченное за- |
|
кладной на собственность |
debt |
- долг |
to delegate |
- передавать полномочия |
destiny |
- судьба |
draft |
- кредит |
to draw up a deed |
- составить документ |
to declare |
- объявлять |
equity |
- обыкновенная акция (без фиксированного ди- |
|
виденда) |
eventually |
- в конечном итоге |
to expand |
- расширять |
grocer |
- бакалейщик |
fragmented |
- раздробленный |
insolvent |
- неплатѐжеспособный |
(to) issue |
- выпуск; выпускать |
interest |
- процент на капитал - процентный |
rate of interest |
- процентная ставка |
(to) lack |
- отсутствие, нехватка; испытывать недостаток |
loan |
- заѐм, ссуда |
mortgage |
- закладная |
newsagent |
- владелец газетного киоска |
to owe |
- быть должным |
overdraft |
- превышение кредита |
part owner |
- совладелец |
to pay |
- расплачиваться; приносить доход |
partnership |
- товарищество, компания |
private limited company |
- частная акционерная компания закрытого типа |
(ltd) |
с ограниченной ответственностью |
public limited company |
- публичная акционерная компания открытого |
(plc) |
типа с ограниченной ответственностью |
property |
- имущество |
to prosper |
- процветать |
(to)reward |
- вознаграждение, компенсация; награждать |
(to) share |
- акция, доля; делить |
ordinary share |
- обыкновенная акция |
deferred share |
- акции с ограниченным дивидендом; отсрочен- |
|
ные акции |
preference share |
- привилегированная акция |
to raise capital |
- получать капитал |
|
13 |
to save |
- сберегать (деньги); экономить; спасать |
savings |
- сбережения |
saver |
- вкладчик |
to secure smb from smth |
- защищать кого-либо от чего-либо |
security |
- гарантия, обеспечение |
securities |
- ценные бумаги |
to set |
- устанавливать |
to set down |
- записывать |
sole |
- единственный, единоличный |
sufficient |
- значительный |
wages |
- заработная плата |
II. Translate the following pairs of words paying attention to the suffixes of nouns -ity, -(a)tion, -(t)ion, - (s)sion, -or, - er:
available – availability, responsible – responsibility, probable – probability, particular – particularity, real – reality, liable – liability, difficult – difficulty; delegate – delegateon, add – addition, communicate – communication, organize
– organization;
permit – permission, expand – expansion, decide – decision, admit – admission; control – controller, debt – debtor, credit – creditor, part – partner, trade – trader, delegate – delegator, save – saver, own – owner, borrow – borrower.
III. Make adverbs by adding "-ly" and translate them:
real, immediate, probable, ordinary, successful, particular, large, original, independent, sufficient, eventual, ideal.
IV. Read the international words and guess their meanings:
person, to start, to invest, expert, firm, partner, form, to limit, detail, maximum, basis, dividend, interval, portion, risk.
V. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words from the active vocabulary:
1. The preference share pays a fixed rate of interest. 2. A person may raise the capital by obtaining a bank loan. 3. The success of the one man business depends on the efforts made by the owner. 4. If the one man business makes no profit the owner gets no wages. 5. The partnership has more capital available for expansion than the one man business. 6. If a person buys shares in a public limited company he immediately becomes a part owner of the business. 7. Proper- ties and other assets of the firm can be readily convertible to cash. 8. Ordinary shareholders may attend shareholders‟ meetings and have voting rights. 9. If the firm goes bankrupt the ordinary shareholders lose the whole of their investments.
14
VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to Indefinite, Continuous, Perfect Tenses in the Passive Voice.
1. A deed of partnership is being drawn up between the partners now.
2.The new partners have been delegated responsibilities by the original owner.
3.His business had been closed down by the end of the year. 4. By the end of the month the question of the partnership will have been solved. 5. The private assets of an unsuccessful businessman are usually taken by the creditors. 6. Much capital has been brought to the company by new partners. 7. The shares of a new public limited company were being sold to the members of this company the whole week. 8. The positive results had not been obtained until computers and displays were installed. 9. The dividends of this company will have been declared by the end of the year.
VII. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the peculiarities of the Passive Voice.
1.Ordinary shares are sometimes referred to as equities.
2.A deed of partnership was much worked at.
3.The company‟s independent legal status and its limited liability are thought of as the main advantages of the private limited company.
4.The problem of raising additional capital was spoken of at the shareholders‟ meeting.
5.Chairman of the board will be spoken to on the question of issuing more shares.
6.In drawing up this document he can be fully relied upon.
7.The details of arrangements between partners are paid much attention to.
VIII. Complete the following sentences using appropriate verb forms.
1. The one man business organization usually ... by one man.
a) is being controlled |
b) has been controlled |
c) is controlled |
|
2. |
The unlimited number of shareholders of the private limited compa- |
||
ny ... by the Company Act since 1980. |
|
||
|
a) is permitted; |
b) has been permitted; |
c) is being permitted |
3. |
If the firm goes bankrupt the whole of the investment of the ordinary |
||
shareholder … . |
|
|
|
|
a) will be lost; |
b) will have been lost; |
c) are being lost |
4. |
Debenture capital … to debenture holders by the firm by the end of |
||
the month. |
|
|
|
|
a) was repaid; |
b) was being repaid; |
c) had been repaid |
5. |
Аs his company went bankrupt all money … bу him and his partners |
||
|
a) was lost; |
b) had bееn lost; |
c) was being lost |
6. |
A public limited company … by the shareholders. |
||
a) is being controlled; |
b) is controlled; |
c) has been controlled |
|
15

7. The capital for setting up a new business ... from different resources
by the time the bank made a loan to them. |
|
|
a) was raised; |
b) was being raised; |
c) had been raised |
TEXT A
BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
The particular way in which a business is organized and controlled will depend largely on its size and what it does.
There are four types of business organization:
1)the one man business (sole trader);
2)the partnership;
3)the private limited company;
4)the public limited company.
When considering business organizations three questions must always be asked:
1.Who owns the business?
2.Who controls the business?
3.Who provides the capital for the business?
The One Man Business
This is the smallest type of business organization and is owned and controlled by one man. It is often a retail shop such as a grocer, butcher, newsagent, etc. When a person wishes to start a one-man business, he raises the capital from:
1) his own resources;
2) by borrowing from friends and relatives;
He may have difficulty in obtaining a bank loan.
Advantages
1. The owner has full control and is the sole owner.
2. All of the profits are taken by the owner.
3. He sets his own working hours, conditions, holidays, etc.
4. The business succeeds or fails according to the efforts made by the owner.
16
Disadvantages
1.The one-man business has “unlimited liabilities”. This means that if a business goes into debt the creditors can lawfully take the owner‟s private assets, i.e. an unsuccessful businessman has to sell his house, car, etc. to pay his business debts.
If the owner is ill the business may have to close down.
2.He may have to work very long hours.
3.If he makes no profit he gets no wages (90% of one man business become insolvent in their first 12 months‟ trading).
The Partnership
A successful one man business may often grow into a partnership. Ideally partners may:
1)bring more capital into the business;
2)have an expert knowledge which will help the firm. Advantages
1. The business will grow and the profits will be larger.
2. The original owner can now delegate responsibility to the new partners. 3. The business has more capital available for expansion.
Disadvantages
1.The original owner now has to share both ownership and control with the new partners.
2.The profits of the business must be shared between the partners.
3.The original owner is not the sole master of the destiny of the firm.
Up to twenty partners may be included in the partnership and a “deed of
partnership” must be drawn up setting down full details of arrangements made between the partners.
The Private Limited Company
Before the 1980 Companies Act the maximum number of shareholders permitted with a private company was 50. The 1980 Act changed the maximum permitted number of shareholders to an unlimited number. Shares in the company may not be sold without the permission of the company. The main advantages of this form of ownership is the company‟s independent legal status and its limited liability.
Public Limited Company
The oneman business, the partnership and the private limited company are all limited in their ability to expand because they may lack sufficient capital. If they wish to build a large factory costing say £5 million they often cannot find enough money from within the firm. They must therefore raise the capital by of-
17
fering shares for sale to members of the public, and becoming a public limited company. Any member of the public may buy shares in a public limited company and. when he does so he immediately becomes a “part owner” of the business. Thus a firm that started in a very small way as a one-man business, owned and controlled by one man, may eventually be owned and controlled by hundreds and sometimes thousands of shareholders. The public limited company is the largest kind of company (fig. 3).
Figure 3. Distribution of basic forms of organization.
Methods of Raising Capital
1) debenture issue;
1) the preference share;
3)the accumulative preference share;
4)the ordinary share;
5)the deferred share.
Debentures
A debenture is a loan made to a company, which must by law be secured against the assets of the firm. By this we mean that the firm must always be in a position to repay debenture capital to debenture holders. It is able to do this by using the capital raised by debenture issues to buy properties and other assets, which are readily convertible to cash. Debentures are sometimes called mortgage debentures. Debentures pay a fixed rate of interest and are really loans to companies. They are a very secure method of investment. Debenture holders are
18
not allowed to vote at shareholders‟ meetings, and pay no part in the ownership and control of the company.
Preference shares
The preference share is the first type of share to be paid after the debentures and pays a fixed rate of interest.
Accumulative preference shares
Most preference shares are accumulative. This means that if a company is unable to pay preference shareholders in the current year then it may decide to pay any money it owes on an accumulative basis and add it to the next year's dividend.
Ordinary shares
Ordinary shares are the main shares of the company and they are sometimes referred to as equities. Ordinary shares carry with them ownership and voting rights and ordinary shareholders may attend shareholders‟ meetings. The more ordinary shares that a person holds the greater his share of ownership of the business. If the company makes only a small profit then the dividend declared will probably be low and the ordinary shareholder will receive a very small dividend, but if the dividend is high the ordinary shareholder does well. If the firm goes bankrupt the ordinary shareholder will probably lose the whole of his investment. Thus it can be seen that the ordinary shareholder carries the major portion of the risks of the firm.
Most companies declare their dividends twice a year at six-monthly intervals.
IX. Find the words from this text that are close in the meaning to the words given below:
to obtain capital, property, to begin, to want, special, to put down details, a signed agreement, to enlarge, to suggest, at once, quickly, to protect, possibly, to take part.
X. Look at the list of seven terms on the right. Guess which term corresponds
to the definition listed in the column on the left.
1.A certificate showing that money has been lent (to a government or business company) on condition that a certain rate of interest is paid regularly until the original sum is paid back
2.Person who takes part with another or others in some activity, especially one of the owners of a business
a)dividend
b)partnership
3. The money earned by a business company and divided among c) interest rate those who have shares
19
4. |
A joint business including up to twenty partners |
d) loan |
5. |
A some of money lent to another |
e) share |
6. |
Payment made by a borrower for a loan, expressed as a per- |
f) partner |
|
centage |
|
7. |
One of the equal parts into which the capital of a business |
g) debenture |
|
company divided |
|
XI. Complete the following statements using the information of the text. The first letter of each missing word is given to help you.
1.The public limited, company raises capital bу selling s… to members of the p… .
2.A debenture is a 1… made by a person to a company.
3.A company must always be in a position to r… debenture holders.
4.Debenture pays a f… rate of interest.
5.Debenture holders are n… entitled to v… at shareholders‟ m… .
6.Ordinary shares are sometimes called e… .
7.Ordinary shareholders have o… and v… rights.
8.If the company does well and makes a good profit the ordinary shareholder will receive a h… dividend.
9.If the company does badly the ordinary shareholder is paid a 1... dividend or no dividend.
10.If the company goes bankrupt the ordinary shareholders may 1... their i… .
XII. Choose the sentences where the verbs “to have” and “to be” have the
modal meaning.
1. A private business is defined as one that does not have to publish its financial record. 2. A deed of partnership has been drawn up. 3. Fог some owners the business has developed from years of hard work. 4. In sole ownership the business will be a private company where the founder of the business will have to hold a number of basic principles on production processes. 5. The employed professional managers are to operate the business and to formulate its strategy. 6. Multinationals have different styles of management.
XIII. Your classmates are answering questions about reorganization of Vladimir Tractor Plant. Make questions to which the following could be answers.
1. Was …
 Yes, it was. The Tractor Plant was converted into public limited company. 2. When ...
Yes, it was. The Tractor Plant was converted into public limited company. 2. When ...
It was converted into the public limited company last year.
20
