
- •22. How can you find exact values for dimensioning technological object-Capacity?
- •23. What are the characteristics of Shop floor production ?
- •24. What are typical planning problems of Flow production lines?
- •25. What is the cooperation level - ηK
- •26. What are the objectives of the cost-benefit analysis ?
- •27. For what is the procedure by Schwerdtfeger used and how are they doing this?
- •28. How will the modified triangle method of Schmigalla applied?
- •29. Find an optimal arrangement of objects using the modified method of triangle Schmigalla for subsequent transport intensity matrix
- •30. What factors influence the arrangement of objects?
- •31. What are the advantages and disadvantages by Line arrangement of objects?
- •32. What are the influences for object distances?
- •33. From which depends the building forms
- •35. Describe the Varignon’sche Apparatus
1. What is meant by factory planning process?
The factory design process involves the continuous solution of problems in planning implementation and commissioning of factories and production systems. In this case three planning areas can be distinguished.
2. What are the fields of factory planning?
Factory layout planning - dimensioning and structuring of production and logistics systems, including the necessary personal and organizational planning.
General building developing – design of development plans, including the choice of the arrangements of buildings and room systems.
Location planning – determination of locations including the area selection.
3. What is meant by Manufacturing process management (MPM)?
Is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufacturing.
4. What is a lot and how can you calculate the annual quantity of items?
Lot: closed position to a product or assembly is generated continuously without interruption by the production other product types.
On the basis of the structural parts list, and number of pieces in lot size, can be calculate the annual quantity of items
nj= zL. nL
Body nj= 420 Lots/ax 10 pieces/a
nj=4200 pieces/a
5. According to which criteria ranking is used to select the type of representatives?
Working time
Own performance
price
geometric parameters
mass
6. Determining a type of fictional representative mass criterion
For four products A, B, C, D is a fictional type preventative of the weighted arithmetic mean can be determined.
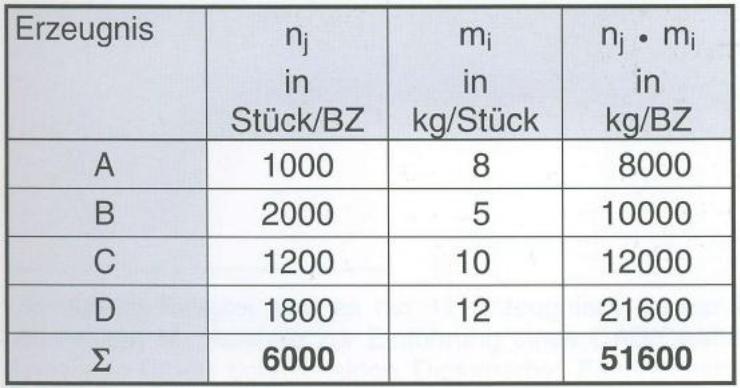

The configuration can be expected with a fictional type representatives from 6000 pieces are produced in the accounting period with a mass of 8.6 kg/unit. If a shape consistent solution is required, then the product A would be set as type representatives.
7. What are the differences A, B and C parts by ABC-analysis?
Class A: high importance;
This class includes a relatively small number of elements is expected that a high proportion of total earnings.
Class B: normal importance;
This group of elements contributing approximately proportional to their number in the considered outcome.
Class C: Low importance;
This relatively large number of elements has only a small proportion of total earnings.
8. ABC-analyze example
9. What is meant by the planning activity structuring?
The structuring of production systems has a spatial and a temporal component. The temporal component is reflected in the scheduling— the spatial component corresponds to the structure as it forms part of the factory planning, the elements of the factory will be located in their spatial location.
10. What are the Objectives for the ideal layout?
Flexible, modular expandability of Capacity- and technology leap
Demand-oriented communication structures
Optimized logistics links (short distances to the sink)
Decoupling of the personnel and material flows
Focusing on core technologies
11. How can be used a flow chart by production planning?
Flow charts graphically or numerically reflect the planned technological and organizational flow of production order through manufacturing and assembly systems.
12. What is the Dilemma of scheduling?
Minimization of cycle time
Maximization of the capacity utilization
Consideration of appointments
13. Define three priority rules?
FIFO First In First Out:
Selection of the operation with the earliest start time (i.e. availability date first step in order)
FCFS First Come First Serve:
Selection of the operation, that queue of the unit reached first
SPT Shortest Processing Time:
Selection of the operation with shortest cycle time
LPT Longest Processing Time:
Selection of the operation with the largest cycle time
SRPT Shortest Remaining Processing Time:
Selection of the operation, with the smallest sum of the following cycle times
LRPT Longest Remaining Processing Time:
Selection of the operation, with the highest sum of the following cycle times
FOPR Fewest Remaining Operations:
Selection of the operation with the smallest number of the following steps in order
MOPR Most Remaining Operations:
Selection of the operation with the highest number of the following steps in order priority rules
SLACK slip control:
Selection of the operation with the smallest difference between remaining time until the desired end of order by sum over the cycle times of the unrecognized order
EXT external priority:
Selection according to the predetermined (external) Priority
END desired end date:
Selection of the operation with the nearest specified set cycle time
14. What is a Kanban and what are the benefits?
Kanban (Japanese: card)
serve as an element of control
usually divided into kaban production and transport benefits
Low material stocks (lower capital lockup)
Clear material flow (Simplified inventory control)
Low effort control (remote control)
15. What is the relationship between the planned production volume and the cycle time?
Given production rate
X= 42 parts per shift, d. h. 42 parts in T = 452 [Minutes]
Cycle time to use
(=Reciprocal of the predetermined production rate)
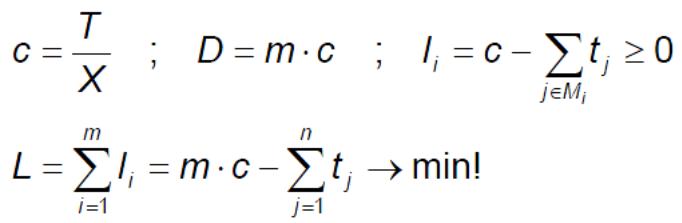
C = T/X = 462 [Minutes] /42 [parts] = 11 Minutes per part
16. What is the theoretical minimum number of workstations required?
Given: element times ti (i: 1, 2. . . 10)
Specified cycle time C = 11 per part
minimum number of (theoretical minimum number) of stations
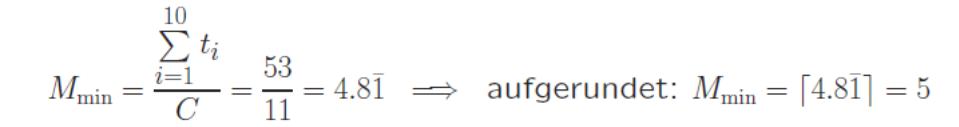
17. Which priority indicators do u know?
Position value (Helgeson / Birnie, 1961): own processing time plus those of all subsequent elements
time of elements (Moodie / Young 1965)
Number of direct subsequent elements (Tonge, 1965)
Total number of subsequent elements (Talbot, 1984)
18. Line Balancing
19. How can be used a flow chart by production planning?
Flow charts graphically or numerically reflect the planned technological and organizational flow
20. How can you visualize a manufacturing process?
Flow charts
(Which orders are processed on which object)
Processing order
Entry occupancy times of objects
Graphical object-group-related flow chart
(Derive) theoretical production order lead times
21. How can you define object allocation time?
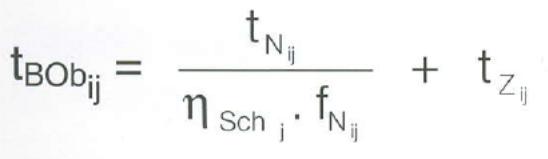
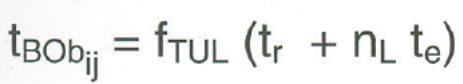
tBOj Object allocation time [TU/PO]
I Production order number i = 1(1)m
J Object number j = 1(1)n
Tnj Standard time of Production order [TU/PO]
ηSchj shift utilization degree [%]
FNij Standard compliance factor 0,95 ≤ Fnij ≤ 1,15
Tzj additional time [TU/PO]
fTUL Factor for Transport Handling Storage time at Object (1,05…1,15)
Tr setup time
nL lot size
Te part production time
22. How can you find exact values for dimensioning technological object-Capacity?
Z*ob = ZL ( tR + nL * te ) / tnom,ob * ηsch
Z*Ob calculated number of objects
ZL number of lots/a
tR setup time [min/Lot]
nL Lotsize [parts/lot]
te time per part [min/part]
Tnom,Ob nominal object time fund time available per object e.g. per year [min/a]
ηSch utilization shift
tnom,Ob = tj * Zsch * tsch * 60min/h
tj working days per year
ZSch shifts a day
tSch hours per shift
tnom,Ob = 251 * 2 *7.5 * 60 = 225900
23. What are the characteristics of Shop floor production ?
wide product range, many different products, dynamically fluctuating demand, small size of orders("small series production")
to certain specialized systems of work, that must supply the production of various products (competition of products for limited resources)
Summary of work systems function the same in each case of workshop (on the principle of groupwork
based on the product variety of networked material flow between the workshops
24. What are typical planning problems of Flow production lines?
Determination of the number of stations and the cycle time, assigning operations to stations, buffer allocation => performance tuning, configuration and capacity planning
Variety in production: Simultaneous determination of lot size and its production sequence => avoiding overlaps in the system allocation
In mass production with customer related variants: determining the dispatching sequence => workload smoothing
25. What is the cooperation level - ηK
The arithmetic average is the average number of collaborations with other objects of an object within manufacturing section under consideration
With the aid of the determined cooperation level and a dependencies between ηK and the number of objects z observed in the manufacturing section reflect the functional behavior it is possible to predetermine the best spatial structure type
ηK = ∑zi / z
ηK average number of cooperative relationships of an object to other objects
zi number of cooperative relationships Object to other objects
z number of objects In the section Considered
26. What are the objectives of the cost-benefit analysis ?
The cost-benefit analysis less determines the efficiency of a project, rather than effectiveness, the total project contribution to given targets. The overall target or the total benefit resulting from sum of individual targets.
27. For what is the procedure by Schwerdtfeger used and how are they doing this?
Is a graphical method for placement optimization of resources. It is by trying on a circular arrangement
Arrangament of resouroes on circular
Representation of relations by connecting lines
Thickness of lines correspond to the importance
Regroup to try to not more important connections run through the circle and are close together
28. How will the modified triangle method of Schmigalla applied?
There is an optimized arrangement order for a group of determined objects to be placed in a manufacturing area and which are mutually coupled by transport links
Objective function of optimization problem is to minimize the total transportation capacity
The optimized arrangement order is iteratively determined under the assumption that the objects to each other have the maximum intensities transportation, and priority to the minimum possible distance to the corners of an equilateral triangle grid are to be arranged
