
- •Introduction to control Part I
- •Text 1. Control System
- •8. Make a list of terms from Text 1 referring to control and memorize them.
- •9. Read and translate Text 2 Text 2. Basic Feedback Loop
- •10. Make a list of terms from Text 2 referring to control and memorize them.
- •11. Read and give a short summary of Text 3 Text 3. An example
- •12. Make a list of terms from Text 3 referring to control and memorize them.
- •13. Translate Text 4 in written form: Text 4. Regulators and Servomechanisms
- •16. Supply synonyms for the following words:
- •17. Analyse the grammatical structure of the following sentences and translate them:
- •Text 5. Stability and performance
- •19. Make a list of terms from Text 5 referring to control and memorize them.
- •23. Supply synonyms for the following words: Meet, to take place, because of, as regards, breakdown, to consider
- •24. Analyse the grammatical structure of the following sentences and translate them:
- •25. Translate Text 6: Text 6. The uncertainties
- •25. Make a list of terms from Text 6 referring to control and memorize them.
- •26. Read and translate Text 7. Text 7
- •27. Make a list of terms from Text 7 referring to control and memorize them.
- •28. Read and translate Text 8 without a dictionary. Text 8. Representations of Uncertainty
- •30. Give derivatives of the following words and translate them into Russian:
- •32. Supply synonyms for the following words:
- •Text 9. Servomechanism
- •Text 10. Performance: Tracking and Disturbance Rejection
- •43. Make a list of terms from Text 10 and memorize them. Rart II
- •1. Read and translate Text 11.
- •Text 11. The Philosophy of Classical Control
- •Make a list of terms from Text 11 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 12. Text 12. Classical control theory: the closed-loop controller
- •Make a list of terms from Text 12 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 13. Text 13. Controllability and Observability
- •Make a list of terms from Text 13 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 14. Text 14. Control Specifications
- •Make a list of terms from Text 14 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 15. Text 15. Model Identification and Robustness
- •System identification
- •Analysis
- •Constraints
- •Make a list of terms from Text 15 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 16 Text 16. Control Objectives
- •Make a list of terms from Text 16 and memorize them
- •Give a short summary of Text 17 Text 17. Control Objectives
- •(From Ch.Schmid. Course on Dynamics of multidisplicinary and controlled Systems )
- •Make a list of terms from Text 17 and memorize them
- •Give a short summary of Text 18 (in written form) Text 18. Main control strategies
- •Pid controllers
- •Optimal control
- •Adaptive control
- •Intelligent control
- •17. Make a list of scientific terms that are used in Text 18, give their Russian equivalents and memorize them.
- •18. Give a short summary of Text 19 (in written form) Text 19. Feedback
- •Application of feedback in mechanical engineering
- •Make a list of terms from Text 19 and memorize them.
- •Give a short summary of Text 20 Text 20. Pid controller
10. Make a list of terms from Text 2 referring to control and memorize them.
11. Read and give a short summary of Text 3 Text 3. An example
Consider an automobile's cruise control, which is a device designed to maintain a constant vehicle speed; the desired or reference speed, provided by the driver. The system in this case is the vehicle. The system output is the vehicle speed, and the control variable is the engine's throttle position which influences engine torque output.
A simple way to implement cruise control is to lock the throttle position when the driver engages cruise control. However, on hilly terrain, the vehicle will slow down going uphill and accelerate going downhill. In fact, any parameter different than what was assumed at design time will translate into a proportional error in the output velocity, including exact mass of the vehicle, wind resistance, and tire pressure. This type of controller is called an open-loop controller because there is no direct connection between the output of the system (the engine torque) and the actual conditions encountered; that is to say, the system does not and can not compensate for unexpected forces.
In a closed-loop control system, a sensor monitors the output (the vehicle's speed) and feeds the data to a computer which continuously adjusts the control input (the throttle) as necessary to keep the control error to a minimum (to maintain the desired speed). Feedback on how the system is actually performing allows the controller (vehicle's on board computer) to dynamically compensate for disturbances to the system, such as changes in slope of the ground or wind speed. An ideal feedback control system cancels out all errors, effectively mitigating the effects of any forces that may or may not arise during operation and producing a response in the system that perfectly matches the user's wishes.
12. Make a list of terms from Text 3 referring to control and memorize them.
13. Translate Text 4 in written form: Text 4. Regulators and Servomechanisms
The block diagram of a typical feedback control system is shown in Figure 3.
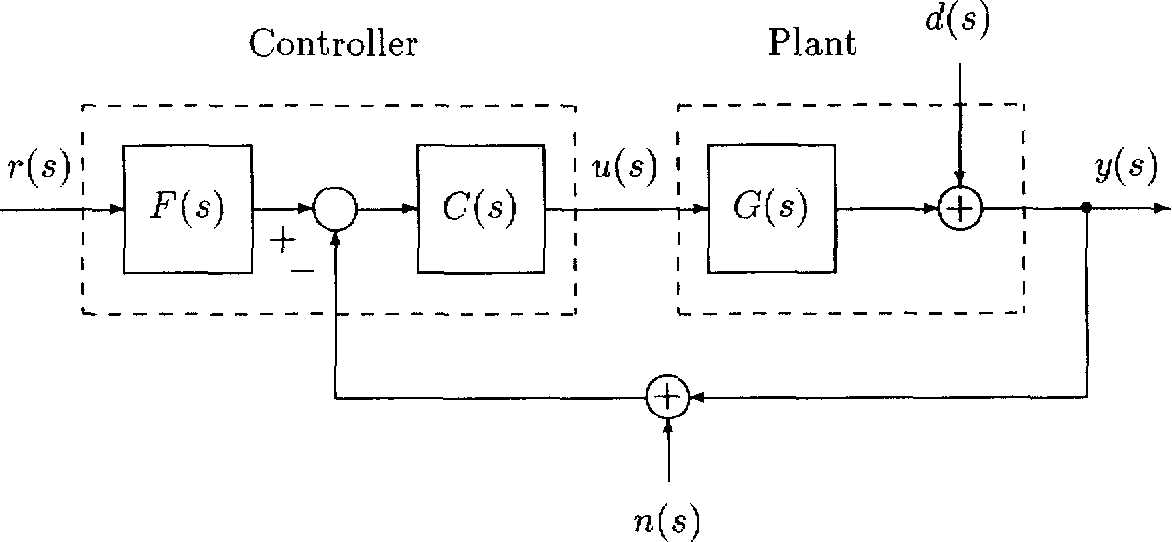
Figure 3. General feedback configuration
Here we are considering linear time invariant systems which can be represented, after Laplace transformation, in terms of the complex variable s. In Figure 3 the vectors u and у represent (the Laplace transforms of) the plant inputs and outputs respectively, d represents disturbance signals reflected to the plant output, n represents measurement noise and r represents the reference signals to be tracked. The plant and the feedback controller are represented by the rational proper transfer matrices G(s), and C(s) respectively, while F(s) represents a feedforward controller or prefilter. The usual problem considered in control theory assumes that G(s) is given while C(s) and F(s) are to be designed. Although every control system has a unique structure and corresponding signal flow representation the standard system represented above is general enough that it captures the essential features of most feedback control systems.
(from S.P.Bhattacharyya, H. Chapellat, L.H.Keel. Robust Control. The Parametric Approach)
14. Give derivatives of the following words from Text 5 and translate them into Russian:
Instability, performance, uncontrollably, excessive, acceptable, excessive, linear, invariant, simplification, validity, reliably.
15. Read Text 5 and try to give the Russian equivalents of the following terms. When necessary, look them up in a dictionary:
Stability, performance, external excitation, to decay to zero, open loop plant, to track the reference input, robust stability, to reject disturbances, nominal mathematical model, time invariant.
