
- •Introduction to control Part I
- •Text 1. Control System
- •8. Make a list of terms from Text 1 referring to control and memorize them.
- •9. Read and translate Text 2 Text 2. Basic Feedback Loop
- •10. Make a list of terms from Text 2 referring to control and memorize them.
- •11. Read and give a short summary of Text 3 Text 3. An example
- •12. Make a list of terms from Text 3 referring to control and memorize them.
- •13. Translate Text 4 in written form: Text 4. Regulators and Servomechanisms
- •16. Supply synonyms for the following words:
- •17. Analyse the grammatical structure of the following sentences and translate them:
- •Text 5. Stability and performance
- •19. Make a list of terms from Text 5 referring to control and memorize them.
- •23. Supply synonyms for the following words: Meet, to take place, because of, as regards, breakdown, to consider
- •24. Analyse the grammatical structure of the following sentences and translate them:
- •25. Translate Text 6: Text 6. The uncertainties
- •25. Make a list of terms from Text 6 referring to control and memorize them.
- •26. Read and translate Text 7. Text 7
- •27. Make a list of terms from Text 7 referring to control and memorize them.
- •28. Read and translate Text 8 without a dictionary. Text 8. Representations of Uncertainty
- •30. Give derivatives of the following words and translate them into Russian:
- •32. Supply synonyms for the following words:
- •Text 9. Servomechanism
- •Text 10. Performance: Tracking and Disturbance Rejection
- •43. Make a list of terms from Text 10 and memorize them. Rart II
- •1. Read and translate Text 11.
- •Text 11. The Philosophy of Classical Control
- •Make a list of terms from Text 11 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 12. Text 12. Classical control theory: the closed-loop controller
- •Make a list of terms from Text 12 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 13. Text 13. Controllability and Observability
- •Make a list of terms from Text 13 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 14. Text 14. Control Specifications
- •Make a list of terms from Text 14 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 15. Text 15. Model Identification and Robustness
- •System identification
- •Analysis
- •Constraints
- •Make a list of terms from Text 15 and memorize them.
- •Read and translate Text 16 Text 16. Control Objectives
- •Make a list of terms from Text 16 and memorize them
- •Give a short summary of Text 17 Text 17. Control Objectives
- •(From Ch.Schmid. Course on Dynamics of multidisplicinary and controlled Systems )
- •Make a list of terms from Text 17 and memorize them
- •Give a short summary of Text 18 (in written form) Text 18. Main control strategies
- •Pid controllers
- •Optimal control
- •Adaptive control
- •Intelligent control
- •17. Make a list of scientific terms that are used in Text 18, give their Russian equivalents and memorize them.
- •18. Give a short summary of Text 19 (in written form) Text 19. Feedback
- •Application of feedback in mechanical engineering
- •Make a list of terms from Text 19 and memorize them.
- •Give a short summary of Text 20 Text 20. Pid controller
Introduction to control Part I
Pronounce the following words:
Variable, dynamic, servomechanism, actual, disturbance, uncertainty.
Give derivatives of the following words and translate them into Russian:
Variable, uncertainty, disturbance, reference, automatic, control, regulator
Give the Russian equivalents of the following terms. If necessary, you may use a dictionary:
Control system, controller, plant, uncertainty, disturbance, reference, feedback, unity feedback or closed loop system, tracking error.
Supply synonyms for the following words:
In spite of, plane, aim, purpose, to force, to influence, to use, moment, input
Analyse the grammatical structure of the following sentences and translate them:
The mechanism makes certain variables behave in a prescribed manner.
It makes the system output follow a reference input.
The system to be controlled is a dynamic system.
It is based on the difference, at each instant of time, between the actual value of the plant output to be controlled and the prescribed reference.
6. Translate Text 1:
Text 1. Control System
A control system is a mechanism which makes certain physical variables of a system, called a plant, behave in a prescribed manner, despite the presence of uncertainties and disturbances.
The plant or system to be controlled is a dynamic system, such as an aircraft, chemical process, machine tool, electric motor or robot, and the control objective is to make the system output y(t) follow a reference input r(t) as closely as possible despite the disturbances affecting the system. Automatic control is achieved by employing feedback. In a unity feedback or closed loop system (see Figure 1), control action is taken by applying the input u{t) to the plant, and this is based on the difference, at each instant of time t, between the actual value of the plant output to be controlled y(t) and the prescribed reference or desired output r(t).
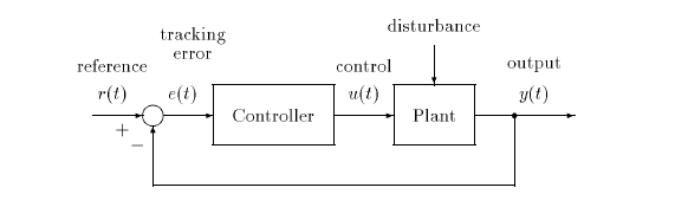
Figure 1. Unity feedback control system
The controller is designed to drive this difference, the tracking error e(t) to zero. Such control systems are also called regulators or servomechanisms.
(from S.P.Bhattacharyya, H. Chapellat, L.H.Keel. Robust Control. The Parametric Approach)
7. Answers the following questions:
What is a control system?
Give examples of the plant?
What is the control objective?
How is automatic control achieved?
How is control action taken in a closed loop system?
What is the function of the controller?
8. Make a list of terms from Text 1 referring to control and memorize them.
9. Read and translate Text 2 Text 2. Basic Feedback Loop
The most elementary feedback control system has three components: a plant (the object to be controlled, no matter what it is, it is always called the plant), a sensor to measure the output of the plant, and a controller to generate the plant’s input. Usually, actuators are lumped in with the plant.

Figure 2. Elementary control system
In the block diagram in Figure 2 each of the three components has two inputs, one internal to the system and one coming from outside, and one output. These signals have the following interpretations:
r – reference or command input
v – sensor output
u – actuating signal, plant input
d – external disturbance
y – plant output and measured signal
n – sensor noise
(from J.Doyle, B.Francis, A.Tannenbaum. Feedback Control Theory)
