
5 Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction Event

Type: Largest known Earthbound explosion
About 65 million years ago, an event known as the Cretaceous-Tertiary Event caused the extinction of many organisms, but is most famous for causing the extinction of the dinosaurs. Many scientists believe that this was caused by an asteroid impact that created the Chicxulub Crater located off the coast of the Yucatan Peninsula. It is estimated that the explosive force of this impact would have been the equivalent of 96 teratons of TNT, or about 1.7 million Tsar Bombas. This would make the impact the greatest explosion to ever occur on earth, for which there is sufficient geological evidence. The impact would have caused climate change, much like Mt. Tambora but much more drastic, and this climate change is believed to be what ultimately killed the dinosaurs.
4 GRB 080319B
T ype:
Largest explosion ever directly witnessed by humans
ype:
Largest explosion ever directly witnessed by humans
Gamma-ray11 bursts are among the most violent known events in the universe. The exact cause of Gamma-ray bursts is not fully understood, although most astronomers hold that they are linked to extremely large supernovae. Gamma-ray bursts usually last12 20 to 40 seconds and shine gamma-rays (hence the name) in a relatively narrow direction. Gamma-ray bursts are extremely rare, with one occurring every few hundred thousand years in each galaxy. On March 19, 2008, a gamma-ray burst called GRB 080319B occurred, and was visible to the naked eye for about 30 seconds. The explosion took place 7.5 billion light-years away, making the most distant object viewable without a telescope. The explosion is estimated to have generated the equivalent of 2×1034 tons of TNT, or about the equivalent of 10,000 times the Sun’s weight in TNT detonating all at once.
3 SN2006gy
T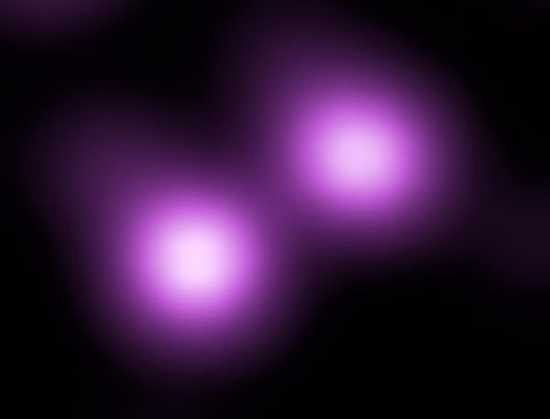 ype:
Largest known supernova
ype:
Largest known supernova
On September 16, 2006, the largest known supernova, SN2006gy, was discovered. Supernovae occur when stars run out of fuel, collapse on themselves, and then explode. Extremely large supernovae, or hypernovae, are among the most violent events in the universe, and are believed by many to be the source of gamma-ray bursts. SN2006gy occurred 230 million light years away, when a star about 150 times as massive as the Sun collapsed on itself. The amount of energy output by this hypernova is estimated to be approximately equivalent to 2.5×1035 tons of TNT, which is roughly13 the same amount of energy put out by all the stars in the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies in one minute. An interesting fact: Because hypernova are usually caused by very large stars, there is usually enough remaining material from the star to continue collapsing after the explosion. This remaining material will sometimes collapse until its volume14 reaches zero. This means that many hypernova form black holes.
2 GRB 080916C
Type: Largest true explosion ever
The universe is a big place. Astronomically large objects are difficult to comprehend, and the largest known explosion, GRB 080916C is no different. GRB 080916C was a gamma-ray burst that was first recorded on September 16, 2008. The burst occurred about 12.2 billion light-years away and lasted 23 minutes, which is a very long duration for a gamma-ray burst. For those 23 minutes, the gamma-ray burst was putting out more energy than most galaxy superclusters. It is estimated that the blast had the equivalent amount of energy of 2×1038 tons of TNT. That’s the same as a trillion Tsar Bombas going off15 every second for 110 billion years, or about 7,000 times the amount of energy that the Sun is expected to put out in its lifetime.
