- •Memorize the words and word combinations and their equivalents.
- •Find the words and combinations of words in the text and translate the sentences containing them.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Translate the word combinations from the text:
- •Point out the sentences in the text in which the word “to make” should be translated as “примушувати”.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Find the sentences in the text telling you about two problems facing the simple two pole dc motor. Text b Compensation for stator field distortion
- •Make sure that you know these words and word combinations.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Text c Dynamo Design Variations
- •Read and memorise the words and word combinations.
- •Permanent magnet motor – двигун з постійним магнитом
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Listen to the words and word combinations from the text. Pay attention to their meaning.
- •Memorize the words and word combinations and their equivalents.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Match the words and word combinations (a-e) to the sentences (1-5)
- •Answer the questions to the text
- •Say if the statement to the text is true or false
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to Indefinite Tenses in Active and Passive. Correct the mistakes in the sentences.
- •Text b Basic construction
- •Listen to the words and word combinations from the text. Pay attention to their meaning.
- •Memorize the words and word combinations and their equivalents
- •Read and translate the text
- •Match the words and word combinations (a-e) to the sentences (1-5)
- •Answer the questions to the text
- •Say if the statements to the text are true or false
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to Indefinite Tenses in Active and Passive. Correct the mistakes in the sentences.
- •Text c Principles of operation
- •Listen to the words and word combinations from the text. Pay attention to their meaning.
- •Find the words and combinations of words in the text and translate the sentences containing them.
- •Memorize the words and word combinations and their equivalents.
- •Read and translate the text
- •Match the words and word combinations (a-f) to the sentences (1-6)
- •Answer the questions to the text
- •Define the functions of Participle I and Participle II in the following sentences
- •Say, which of the sentences are in the Active and which are in the Passive Voice
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to the Sequence of Tenses
- •Translate the following Conditional sentences
- •Transformer Text a
- •Read and memorize words and word-combination
- •Make sure that you know these words and word combinations.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Math the following English words with the Ukrainian ones.
- •Find English equivalents to the words:
- •Translate the word combinations from the text:
- •Answer the questions to the text.
- •Text b Operation at different frequencies
- •Read and memorize the words and word-combinations
- •Be sure that you know these words
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Text c Limitations
- •Make sure that you know these words and word combinations.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Find the equivalents to the following.
- •Text d Construction
- •Read and memorise the words and word combinations
- •Read and translate the text. Cores
- •Find the equivalents to the folloving English words:
- •Point out English equivalents to the words:
- •Translate the word combinations.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read the passage about steel cores. Retell it. Text e Windings
- •Listen to the words and word combinations from the text and memorize them.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Match the English words and word combinations with the Ukrainian ones.
- •Insulation of windings
- •Text g Shielding
- •Supplement Speed control
- •Dc motor starters
- •Shielding
- •Autotransformers
- •Voltage transformers
- •Pulse transformers
- •3 Phase electrical power Transformer
- •3 Phase Transformer Delta and Wye Connections
- •Перелік скорочень
Voltage transformers
Voltage transformers (VTs) or potential transformers (PTs) are another type of instrument transformer, used for metering and protection in high-voltage circuits. They are designed to present negligible load to the supply being measured and to have a precise voltage ratio to accurately step down high voltages so that metering and protective relay equipment can be operated at a lower potential. Typically the secondary of a voltage transformer is rated for 69 or 120 Volts at rated primary voltage, to match the input ratings of protection relays.
The transformer winding high-voltage connection points are typically labelled as H1, H2 (sometimes H0 if it is internally grounded) and X1, X2, and sometimes an X3 tap may be present. Sometimes a second isolated winding (Y1, Y2, Y3) may also be available on the same voltage transformer. The high side (primary) may be connected phase to ground or phase to phase. The low side (secondary) is usually phase to ground.
The terminal identifications (H1, X1, Y1, etc.) are often referred to as polarity. This applies to current transformers as well. At any instant terminals with the same suffix numeral have the same polarity and phase. Correct identification of terminals and wiring is essential for proper operation of metering and protection relays.
While VTs were formerly used for all voltages greater than 240V primary, modern meters eliminate the need VTs for most secondary service voltages. For new, or rework, meter packages, VTs are typically only installed in primary voltage (typically 12.5kV) or generation voltage (13.2kV) meter packages.
Pulse transformers
A pulse transformer is a transformer that is optimised for transmitting rectangular electrical pulses (that is, pulses with fast rise and fall times and a constant amplitude). Small versions called signal types are used in digital logic and telecommunications circuits, often for matching logic drivers to transmission lines. Medium-sized power versions are used in power-control circuits such as camera flash controllers. Larger power versions are used in the electrical power distribution industry to interface low-voltage control circuitry to the high-voltage gates of power semiconductors. Special high voltage pulse transformers are also used to generate high power pulses for radar, particle accelerators, or other high energy pulsed power applications.
To minimise distortion of the pulse shape, a pulse transformer needs to have low values of leakage inductance and distributed capacitance, and a high open-circuit inductance. In power-type pulse transformers, a low coupling capacitance (between the primary and secondary) is important to protect the circuitry on the primary side from high-powered transients created by the load. For the same reason, high insulation resistance and high breakdown voltage are required. A good transient response is necessary to maintain the rectangular pulse shape at the secondary, because a pulse with slow edges would create switching losses in the power semiconductors.
The product of the peak pulse voltage and the duration of the pulse (or more accurately, the voltage-time integral) is often used to characterise pulse transformers. Generally speaking, the larger this product, the larger and more expensive the transformer.
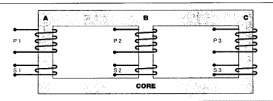
3 - Phase Transformers
3 - Phase Electrical Power Transformer In a 3 phase transformer, there is a three-legged iron core as shown below. Each leg has a respective primary and secondary winding.
Most power is distributed in the form of three-phase AC. Therefore, before proceeding any further you should understand what is meant by 3 phase power. Basically, the power company generators produce electricity by rotating (3) coils or windings through a magnetic field within the generator . These coils or windings are spaced 120 degrees apart. As they rotate through the magnetic field they generate power which is then sent out on three (3) lines as in three-phase power. 3 phase transformers must have (3) coils or windings connected in the proper sequence in order to match the incoming power and therefore transform the power company voltage to the level of voltage we need and maintain the proper phasing or polarity.
3 - Phase Power Is More Efficient Than Single Phase Three phase electricity powers large industrial loads more efficiently than single-phase electricity. When single-phase electricity is needed, It is available between any two phases of a three-phase system, or in some systems , between one of the phases and ground. By the use of three conductors a 3 phase system can provide 173% more power than the two conductors of a single-phase system. Three-phase power allows heavy duty industrial equipment to operate more smoothly and efficiently. 3 phase power can be transmitted over long distances with smaller conductor size.
Also read about 3 phase isolation transformers here. For an excellent source for these all transformer types check out TEMCo 3 phase transformers. Or check with Isolation Transformer Sales for 3 phase isolation transformers. These two companies manufacture some of the most recognized high quality 3 phase transformers available today.
In a three-phase transformer, there is a three-legged iron core as shown below. Each leg has a respective primary and secondary winding.