
- •Infertility - Безпліддя
- •Infertility
- •Causes in either sex
- •Medical treatments
- •Case history #1
- •Case history #2
- •Influenza - Грип
- •Influenza
- •Avulsion
- •… Any tumour composed of nerve tissue.
- •Карцинома (також рак) — злоякісна пухлина з епітеліальної тканини.
- •Exercise 9. Read the text, fill in the gaps with the words given in the table below. Express your opinion on the contents of the article. World Cancer Day 2013
- •Case history #1
- •Case history #2
- •Cardiovascular Drugs
- •Побічна дія лікарських засобів.
- •Oral hygiene – Гігієна ротової порожнини
- •Oral Hygiene and the Prevention of Dental Disease
- •Oral hygiene
- •Tooth brushing
Influenza - Грип
Learn the new words and word combinations:
|
influenza (flu) [ˌɪnflʊˈɛnzə] - грип contagious [kənˈteɪdʒəs] - заразний chill [tʃɪl] - озноб prostration [prəsˈtreɪʃn] - знемога; занепад сил; прострація confuse [kənˈfjuːz] - сплутувати |
common cold – звичайна застуда suppress [səˈprɛs] - пригнічувати rejection [rɪˈdʒɛkʃn] - відторгнення detergent [dɪˈtɜːdʒənt] - миючий засіб antiviral [ˌæntɪˈvaɪrəl] - противірусний |
Read the word combinations containing the new words and translate them into Ukrainian:
Influenza viruses,the incubation period of influenza, influenza-like illnesses, influenza's effects, the onset of influenza, a contagious disease, chills and fever, severe prostration, confuse with other flu-like illnesses, confuse with the common cold, suppressed immune system, prevent transplant organ rejection, inactivated by sunlight, disinfectants and detergents, antiviral drugs.
Match the terms with their explanations:
|
|
There are different types of diseases, give examples of the following ones:
|
Congenital diseases |
|
|
Hereditary diseases |
|
|
Acute diseases |
|
|
Chronic diseases |
|
|
Infectious diseases |
|
|
Communicable diseases |
|
|
Non-communicable diseases |
|
Answer the following questions:
What diseases of the cardio-vascular system do you know?
What diseases of the respiratory system do you know?
What diseases of the digestive system do you know?
What diseases of the endocrine system do you know?
What diseases requiring surgical intervention do you know?
Read and translate the text:
Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an acute infectious disease occurring in endemic, epidemic and pandemic forms. It is caused by the influenza viruses. The disease is contagious and spreads directly from person to person by talking, coughing and sneezing. Healthy carriers may spread the disease. The incubation period is from 1-3 days. The onset is sudden with chilly sensation, followed by fever. The most common symptoms are chills, fever, sore throat, muscle pains, headache (often severe), coughing, weakness/fatigue and general discomfort. The temperature ranges between 37,7 and 40 and persists from 2 to 5 days. The respiratory rate is moderately increased. The pulse in accelerated. Vomiting and diarrhea are frequent. The tongue is dry and coated, the pharynx usually reddened. In some cases catarrhal symptoms are replaced by nervous symptoms or prostration, insomnia, mental depression, intense headache, general pains.
The flu is often confused with other influenza-like illnesses, especially the common cold, but influenza's effects are much more severe and last longer than those of the common cold. Most people will recover completely in about one to two weeks, but others will develop life-threatening complications (such as pneumonia). Influenza, thus, can be deadly, especially for the weak, young and old, or chronically ill. People with a weak immune system, such as people with advanced HIV infection or transplant patients (whose immune systems are medically suppressed to prevent transplant organ rejection), suffer from particularly severe disease. Other high-risk groups include pregnant women and young children. The flu can also worsen chronic health problems. People with emphysema, chronic bronchitis or asthma may experience shortness of breath while they have the flu, and influenza may cause worsening of coronary heart disease or congestive heart failure.
Influenza viruses can be inactivated by sunlight, disinfectants and detergents. As the virus can be inactivated by soap, frequent hand washing reduces the risk of infection. Vaccinations against influenza are usually available to people in developed countries. Antiviral drugs are used for the treatment of the disease. People with the flu are advised to get plenty of rest, drink plenty of liquids, avoid using alcohol and tobacco and, if necessary, take medications such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) to relieve the fever and muscle aches associated with the flu. Since influenza is caused by a virus, antibiotics have no effect on the infection; unless prescribed for secondary infections such as bacterial pneumonia.
Answer the questions:
What is another name for influenza?
What kind of disease is influenza?
What is influenza caused by?
How does influenza spread?
How long does the incubation period in influenza last?
What are the most common flu symptoms?
What is the difference between the flue and the common cold?
How can influenza viruses be inactivated?
Who usually suffers from a particularly severe form of influenza?
What drugs are used for the treatment of the flu?
Find the equivalents of the following word combinations in the text:
Гостре інфекційне захворювання; заразна хвороба; здорові носії; раптовий початок хвороби; відчуття ознобу; біль у горлі; біль у м’язах; температура триває; помірно підвищена швидкість дихання; прискорений пульс; обкладений язик; безсоння; схожі з грипом захворювання; звичайна застуда; повністю одужати; ускладнення, які загрожують життю; низька смертність; пригнічена імунна система; відторгнення трансплантованого органу; особливо важке захворювання; погіршувати хронічні проблеми зі здоров’ям, відчувати задишку; дезактивувати за допомогою сонячного світла, дезінфекційних та миючих засобів; зменшувати ризик інфекції; противірусні ліки; пити багато рідини.
a) Match two parts of the word combinations:
|
complications |
|
onset |
|
infection |
|
by talking, sneezing or coughing |
|
rate |
|
form |
|
pharynx |
|
groups |
|
chronic health problems |
|
disease |
|
cold |
|
carriers |
b)Make your own sentences with the word combinations.
Put questions to the underlined words:
The flu can occasionally lead to pneumonia.
Influenza may produce nausea and vomiting.
Influenza is transmitted through the air.
Influenza viruses can be inactivated by sunlight, disinfectants and detergents.
Frequent hand washing reduces the risk of infection.
Influenza spreads around the world in seasonal epidemics.
In the 20th century three influenza pandemics occurred.
These pandemics killed millions of people.
These pandemics were caused by the appearance of a new strain of the virus in humans.
Antiviral drugs such as the neuraminidase inhibitor (Tamiflu) have been used to treat influenza.
Open the brackets using the verbs in the appropriate form, translate the sentences:
He (to be) ill with the flu since last week.
Antiviral drugs (to use) to treat influenza.
Influenza often (to confuse) with the common cold.
Antibiotics (to prescribe) for the treatment of bacterial pneumonia.
He (to hospitalize) with a severe form of the flu last week.
After two days of being ill with influenza he (to start) having trouble breathing.
Patients with the flu (to recommend) to have plenty of rest and drink lots of liquids.
Influenza in which no complications occur usually (to last) from 3 to 5 days.
The headache and general pains (to relieve) by the use of Aspirin.
Many patients (to have) respiratory symptoms such as laryngitis or tracheitis.
Explain the following terms in 5 sentences:
Influenza
Common cold
Antiviral drugs
TEST
1. Influenza is …
a) a congenital disease b) an acute infectious disease c) a hereditary disease
d) a chronic disease
2. Influenza is caused by…
a) bacteria and fungi b) stress c) the influenza viruses d) genetic mutations
3. The incubation period is from … days.
a) 5-6 b) 1-2 c) 1-3 d) 3-7
4. The flu is often confused with…
a) atherosclerosis b) the common cold c) bronchitis d)pneumonia
5. Most people with influenza will recover completely in about …
a) one to two weeks b) one to two days c) three to seven days
d) two to three months
6. Influenza viruses can be inactivated by ...
a) antibiotics b) vaccination c) electric light d) sunlight, disinfectants and detergents
7. … are used for the treatment of the disease.
a) depressants b) anticoagulants c) antiviral drugs d) antibiotics
8. People with the flu are advised to …
a) get plenty of rest, drink plenty of liquids, avoid using alcohol and tobacco
b) change their lifestyle c) take antibiotics d) be hospitalized
9. Antibiotics…
a) are used for treatment influenza b) treat all viral diseases
c) have no effect on influenza d) are used to relieve influenza symptoms
10. Paracetamol is used to …
a) treat influenza b) to relieve the fever and muscle aches associated with the flu
c) to relieve nausea and vomiting d) to help the patient sleep
TETANUS - Правець
Exercise 1. Practise the pronunciation:
Bacillus [bə ' siləs]
Tetanus ['tetənəs]
Vague [veig]
Nightmare [ `nait meə]
Delirious [di 'liriəs]
Lockjaw [` lɔkdʒɔ:]
Trismus [trizməs]
Height [hait]
Drawing [drɔ:iŋ]
Clenched [klentt]
Protruded [prə 'tru:did]
Opisthotonus [ou 'pisə…]
Seizure ['si: ʒ ə]
Afebrile [ei 'fi:bril]
Ensue [in ' sju:]
Lessening [lesəniŋ]
Exercise 2. Topic vocabulary:
Bacillus (pl. bacilli) бацила, паличка
Vague нечіткий, неясний, туманний
Nightmare кошмар, жах, страшний сон
To become delirious стати шаленим, божевільним
Lockjaw тризм щелепи, правець
Trismus трізм ( судорожне зціплення щелеп )
Height of disease розпал (пік) хвороби
To draw up витягувати
Clenched міцно стиснутий
Protruded (lips) випнуті губи
Opisthotonus опістотонус
Seizure приступ, напад, припадок
Afebrile безгарячковий
To ensue виникати, випливати
To lessen скорочувати, зменшуватися
Exercise 3. Read the words paying attention to the rules of reading:
c,s,t, before ia, ie, io [ ]
Position, sufficient, remission, initial, patient, urination, expression, artificial, potential, incubation, special, infectious, facial, essential, permission, insufficient, motion, deficiency.
Exercise 4. Form the words with the help of negative prefixes. Translate them into Russian:
Dis – like, function, connect, agree, locate, place, continue, section, solvent.
Ir – regular, responsible, relevant, resistible, radiation, reversible, reducible.
Im – possible, practical, mobile, moral, balance, maturity, potency, purity.
Un – necessary, reliable, fortunately, consciousness, dress, infected, mixed.
Mal – formation, nutrition, occlusion, position, treatment, presentation, rotation.
Exercise 5. Read the words with the same root. State the part of speech and translate them into Russian:
Face – facial, slow – slowly; connect – connection; pelvis – pelvic; compose – composition; rapid – rapidly; base – basic; recover – recovery; remove – removal; survive – survival; tender – tenderness, restless – restlessness; breath – breathing.
Exercise 6. Translate the following word combinations:
Incubation period, infectious disease, to open the mouth, typical facial expression, urination, in case, to gain entrance into the body, painful spasms, characteristic picture, angles of the mouth, severe headache , masticating muscles, severe pain, attack, fever.
Exercise 7. Match medical terms with the proper definitions:
|
1. tetanus 2. tetany
3. toxin
4. urination
5. spasm
6. trismus
|
Spasm of the jaw muscles, keeping the jaw tightly closed. An acute infectious disease, affecting the nervous system, caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. The periodic discharge of urine from the bladder through the urethra. Spasm and twitching of the muscles, particularly those of the face, hands, and feet. A poison produced by a living organism, especially by a bacterium. A sustained involuntary muscular contraction, which may occur either as part of a generalized disorder, such as a spastic paralysis, or as a local response to an otherwise unconnected painful condition. |
Exercise 8. Translate the following sentences. Pay attention to the sentences with construction: one (ones), that of (those of).
The condition of patient V. is worse than that of patient C.
The number of the vertebrae in the coccyx is less than the number of those in the beck.
The bones of the lower extremities are longer than those of the upper ones.
This lecture is more interesting than the one I attended last week.
The walls of the left atrium are thicker than those of the right.
Some muscles are more elastic than the other ones.
I will examine your patient and that of Dr. Ivanov.
The wards in the new hospital are better equipped than those in our old one.
Exercise 9. Read and translate the text:
TETANUS
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease characterized by painful spasms of the muscles and caused by the Bacillus tetani which gains entrance into the body through a wound or break in the skin. The tetanus bacillus produces a toxin which is one of the most powerful poisons.
The incubation period varies on an average from 5 to 15 days. In general, the shorter the incubation period the more serious is the disease. The earliest symptoms are vague. The patient is restless, irritable; he suffers from nightmare, and may become delirious. Severe headache, difficulty in urination, and sweating may be noted. In the majority of cases following a short period when there is pain in the back of the neck and in the muscles of the jaw, a tonic spasm of the masticating muscles occurs so that the patient is unable to open his mouth, producing the characteristic picture known as lockjaw (trismus). Gradually all muscles of the body become affected except those of the forearm and of the hand. At the height of the disease there occurs the typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus, where the patient appears to be laughing, due to the drawing up of the angles of the mouth. The brows are contracted, the eyes are partly closed, the teeth are clenched tightly and the lips are slightly protruded. The body is arched in the position known as opisthotonus. Upon the slightest stimulus the entire body may go into a convulsive seizure of the utmost severity, accompanied by severe pain.
There is no characteristic temperature; the patient may be afebrile or ran a fever as high as 104°F during the attacks.
Death may ensue within the first 48 hours or at any time up to one week after onset. If the patient survives the first week, his chances of recovery are greatly improved, the spasms gradually lessening in frequency and severity.
Exercise 10. Answer the following questions.
What is tetanus caused by?
What is toxin?
What is the incubation period of tetanus?
What are the symptoms of tetanus?
When does a tonic spasm of masticating muscles occur?
How can you describe such typical facial expression known Risus Sardonicus?
When are the changes of recovery greatly improved?
How does Bacillus tetani gain entrance into the body?
Exercise 11. Complete the following sentences using the text.
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease characterized by … .
Severe headache, difficulty in urination, and sweating … .
The patient is unable to open his mouth, producing the … .
Gradually all muscles of the body become … of the forearm and of the hand.
… there occurs the typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus.
The body … known as opisthotonus.
The patient may be …during the attacks.
Death may ensue within … after onset.
Exercise 12. Read the sentences and say whether the following ones are true to the text:
Tetanus is an acute inherited disease characterized by painful spasms of the muscles.
Tetanus is caused by the Bacillus tetani which gains entrance into the body through the blood.
The tetanus bacillus produces a toxin.
The incubation period varies on an average from 15 to 25 days.
Gradually all muscles of the body become affected inclusive those of the forearm and of the hand.
The typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus, where the patient appears to be crying, due to the drawing up of the angles of the mouth.
The body is arched in the position known as opisthotonus.
There is no characteristic temperature; the patient may be afebrile or ran a fever as high as 40,00°C during the attacks.
Exercise 13. Translate the following word combinations.
Cупроводжуватися сильним болю, спазма жувальних м`язів, проникати крізь розрив шкіри, характерна картина хвороби, поступово зменшуватися по частоті та тяжкісті, інкубаційний період хвороби, міцно стиснуті зуби, пік хвороби, сардонічний сміх, сильнодіюча отрута, випадок.
Exercise 14. Translate Russian sentences into English using Complex Subject Construction.
Известно, что столбняк является острым хроническим заболеванием, которое характеризуется болезненными спазмами мышц.
Оказывается, что при столбняке Bacillus tetani проникает в организм через рану или через разрыв кожи.
3.Известно, что инкубационный период болезни меняется в среднем от 5 до 15 дней.
4. Первичными симптомами столбняка, вероятно, будут возбужденное состояние, раздражительность, кошмарные сновидения, и делирий.
5.Говорят, что в разгар болезни, у пациента часто случалось типичное выражение лица, известное как risus sardonicus.
6.Было отмечено, что при столбняке повышение температуры обычно не наблюдается.
7.Говорят, что смерть может наступить в течение 48 часов или же в любое время после начала приступа.
8. Несомненно, шансы у пациента на выздоровление увеличатся, если он выживет в первую неделю.
Exercise 15. Put questions to the underlined words.
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease characterized by painful spasms of the muscles.
The Bacillus tetani gains entrance into the body through a wound or break in the skin.
The tetanus bacillus produces a toxin.
The patient is restless, irritable and suffers from nightmare, and may become delirious.
Gradually all muscles of the body become affected except those of the forearm and of the hand.
At the height of the disease there occurs the typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus.
The patient appears to be laughing, due to the drawing up of the angles of the mouth.
The patient may be afebrile .
Exercise 16. Use the verbs in brackets in the appropriate tense. Translate them into Russian.
1. The incubation period is likely (to vary) on an average from 5 to 15 days in future.
2. The patient (to suffer) from nightmare, and (to become) delirious.
3. At the height of the disease there (to occur) the typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus.
4. The brows (to contract), the teeth (to clench) tightly and the lips (to protrude) slightly.
5. Now the patient’s body is reported (to arch) in the position known as opisthotonus.
6. Upon the slightest stimulus the entire body just (to go) into a convulsive seizure of the utmost severity, accompanied by severe pain.
7. It was said that the patient (to ran) a fever as high as 104°F during the attacks for a weak.
8. Death (to ensue) within the first 48 hours or at any time up to one week after onset.
Exercise 17. Topic vocabulary.
|
Nouns |
Verbs |
Adjectives |
|
Recovery Severity Onset Seizure height of the disease lockjaw break in the skin nightmare urination angles of the mouth sweating expression the muscles of the jaw headache wound |
Lessen Improve Survive Ensue Accompany Gain Appear Occur To be due to To be characterized
|
Infectious Painful Powerful average restless irritable delirious Severe masticating characteristic afebrile
|
TEST
1. Tetanus is caused by the … which gains entrance into the body through a wound or break in the skin.
a. Bacillus anthrax b. Bacillus tetani c. Bacillus drumstick
d. Bacillus gas-producing e. Bacillus Koch’s
2. The incubation period varies on an average … .
a. from 5 to 10 days b. from 15 to 25 days c. from 5 to 25 days
d. from 1 to 5 days e. from 5 to 15 days
3. The patient is restless, irritable; … nightmare, and may become delirious.
a. he suffer from b. he suffers from c. he suffering from
d. he is suffering from e. he suffered from
4. In the majority of cases following a short period when there is pain… , a tonic spasm of the masticating muscles occurs so that the patient is unable to open his mouth, producing the characteristic picture known as lockjaw (trismus).
a. in the back of the head and in the muscles of the jaw
b. in the back of the neck and in the muscles of the face
c. in the back of the neck and in the joints of the leg
d. in the back of the neck and in the muscles of the jaw
e. in the back of the head and in the muscles of the trunk
5. Gradually all muscles of the body become affected except … the forearm and of the hand.
a. that of b. these of c. this of d. of those e. those of
6. At the height of the disease there occurs the typical facial expression known as risus sardonicus, where…, due to the drawing up of the angles of the mouth.
a. the patient appears to be laughing
b. the patients appears to be laughing
c. the patient appears be laughing
d. the patient appears to laughing
e. the patient appears to be being laughing
7. …the slightest stimulus the entire body may go into a convulsive seizure of the utmost severity, accompanied by severe pain.
a. On b. At c. Before d. In e. Upon
8. There is no characteristic temperature; the patient may be afebrile or … during the attacks.
a. rans a fever as high as 104°F b. ran a fever as high as 104°F
c. ranning a fever as high as 40°C d. run a fever as high as 104°F
e. ran a fever as low as 104°F
9. Death may ensue … or at any time up to one week after onset.
a. in the first 28 hours b. within the first 48 hour
c. within first 48 hours d. within the first 48 hours
e. after the first 48 hours
10. … the first week, his chances of recovery are greatly improved, the spasms gradually lessening in frequency and severity.
a. If the patients survives b. If the patient survives
c. If the patient survive d. If the patient survived
e. If the patient to survive
DIPHTHERIA - Дифтерія
Exercise 1. Practice the pronunciation:
Deleterious [ delitiəriəs ], temperate [ 'tempərit ], throughout [θru(:)'aut ], susceptible [sə'səptəbl], menace [ 'menəs ], robust [ rəu'bΛst], faucial [ fə:siəl ], raw [rə:], myocarditis [maio(u)ka:daitis], mandatory [ 'mændətəri ], quarantine
['kwərənti:n ], successive [sək'sesiv ].
Exercise 2. Topic vocabulary:
fibrin – фибрин
deleterious – вредный , вредоносный
temperate – умеренный
dissemination – распространение
experience – испытывать
susceptible – восприимчивый
menace – угроза, опасность
predispose – предрасполагать
robust – крепкий, здоровый
pillar of fauces – небные дужки
dreadful – плохой, ужасный
apt to smth – склонный, подверженный
employment – использование, применение
stiffness – онемение, одеревенение, окостенелость
raw – лишенный кожи, свежий, чувствительный
mandatory – обязательный, принудительный
successive – следующий один за другим, последующий
culture – выращивание бактерий
Exercise 3. Match the following English word combinations with Russian ones:
1. absorbed by blood stream 1. распространяться при прямом контакте
2. produce deleterious effect on 2. внезапное начало
3. spread by direct contact 3. всасываться кровотоком
4. put in an appearance 4. производить вредное действие на
5. healthy carrier 5. по расположению
6. according to the distribution 6. появиться ненадолго
7. insidious onset 7. здоровый носитель
Exercise 4. Read and translate the following sentences. Define the form and function of Participle I in the sentences:
1. Looking at some case reports the doctor explained something to his assistants. 2. The student is examining the patient together with the doctor- in-charge. 3. As the patient complains of a severe headache the nurse is giving him some medicines. 4. Examining the patient the doctor noticed some changes in his recovery. 5. The moaning patient didn’t hear when the doctor on duty entered the ward.
Exercise 5. Read and translate the text:
DIPHTHERIA
Diphtheria is an acute contagious disease caused by specific organism bacillus diphtheria.
It is characterized by local inflammation with fibrin formation of the mucous membranes, usually of the upper respiratory tract, with production of a toxin which when absorbed into the blood stream may produce deleterious effects on various parts of the body, especially the heart and peripheral nerves.
The disease exists throughout the world but is more common in temperate zones and during the colder months, autumn and winter. It is commonly spread by direct contact which must be fairly intimate. Dissemination by third objects such as clothes, toys, etc. may also occur and carriage by milk has been reported many times. Healthy carriers may disseminate the disease to susceptible persons and thus constitute a menace to public health. Children appear to be more liable to diphtheria than adults; although the most robust people may be attacked and those whose health is weakened by any cause are especially predisposed.
The incubation period is three to ten days. The disease may be divided into three main forms according to the anatomical distribution of the membrane: a) faucial or pharyngeal; b) laryngeal; c) nasal.
The onset of the disease is insidious with relatively moderate temperature reaction. In general, following an incubation period of about two days, symptoms set in like those commonly accompanying a cold. A slight feeling of uneasiness in the throat is experienced along with some stiffness of the back of the neck. The earliest objective manifestation of the disease is the formation of a thin film of fibrin on the tonsils which increases in thickness to form characteristic yellowish-white or grayish-white pseudomembrane.

The throat appears to be reddened and somewhat swollen. If the pseudomembrane is forcibly removed, it is found to separate from the underlying true mucous membrane with difficulty and leaves a raw, bleeding surface on which in the untreated cases a fresh membrane rapidly reforms. The lesion tends to spread over the pillars and onto the soft palate and uvula. Hence any membranous formation on pharyngeal tissues should immediately be regarded as a suspicion of diphtheria.
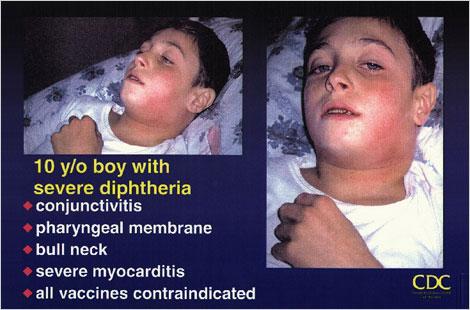
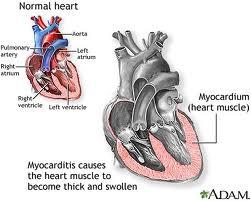
Myocarditis is the most dreadful of all complications of diphtheria. It is due to direct action of the toxin on the heart muscle.
Another severe complication is peripheral neuritis. It occurs in the form of paralysis affecting the soft palate and throat. Other forms of paralysis are paralysis of eye or even respiratory muscles, paralysis of a limb or both legs. These symptoms, however, after continuing for a variable length of time, almost always ultimately disappear.
The outcome of the disease depends mainly on one factor, namely, the early administration of adequate doses of antitoxin. Its employment in any recognized or even suspected case of diphtheria is mandatory and no physician can delay its administration. The second important measure is rest, the patient being kept strictly flat.
Patients suffering from diphtheria should be isolated for at least two weeks after the onset of the disease, and then until three successive cultures from the nose and throat taken not less than 48 hours apart are negative.
Exercise 6. Answer the following questions:
1. What is diphtheria caused by?
2. Is it contagious disease?
3. What is the disease characterized by?
4. Where is diphtheria more common?
5. Who is more liable to diphtheria?
6. What is the incubation period of the disease?
7. What are the main forms of diphtheria?
8. What are its main symptoms?
9. What are its main complications?
10.What does the outcome of the disease depend on?
Exercise 7. Translate into English and make up 5 sentences with them:
oстрое инфекционное заболевание, местное воспаление, всасываться кровотоком, слизистая оболочка, вредное воздействие, во всем мире, распространяться при непосредственном контакте, здоровый носитель, быть более подверженным, самые здоровые ( крепкие ) люди, быть особенно предрасположенным, появляться ненадолго, отложить назначение, по крайней мере, начало заболевания.
Exercise 8. Fill in the gaps to read the words and word combinations.
_i_ _e_in_t_o_
l…c…l in…la…ma…io…
_u_ _u_
_e_ _r_n_
_e_ _t_r _ _ _s e_f_ct
m_n_c_
r_s_i_e__r_ _u_c_es
_ n_ _ _a_i_n _ e_ _ o_
_t_f_n_ _s
a_ _it_xi_
_re_i_ _o_e_
Exercise 9. Give English equivalents to the words in braсkets:
1. Diphtheria is an (острое инфекционное) disease.
2. It is characterized by (местным воспалением) with fibrin formation of the (слизистой оболочки) of the (верхних дыхательных путей).
3. The disease exists (по всему миру) but is more common (в умеренных зонах).
4. It is commonly spread (при прямом контакте).
5. Сhildren appear to be (более подвержены) to diphtheria than (взрослые).
6. Most (крепкие) people may be (инфицированы) and those whose health is weakened by any cause are especially (предрасположены).
7. The earliest objective (проявление) of the disease is the formation of (тонкой пленки на миндалинах).
8. If the pseudomembrane is forcibly removed, it leaves (свежую кровоточащую) surface.
9. (Исход заболевания) depends largely on one factor, namely, (назначения соответствующей дозы антитоксина).
10. Patients suffering from diphtheria should be (изолированы) for at least two weeks after (начала заболевания).
Exercise 9. Fill in the articles where necessary.
The old man was seriously ill. He was running … high temperature.
I’ve … bad cold in … head. I must have caught … cold yesterday when I ran out into … yard without … cap on.
She overworked and had … bad headache. People who do not get enough … sleep often have … headaches.
I have only … slight headache. No pills for me, thank you.
I have … splitting headache and … bad cold in … head. I must have caught … cold. I am afraid I shall fall ill with … flu.
I have … sore throat. I feel … pain in my side. – You must stay in … bed and call … doctor in.
Take … table spoonful of … mixture twice … day after … meals.
I had … bad cold. I went to bed and drank … cup of hot tea with raspberry jam. It helped to beat down … temperature.
… weather was bad yesterday. I must have caught … cold when I was going … home from … work.
He stayed at … home and called … doctor in. … doctor diagnosed … case and prescribed him … medicine.
Exercise 10. Put the verbs in brackets in the appropriate tense:
1. Whom … the doctor … at the hospital every day? (treat)
2. What … you … now? (study)
3. What … the surgeon already …? (transfuse)
4. What … the surgeon … for two hours? (perform)
5. What … the lecturer … yesterday at 3 o’clock? (report on)
6. What … you … to do before you saw me? (decide)
7. What … the nurse … for an hour before the surgeon began the operation? (sterilize)
8. What … you … tomorrow at 6 o’clock? (do)
9. What … you … tomorrow? (take part in)
10. How many patients … the doctor … tomorrow by 5 p.m.? (hospitalize)
Exercise 11. Speak on following items:
Epidemiology of diphtheria.
Symptomatology.
Treatment.
Complications.
Quarantine.
Exercise 12. Compose a case history using the key words:
To be admitted to the hospital, to complain of, on physical examination, symptoms, to reveal, laboratory findings, antitoxin treatment, the course of the disease, convalescence.
TEST
1. Diphtheria is an acute contagious disease ... by specific organism bacillus diphtheria.
a) is caused b) caused c) causes d) has been caused e) causing
2. The disease … .throughout the world.
a) exists b) existed c) exist d) is existing e) was existing
3. The incubation period … days.
a) 1-2 b) 7 to 9 c) 30 d) 3 to 10 e) 5 to 10
4. A thin film of fibrin on the tonsils forms characteristic … pseudomembrane.
a) yellowish-white b) white c) grayish d) bluish e) bleeding
5. Children ... to be more liable to diphtheria.
a) appears b) appeared c) is appeared d) appear e) appearing
6. The lesion ... to spread over the pillars and onto the soft palate.
a) tend b) tending c) is tended d) to tend e) tends
7. What ... the outcome of the disease depend on?
a) will b) would c) does d) did e) do
8 The disease may be divided ... 3 main forms.
a) to b) into c) for d) in e) at
9. Peripheral neuritis occurs in the forms of... affecting the soft palate and throat.
a) inflammation b) disorder c) insufficiency d) paralysis e) affliction
10. The outcome of the disease depends mainly on one factor, namely, the early administration of…
a) antibiotic b) vaccine c) laxative d) expectorant e) antitoxin
MALARIA - Малярія
Exercise 1. Practise the pronunciation:
Parasite ['pærəsait], swamp [swəmp], gnat [næt], endeavour [in'devə], tertian ['tə:∫ (ə) n], quartan ['kwə:tn], eventually [iventjuəli], heap [hi:p], height [hait], duly ['djuli], quinine [ 'kwini:n ], drastic [ 'dræstik ].
Exercise 2. Topic vocabulary:
swamp – болото
pool – ставочок, калюжа
gnat – комар
flourish – процвітати
endeavour – намагатися, докладати зусиль
tertian – триденна пропасниця
quartan – чотириденна малярія
respectively – відповідно
offspring – паросток, нащадок
eventually – кінець кінцем, зрештою
betake – утікати, дременути
heap – нагромаджувати, складати
flush – прилив крові, рум'янець
height – пік
break out –спалахнути
duly – у належний час
drastic – радікальний
locality – місцевість
sanitate – поліпшувати санітарні умови
survey – огляд
Exercise 3. Match the following word combinations:
Onset of the attack 1. своєчасно призначене лікування
Course of the disease 2. радикальні заходи
Duly administered treatment 3. поліпшувати санітарні умови місцевісті
Drastic measures 4. огляд населення
To sanitate locality 5. початок приступа
Survey of population 6. течія ( хід ) захворювання
A cause of the disease 7. пік хвороби
A height of the disease 8. причина захворювання
Exercise 4. Choose one or more adjectives from the list B to modify nouns from the list A so as to make sense. Translate the word combinations into the native language.
List A: complications, measures, treatment, stage, form, climate, gland, headache, attack, phase, corpuscles, course, preparations.
List B: drastic, duly, sweating, salivary, red, tropical, severe, administered, hot, tertian, temperate, endocrine, thyroid, bad, malarial, blood.
Exercise 5. Form the following adverbs and translate them.
Model: local- locally
Probable, considerable, chief, late, recent, severe, main, clear, different, deep, necessary, sufficient, tropical, respective, final, successful, extreme.
Exercise 6. Memorize the meaning of the following term-elements.
Cry(o) - [kriəu] – combining form of Greek origin denoting cold
Therm(o) – [Ɵə:məu] – combining form of Greek origin denoting heat, temperature
End(o) – [endəu] – combining form of Greek origin denoting within or inner
1.Absence of the ability to sense heat and coldness - … .
2. Exceptional sensitivity to low temperature -… .
3. A technique for measuring and recording the heat produced by different parts of the body - … .
4. Within the material of a cartilage - … .
5. A device for registering temperature - … .
6.The use of heat to alleviate pain and stiffness in joints and muscles -… .
7. A parasite that lives inside its host - … .
8. Preservation of tissues by freezing - … .
9. A chamber in which frozen tissue is sectioned with a microtome - … .
10. Arising within or derived from the body - … .
11. The physiological process of regulating or adjusting body temperature - … .
12. An abnormal sense of pain that is felt when part of the body is warmed - …
13. The inner cytoplasm of cells - … .
14. The use of extreme cold in a localized part of the body to freeze and destroy unwanted tissue - … .
(Thermometer, thermotazis, thermoanaesthesia, thermoalgesia, thermotherapy, thermography, cryostat, cryopreservation, cryasthesia, cryosurgery,endogenous, endoscope, endochondral, endoplasm, endoparasite )
Exercise 7. Translate into Russian paying Attention to the Complex Subject:
1.The disease is known to exist all round the world.
2. It has long been noticed that gnats seem to flourish together with malaria.
3. The temperature is found to be considerably raised in this patient.
4. Some metastatic liver lesions are found to displace vessels.
5. The drug appears to produce no side effect .
6. Patients with perforated ulcers are known to complain of an acute pain in the stomach.
7. This diagnosis is found to be correct in only a few cases.
8. Penicillin is considered to be the most effective drug in treatment of inflammation.
9. Respiratory function is known to vary considerably.
10. Vitamins are known to be divided into water-soluble and fat- soluble.
Exercise 8. Read and translate the text:
MALARIA
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by the presence in the human blood of the Plasmodium malariae.
The disease is known to exist all round the world but is chiefly found in tropical climates spreading here and there into temperate regions where it occurs in summer and autumn. The presence of swamps, pools are also important factors. It has long been noticed that gnats or as they called in the tropics mosquitoes seem to flourish together with malaria and several scientists endeavoured to establish a connection between the two.
There are three main kinds of malarial parasites to be distinguished; those causing the tertian, the quartan and the tropical forms of malaria respectively. The malarial parasite, Plasmodium malaria, passes one phase of its lifecycle in man (the asexual phase) and the other in the stomach and tissues of the mosquito (the sexual phase). After its development in the mosquito’s stomach the resulting offspring eventually find their way into the mosquito’s salivary glands. When the infected female mosquito bites a human being these parasites enter human red blood corpuscles.
The acute malarial attacks have in general three stages. These are the cold stage, the hot stage and the sweating stage.
The cold stage begins with a feeling of chilliness even in the hottest weather. This increases till the person has to betake him to bed and heap himself with clothes, face and nails being blue and the whole body shaken with shivering. Nevertheless the temperature is found to be considerably raised. This stage lasts an hour or less.
The hot stage comes on as the temperature of the body rises, beginning with hot flushes which lengthen till the body feels burning hot, the temperature rising to 40’ or 41’C. There are also headache, sickness, pains throughout the body and sometimes even delirium. This stage may last several hours.
The sweating stage comes on after the fever reaches its height, as the temperature begins to fall. Profuse perspiration breaks out, the person begins to feel better, and the headache and pains at the same time pass off. Finally after three or four hours the patient feels quite well though much weakened.
Having gone through the three stages of a malarial attack patients feel recovered until the onset of the next attack.
Severe vomiting and diarrhea may sometimes complicate the course of the disease. Duly administered treatment with quinine or other preparations as a rule soon interrupts the course of malarial attacks.
As it is generally known that “prevention is better than cure” drastic measures should be taken to sanitate localities, to reduce the number of mosquitoes, to detect carriers and to carry out the survey of the population.
Exercise 9. Answer the following questions:
1. What is malaria caused by?
2. Where is the disease chiefly found?
3. What are the three main forms of malaria?
4.When do the parasites enter human red blood corpuscles?
5. What three stages have the acute malarial attacks?
6. What are the symptoms of the cold stage?
7. What stage is characterized by hot flushes?
8. When does the fever reach its height?
9. What complicates the disease?
10.What preventive measures should be taken?
Exercise 10. Translate into English the following word combinations:
Встановити зв'язок між чим-небудь, навіть в найжаркішу погоду, відправлятися в ліжко, надягати багато одягу, трястися від тремтіння, горіти від жари, біль по всьому тілу, відчувати себе досить добре, відчувати себе таким, що видужав, своєчасно призначене лікування медичними препаратами, радикальна міра, проводити санітарну обробку території, пік хвороби.
Exercise 11. Is it true or false?
1. Malaria is a chronic disease.
2. There are many kinds of malarial parasites.
3. The disease is chiefly found in temperate climate.
4. Gnats seem to flourish together with malaria.
5.The cold stage starts with the feeling of burning.
6. The acute malarial attacks have in general three stages.
7. The main complications of the disease are blindness and heart failure.
8. Having gone through the three stages of a malarial attack patients feel recovered until the onset of the next attack.
9. The disease isn’t known to exist all round the world
10. It is better to cure than to prevent the disease.
Exercise 12. IT’S INTERESTING TO REMEMBER:
Fever = pyrexia ( also remember PUO – pyrexia of uknown origin)
Fever is also known as temperature. – I’ve got a temperature.
Adjectives = feverich/ febrile and pyrexial
Opposites = afebrile / apyrexial
Some symptoms of fever: sweating, rigors ( severe shivering and sensation of coldness, also known as chills ).
Describe the state of patient with malaria using the new terms.
Exercise 13. Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions. Translate the sentences.
1. All infectious diseases are similar … origin.
2. The findings of the intradermal tests proved to be … great diagnostic importance.
3. The patient’s sensitivity … penicillin should be studied before the treatment is begun.
4. Much progress has been achieved … treating bronchial asthma … the last few years.
5. The child was noted to be allergic … definite inhalant preparations.
6. Infections differ … other diseases …a number …aspects.
7. The incubation period is the period between the invasion … the tissues by pathogens and the appearance … clinical features of infection.
8. The period … infectivity is the time that the patient is infectious … others. 9. Many infections are preventable … hygienic measures , … vaccines or … drug prophylaxis ( … example, chloroquine to prevent malaria ).
10. Communicability is another factor which differentiates infections … non -infectious diseases.
Exercise 14 . Translate into English using Complex Subject:
1. Як виявилось, значно зменшена вага і сильна лихоманка є ознаками важкого захворювання.
2 . Вакцина виявилася безпечною.
3. Очікується, що клінічні випробування почнуться наступної весни.
4. Виявилось, що у хворого алергія до антибіотиків.
5. Відомо, що молочні продукти містять 100 різних речовин, корисних для людини.
6. Відомо, що просування їжі по кишечнику може тривати від 12 до 72 годин.
7. Виявилось, що характерними клінічними проявами захворювання є кровотеча, блювота і нудота.
TEST
1 .The disease ... to exist all round the world.
a. are known b. know c. knew d. is known e. to be known
2. The drug ... to produce no side effect.
a. to be appeared b. is appeared c. appear d. appears e. are appeared
3. There are... main kinds of malarial parasites to be distinguished.
a. 2 b. 4 c. 3 d. 5 e. 1
4. When the infected female mosquito bites a human being parasites enter
a. red blood corpuscles b. ear c. human body d. white blood corpuscles
e. lungs
5. The cold stage begins with a feeling of ... even in the hottest weather.
a. fever b. chilliness с perspiration d. vomiting e. headache
6. Where ... the disease chiefly ...?
a. does...find b. are ... found с do... find
d. have been found e. is... found
7. When ... the fever ... its height?
a. have... reached b. are ... reached c. does... reach
d. do... reach e. is... reaching
8. Having gone ... the three stages of a malarial attack patients feel recovered until the onset of the next attack.
a. for b. into c. from d. of e. through
9. Duly administrated treatment ...quinine interrupts the course of malarial attack.
a. by b. for c. of d. with e. without
10. As it is generally known preventive measures should be taken to sanitate localities, to reduce the number of mosquitoes, ...
a. to carry out the survey of the population b. to treat the patients
c. to examine the healthy carriers d. to administer duty treatment
e. to prescribe drugs
ACQUIRED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME – Синдром набутого імунодефіциту (СНІД)
Exercise 1. Active Vocabulary:
Acquired [əˈkwaıəd] отриманий
To transmit передавати
Deficiency [dıˈfıʃənsı] недостатність
Mortality смертність
Identify [aıˈdɛntı,faı] визначати
Morbidity захворюваність
Routine [ruːˈtiːn] поточний, звичайний
Sample, specimen зразок
Susceptible [səˈsɛptəbǝl] вразливий
Exposure піддавання
Available [əˈveıləbǝl] доступний
Opportunistic infections оппортунистичні (супровідні) інфекції
To contract (a disease) заразитися
Exercise 2. Form nouns from the words given below:
To identify, to effect, to transmit, to treat, to maintain, to infect, to add, to prevent, to develop, to measure, to assist, to protect, to disturb.
Exercise 3. Translate the following phrases into your native language:
Human immunodeficiency virus, susceptible to opportunistic infections, positive identification, fungi and parasites, available vaccine, bodily fluid, avoid exposure to the virus, reduce mortality and morbidity, routine access, to transmit through direct contact of a mucous membrane.
Exercise 4. Discuss the following problem:
1. What does abbreviation AIDS mean?
2. What organs does AIDS affect?
3. Why is it so widely spoken about?
4. Why is it considered to be so dangerous?
5. Why does it spread so quickly that it becomes pandemic?
6. What is the best way to prevent AIDS?
Exercise 5. Read and translate the text:
ACQUIRED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a disease of the human immune systemcaused by thehuman immunodeficiency virus(HIV).
This condition progressively reduces the effectiveness of the immune system and leaves individuals susceptible to opportunistic infections, which affect nearly everyorgan system, and differenttumorsand cancers. HIV istransmittedthrough direct contact of amucous membraneor the bloodstream with abodily fluidcontaining HIV, such asblood,semenandbreast milk. AIDS is now apandemic.
AIDS was first reported June 5, 1981. The earliest known positive identification of the HIV virus comes from the Congoin 1959 and 1960, though genetic studies indicate that it passed into the human population from chimpanzees around fifty years earlier. Chimpanzees are frequently hunted for food, especially in West-Central Africa, and scientists believe that HIV-1 was introduced into the human population through exposure to chimpanzees’ blood during hunting. Chimpanzees are identical to humans in over 98 percent of their genome (hereditary material), yet they appear to be resistant to the damaging effects of the AIDS virus on the immune system.
The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of infections caused by bacteria,viruses,fungiandparasitesthat are normally controlled by the elements of the immune system that HIV damages.
Additionally, people with AIDS often have systemic symptoms of infection like fevers,sweats(particularly at night), swollen glands, chills, weakness, andweight loss.
Many people are unaware that they are infected with HIV. HIV tests are usually performed on venous blood. Individuals whose first specimen indicates evidence of HIV infection will have a repeat test on a second blood sample to confirm the results. The window (incubation) period(the time between initial infection and the development of detectable antibodies against the infection) can vary since it can take 3–6 months toget positive result.
To be infected with HIV is to be HIV-positive, but only when the virus seriously damages the immune system, does one have AIDS. AIDS is different in every infected person. Some people die a few months after getting infected, while others live fairly normal lives for many years, even after they 'officially' have AIDS. A few HIV-positive people stay healthy for many years even without taking anti-HIV medications.
HIV testing is the first step in your personal education in determining if you are infected with the HIV. HIV tests look for antibodies to HIV. Those antibodies are proteins produced by your immune system to fight germs. Blood tests are the most common HIV test, but newer tests can detect antibodies in mouth fluid, from scrapings inside your cheek, or from your urine. Rapid HIV tests are now capable of test results within 10 to 30 minutes after a sample is taken. Between three weeks and two months after becoming infected with HIV, your immune system produces antibodies to HIV, so you should wait two months before being tested, after you think you were exposed to HIV.
There is currently no available vaccinefor HIV or cure forHIVor AIDS. The only known methods of prevention are based on avoiding exposure to the virus or an antiretroviral treatment which can just slow the course of the disease. But it also has very unpleasant side effects including diarrhea,malaise,nauseaandfatigue. Аntiretroviral treatment reduces both the mortalityand the morbidity of HIV infection, but these drugs are expensive and routine access to antiretroviralmedicationis not available in all countries.
Exercise 6. Answer the questions?
1. Explain the term AIDS?
2. What does AIDS damage or destroy?
3. How is AIDS transmitted?
4. What is the cause of AIDS?
5. Where did AIDS come from?
6. When was AIDS first reported?
7. Why are many people unaware that they are infected with HIV?
8. How is HIV identified?
9. What are the symptoms of AIDS?
10. What is the treatment of AIDS?
Exercise 7. Match English word combinations with their definitions:
|
Immune deficiency |
1. It affects patients only or chiefly when the immune system is depressed |
|
opportunistic infection |
2. protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen. |
|
antiretroviral |
3. failure of the immune system to protect the body adequately from infection |
|
HIV |
4. the time between initial infection and the development of detectable antibodies against the infection |
|
antibody |
5. a virus which reduces people's resistance to illness |
|
window period |
6. denoting drugs which inhibit the activity of retroviruses |
Exercise 8. Write synonyms to the following words:
Syndrome, deficiency, to find out, to spread, neoplasm, damage, sweat, giddiness, medicine, to involve, to decrease, to increase.
Exercise 9. Find the continuation of the sentence:
1. AIDS stands for ___________________________
2. _______________ is the cause of AIDS.
3. AIDS progressively reduces __________________
4. HIV is transmitted__________________________
5. AIDS was first reported _____________________.
6. The earliest known positive identification of the HIV virus comes from __________________.
7. The treatment of AIDS is mostly ______________.
8.__ can reduce mortality and morbidity but there is no ___ .
9.The only known methods of prevention are based on ____.
10.The symptoms of AIDS are __________________.
Exercise 10. Approve or contradict:
1. AIDS affects inner organs such as liver, spleen, stomach.
2. HIV is transmitted through respiratory tract.
3. AIDS originated in the USA in early 90s.
4. The symptoms of AIDS are fever, fatigue, nausea, sometimes vomiting.
5. Many people are unaware that they are infected with HIV because symptoms are vague.
6. The window period can vary from 2-3 years.
7. AIDS is successfully treated with antiretroviral medicine.
8. Antiretroviral treatment has unpleasant side effects including diarrhea, malaise, nausea and fatigue.
9. Patients with AIDS mostly die several months after being infected.
10. Patients no longer live normal lives after the 'official' diagnose of AIDS is made.
Exercise11. Translate the following word-combinations:
Синдром набутого імунного дефіциту, ВІЧ інфекція, смертність, оппортунистичні інфекциі, вразливий, передаватися, кровотік, слизова оболонка, антиретровирусна терапія, зразок, захворюванність, гриби, потовідділення, застуда, втомленність, нудота, уразити органи, передаватися через слизову оболонку.
Exercise 12. Translate the words in brackets into English:
1. Treatment reduces (смертність та захворюваність) of HIV infection.
2. There is currently no (доступної) vaccine or (зцілення) for HIV or AIDS.
3. HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus, it can (жити та розмножуватися) only in the human organism, that is why animals and insects can’t (передавати ВІЛ).
4. HIV progressively (знижує) the effectiveness of the immune system and leaves individuals (вразливими) to opportunistic infections, which affect nearly every organ system.
5. Treatment has (побічну дію) such as (нездужання), (нудота) and dizziness.
6. People living with HIV can take antiretroviral drugs (щоб відкласти початок) of AIDS.
7.Ryan White – the 1st teenager patient who (заразився) AIDS from blood products, as part of his (лікування від гемофілії).
Exercise 13. Translate the sentences into your native language, paying attention to the use of tenses:
1. Nowadays scientists are working furiously to produce an AIDS vaccine.
2. In future scientists will test each sample of potential vaccine in animals.
3. Many scientists thought that an effective vaccine would induce cellular immunity and would stimulate the production of neutralizing antibodies.
4. All WHO member states have already organized AIDS control.
5. Researchers have been struggling for developing of AIDS vaccine since the middle of 20th century.
6. Stool samples should be sent for testing, to help differentiate inflammatory from non-inflammatory causes of diarrhea.
7. Surprising his doctors, Ryan White, a nineteen year old, middle class teenager from Kokomo, lived five years longer than predicted but died in April 1990.
Exercise 14. Put the verbs in brackets in a correct form:
There are 4 stages of AIDS recognized. The 1st stage of infection (to last) for a few weeks and often (to accompany) by a short flu-like illness.
The 2nd stage (to last) for about 10 years and, (to be) free from major symptoms.
At this stage HIV antibodies (to detect) in the blood and a patient (to experience) moderate unexplained weight loss and recurrent respiratory tract infections.
The 3rd stage often (to characterize) by multi-system disease and infections that can occur in almost all body systems.
At this stage a patient (to suffer) from unexplained chronic diarrhea for longer than one month, persistent fever, pulmonary tuberculosis, severe bacterial infections.
At the 4th stage the immune system (to become) more and more damaged, the opportunistic diseases slowly (to progress), leading eventually to an AIDS diagnosis.
AZT (to become) the first anti-HIV drug which (to approve) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
If Ryan White (to survive) he (to become) the 1st person who was cured all over the world.
9. Ryan White (to expel) from school for being a health risk.
10. After the origin of the AIDS epidemic (to clarify), an explanation for why the epidemic arose in the mid-20th century, and not before, still (to remain) a matter of discussion.
Exercise 15. Put questions to the underlined phrases:
1. HIV progressively reduces the effectiveness of the immune system.
2. Protective immune response in this patient was caused by viral preparations.
3. Scientists are studying the molecular structure and properties of viruses.
4. Scientists have observed AIDS in an increasing number of infants.
5. Immunity against pneumonia will be developed soon by prominent scientists.
6. All efforts of scientists are focused on the development of effective anti-AIDS vaccine.
7. AIDS was rumored to be a manufactured virus genetically created to kill the black race.
8. HIV-1 and HIV-2 were introduced into the human population through exposure to Chimpanzees’ blood during hunting.
9. Incidental transmissions of chimpanzee viruses to humans may have occurred in those wild places throughout history.
10. Chimpanzees being the source of HIV-1 may be the source of its successful control.
Exercise 16. Fill in the table with necessary information:
|
Stage of AIDS |
Duration of the stage |
Symptoms |
|
1st stage |
|
|
|
2nd stage |
|
|
|
3d stage |
|
|
|
4th stage |
|
|
Exercise 17. Text for additional reading:
CASE REPORT
A 43-year-old man with AIDS, was admitted to the hospital with fever and cough. He reported 4 days of fever and malaise, followed by 2 days of cough with blood-streaked sputum. The patient also complained of watery diarrhea.
His medical history was significant for HIV-1 infection diagnosed 12 years earlier. He had been treated for Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) and Candida esophagitis [ˈkandɪdə] in 1999 and again in 2005. He suffered from hypertension, chronic renal insufficiency, and dilated cardiomyopathy. In 2006, he sustained an intraventricular hemorrhage as a result of poorly controlled hypertension. Before his presentation, the patient had not been in medical care for approximately 6 months, and he had discontinued all his antiretroviral and antihypertensive medication. He was not a smoker but drank alcohol daily. The only medication he was consistently taking was dapsone for PCP prophylaxis.
On arrival to the emergency department, the patient was febrile (temperature, 39.7°C). The physical examination revealed rales on the left with bronchial breath sounds and egophony. The results of the initial laboratory tests included an elevated white blood cell count. Results of liver function tests were normal. Chest radiographs confirmed a left lower lobe consolidation. Therapy with piperacillin/tazobactam was started for bacterial pneumonia, and the patient underwent fiberoptic bronchoscopy.
On his third hospital day, hypoxia with respiratory failure developed. The patient was intubated and transferred to the ICU. Azithromycin was added because the initial choice of antibiotics did not help. Blood and urine culture results remained negative. His sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were negative for viral and fungal pathogens. The patient’s antibiotics were narrowed to levofloxacin, and he completed a 21-day course of therapy. He was extubated on hospital day 8 and was eventually discharged home.
Exercise 18. Мокрота з домішками крові, нездужання, хронічна ниркова недостатність, кровотеча (2 синоніма), загальний аналіз крові, палата інтенсивної терапії, ущільнення у легенях, хрипи у легенях, перенести терапію антибіотиками, мокротиння з домішками крові.
Exercise 19. Answer the questions:
1. What were patient’s complains on his admission to the hospital?
2. What did previous medical histories show?
3. What did physical examination reveal?
4. What result did laboratory tests show?
5. What instrumental examinations were used and what were the results?
6. What was prescribed for hypoxia?
7. How long did the course of treatment last?
8. What were the results of the treatment?
Exercise 20. Match terms with definitions:
|
Cardiomyopathy (кардиомиопатия) |
is a pathological condition in which there is a lack of adequate oxygen supply into the body or a region of the body. |
|
Egophony (эгофония) |
is a yeast [jiːst] дрожжевые infection in the esophagus. It is mostly an opportunistic infection accompanying HIV or AIDS. |
|
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) |
"heart muscle disease" is the measurable deterioration of the function of the myocardium (the heart muscle). |
|
Candida esophagitis (Кандидоз стравохіда) |
is the disease of the lungs, being a source of opportunistic infection, it can cause a lung infection in people with a weak immune system and is caused by the yeast-like fungus. |
|
Hypoxia (гипоксия) |
is an increased resonance of voice sounds, heard when auscultating the lungs, often caused by lung consolidation. |
Exercise 21. Describe in 5 sentences: AIDS, HIV, opportunistic infections, antibody, antiretroviral treatment.
TEST
AIDS progressively __________ the effectiveness of the immune system.
a) increases b) improves c) reduces ) strengthens
2. The 1st stage of infection is accompanied by _________.
a) moderate unexplained weight loss b) flu-like symptoms
c) unexplained chronic diarrhea d) severe bacterial infections
3. HIV is transmitted through ______________________.
a) direct contact and patient’s things b) respiratory tract
c) blood, semen and breast milk d) animal’s bites
4. There are ___ stages of AIDS recognized.
a) 3 b) 2 c) 4 d) 5
5. The ____ stage leads eventually to an AIDS diagnosis.
a) 3d b) 2nd c) 4th d) 5th
6. ________ treatment reduces both the mortality and the morbidity of HIV infection.
a) antibiotic b) antibacterial c) antiretroviral d) antipyretic
7. The earliest known positive identification of the HIV virus comes from _________________.
a) the USA at the beginning of the 20th century
b) the Congo in the middle of the 20th century
c) the South Africa in 1959
d) Africa in the middle of the 20th century
8. The 2nd stage lasts for about ______________.
a) several months b) about a month c) 10 years d) 20 days
9. People with AIDS die mostly of ________________.
a) constant fever b) tuberculosis
c) opportunistic infection d) respiratory tract infections
10. Antiretroviral therapy __ the patient ____ all symptoms.
a) both cures .. and removes b) neither cures … nor removes
c) either cures …. or removes d) cures …. but doesn’t remove
11. At the 2nd stage a patient may experience moderate unexplained weight loss and ________________.
a) prolonged diarrhea b) tonsillitis, pharyngitis
c) tuberculosis d) severe bacterial infections
12. For the 1st time HIV was introduced into the human population through exposure to _________________.
a) blood transfusion b) Chimpanzees’ blood
c) mutation of anti-small-pox vaccine d) all variants are true
13. You should wait two months before being tested for HIV because __________.
a) your immune system produces antibodies to HIV
b) you start developing symptoms
c) your immune system starts destroying
d) all variants are true
14. Hypoxia is a pathological condition in which there is _______ into the body or a region of the body.
a) an increased blood supply b) a lack of adequate oxygen supply
c) a misbalance between oxygen supply and demand
d) all variants are true
15. Antibodies are proteins produced by your immune system _____________.
a) to identify germs b) to fight germs
b) to protect organism from germs d) all variants are true
16. Chimpanzees are identical to humans in over 98 percent of _________. yet they appear to be resistant to the damaging effects of the AIDS virus on the immune system.
a) their genome b) blood components c) their constitution
d) all variants are true
17. Chimpanzees appear to be _________ to the damaging effects of the AIDS virus on the immune system.
a) liable b) resistant c) protected d) all variants are true
18. People living with HIV can take antiretroviral drugs to __________.
a) cure AIDS b) to postpone irreversible death
c) to maintain antibody level d) relieve symptoms
19. Many people are unaware that they are infected with HIV because _________.
a) they don’t apply to a doctor b) the widow period is long
c) they don’t make blood tests d) all variants are true
20. An immediate blood test after contraction may not show antibodies because____.
a) widow period is long b) the disease is slowly developing in the body
c) it can take 3–6 months to get positive result d) all variants are true
TYPESOF WOUNDS – Види ран
Part I
OPEN WOUNDS – Відкриті рани
Exercise 1. Learn the following words.
|
[´tɔ:n] |
рваний |
|
[´pʌŋkt∫әd] |
колений |
|
[´blʌnt] |
тупий |
|
[´trɔ:mә] |
травма |
|
[kәn´tјu:ʒn] |
забите місце |
|
[´әʋpәn] |
відкритий |
|
[´klәʋzd] |
закритий |
|
[rɪ ´fɜ:] |
посилатись на |
|
[´dɜ:mɪs] |
дерма , власне шкіра |
|
[´ɒbʤәkt] |
предмет, річ |
|
[ɪn´sɪʒәn] |
надріз, розріз |
|
[ɪn´saizd] |
(роз-, над- )різаний |
|
[,læsә´reɪ∫n] |
розрив |
|
[´lɪnɪә] |
лінійний |
|
[´stelɪt] |
зіркоподібний |
|
[ә´breɪʒn] |
садно |
|
[greɪz] |
подряпина |
|
[,su:pә´fɪ∫әl] |
поверховий |
|
[´slaɪd] |
ковзати |
|
[´rʌf] |
грубий, шершавий |
|
[,penɪ´treɪ∫n] |
проникнення |
|
[´gʌn∫ɔt] |
постріл |
|
[´bulɪt] |
куля |
|
[prә´ʤektaɪl] |
снаряд, куля |
Exercise 2.Guess the meaning of the following words.
Hematoma, pathology, linear, epidermis, contusion, penetration, disintegrate, abrasion, trauma, chronic, medicine, puncture, typical, category, classification, object, period, collection, traumatic, process, diabetic, circulation, infection, systemic, abscess, critical, locally, sepsis, scrape, sterile solution, antiseptic, tablet, history, philosopher, theory, serious, physically.
Exercise 3. Find corresponding equivalents:
|
in (with) reference to… |
відскрібати |
|
to refer to… |
посилатися на… |
|
topmost |
рвана рана |
|
to scrape off |
з посиланням на… |
|
"through -and-through" |
різана рана |
|
incision wound |
стосовно, відносно |
|
relatively |
найвищий |
|
punctured wound |
наскрізний |
|
laceration |
колена рана |
Exercise 4. Complete the table with missing forms.
|
Nouns |
Verbs |
|
|
to injury |
|
tear |
|
|
|
to infect |
|
cause |
|
|
collection |
|
|
|
to puncture |
|
|
to incise |
|
penetration |
|
|
circulation |
|
|
|
to disrupt |
|
reference |
|
|
appliance |
|
|
support |
|
|
|
to relieve |
|
|
to measure |
|
spread |
|
|
|
to damage |
Exercise 5. Read and then translate the following word combinations into the Ukrainian language:
The dermisof the skin; a blunt force trauma; a sharp-edged object; a glass splinter; irregular tear-like wounds; blunt trauma; scrub the injury of any loose materials and tissue; apply some sort of closing technique; stitching; the application of a pressure dressing; realign the edges of the wound; speed healing; lessen scarring; superficial wounds; the topmost layer of the skin; remain intact; a sliding fall; a rough surface.
TYPES OF WOUNDS
Text I: OPEN WOUNDS
In medicine, a wound is a type of injuryin which skinis torn, cut or punctured (an open wound), or where a blunt force traumacauses a contusion(a closed wound). In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermisof the skin.
Open wounds can be classified according to the object that caused the wound. The types of open wound are:
Incisions or incised wounds, caused by a clean, sharp-edged object such as a knife, a razoror a glass splinter.
Lacerations, irregular tear-like wounds caused by some blunt trauma. Lacerations and incisions may be linear (regular) or stellate (irregular). The first step to treat this kind of wound is to stop bleeding, clean and scrub the injury of any loose materials and tissue, and then apply some sort of closing technique, whether through stitching or the application of a pressure dressing. The edges of the wound should be realigned to speed healing and lessen scarring.
Abrasions (grazes), superficial wounds in which the topmost layer of the skin(the epidermis) is scraped off, but the tissue underneath remains intact. Abrasions are often caused by a sliding fall onto a rough surface. Cleansing of the wound and removal of any foreign material is important within the first 24 hours. Treatment is usually non-surgical and consists of the application of a moist dressing to protect the new tissue that forms to heal the abrasion.
Puncture wounds, caused by an object puncturing the skin, such as a nail or needle.
Penetration wounds, caused by an object such as a knife entering and coming out from the skin.
Gunshot wounds, caused by a bulletor similar projectile driving into or through the body. There may be two wounds, one at the site of entry and one at the site of exit, generally referred to as a "through-and-through."
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions:
What are the main two types of wounds?
What does a wound mean in medicine?
What does the wound refer to in pathology?
What can open wounds be classified according to?
What are incisions caused by?
What types of open wounds do you know?
What is the treatment of lacerations?
What is a “through-and-through” wound?
Exercise 2. Translate the following word-combinations into English:
Вогнестрільна рана; рана від проникнення; колоті рани; подряпина і садно; розрив (рвана рана); розріз (різана рана); пошкодження; наскрізна рана; загоювати садно; поверхова рана; залишатися непошкодженим; найвищий шар шкіри; лінійні розрізи;зіркоподібні розрізи; перебудувати краї рани; прискорити загоєння; зменшити рубець.
Exercise 3. Put questions to the underlined words:
Open wounds can be classified according to the object that caused the wound.
Incisions or incised wounds are caused by a clean, sharp-edged object.
The first step to treat this kind of wound is to stop bleeding.
The edges of the wound should be realigned to speed healing and lessen scarring.
The topmost layer of the skinwas scraped off.
Abrasions are often caused by a sliding fall onto a rough surface.
In abrasions, the tissue underneath the epidermis remains intact.
Treatment consists of the application of a moist dressing to protect the new tissue.
Exercise 4. Open the brackets and translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
This type of wounds usually (to refer) to as through-and-through wounds.
Closed wounds (to have) fewer categories than open wounds.
In abrasions, the topmost layer of the skin (to scrape) off.
Abrasions often (to cause) by a sliding fall onto a rough surface.
A moist dressing (to apply) on his wound to protect the new tissue. (2 possible variants)
The doctors (to apply) six stitches on his wound. (2 possible variants)
First, the edges of the laceration (to clean), then realigned.(3 possible variants)
This puncture wound (to cause) by a nail.
Exercise 5. Explain the terms in 5 sentences:
Open wound; incised wound; laceration; abrasion; gunshot wound.
Part II
CLOSED WOUNDS – Закриті рани
Exercise 1. Learn the following words.
|
Contusion |
[kənˈtjuːʒən] |
забите місце |
|
bruise |
[bruːz] |
синець; ґуля |
|
harsh blow |
|
грубий (різкий) удар |
|
сrush injury |
|
роздавлена рана |
|
disrupt |
[dɪsˈrʌpt] |
розривати |
|
disintegrate |
[dɪsˈɪntɪˌgreɪt] |
розкладатися |
Exercise 2. Translate the word combinations into Ukrainian:
Sustain a harsh blow; monitor for symptoms of hematoma; a steadily growing mass; disrupt the tissue; relatively slow process; lead to tissue damage; insufficiency in the circulation; fail and disintegrate; take hold of the site; spread locally.
Exercise 3. Match the words with their definitions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Text II
CLOSED WOUNDS
Closed wounds have fewer categories, but are just as dangerous as open wounds. The types of closed wounds are:
Contusions, more commonly known as bruises, caused by a blunt force trauma that damage tissueunder the skin. When a person sustains a harsh blow, it causes tissue damage and bleeding beneath the skin, but does not tear the skin itself. Most contusions do not require medical treatment, but should be monitored for symptoms of hematoma, which is deep tissue damage. A hematoma can cause skin death over the injury and will need medical treatment. The symptoms of a hematoma are a steadily growing mass beneath the contusion and discoloration, as well as severe pain. These symptoms require immediate medical treatment.
Hematomas, also called a blood tumor, caused by damage to a blood vesselthat in turn causes bloodto collect under the skin.
Crush injury, caused by a great or extreme amount of force applied over a long period of time.
Chronic and Acute Wounds Acute or traumatic wounds are the result of injuries that disrupt the tissue. Chronic woundsare those that are caused by a relatively slow process that leads to tissue damage. Chronic wounds include pressure, venous, and diabetic ulcers. Typically, an insufficiency in the circulation or other systemic support of the tissue causes it to fail and disintegrate. Infection then takes hold of the site and hits a critical point, it can spread locally. Once the infection hits a critical point, it can spread locally or become systemic (sepsis).
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions:
What are the types of closed wounds?
What are contusions caused by?
What should contusions be monitored for?
What can a hematoma cause?
What are the symptoms of hematoma?
What are hematomas caused by?
What is a crush injury?
What do acute wounds result from?
What are chronic wounds caused by?
When can infection spread locally and become systemic?
Exercise 2. Translate the following word combinations into English:
Критична точка; недостатня циркуляція; травматичні поранення; порівняно повільний процес; збиратися під шкірою; розпадатися на складові частини; розривати тканину; забите місце; синець; пошкоджувати кров’яні судини; небезпечні рани; розповсюджуватися локально.
Exercise 3. Choose one or more words from list B to modify the verbs from list A so as to make sense. Translate the word combinations into the native language.
List A: To cause; to refer to; to damage; to be caused by; to appear; to be misused; to collect; to be applied; to scrape off; to be referred to ; to lead to; to hit; to spread.
List B: the topmost layer of the skin;a critical point; as a "through-and-through; tissue damage; over a long period of time; the dermis;locally; a clean, sharp-edged object; under the skin;in reference to incisions; a contusion;a sharp injury; linear (regular) or stellate.
Exercise 4. Find the appropriate sentence endings:
Incisions or incised wounds, caused by…
Contusions, more commonly known as …
Lacerations, irregular tear-like wounds caused by …
Abrasions (grazes), superficial wounds in which the topmost layer of the skin (the epidermis)…
Hematomas, also called a blood tumor, caused by…
Puncture wounds, caused by an object puncturing the skin, such as …
Penetration wounds, caused by an object such as a knife…
Crush injury, caused by a great or extreme amount of…
Gunshot wounds, caused by a bulletor similar projectile driving …
…is scraped off.
…into or through the body.
…entering and coming out from the skin.
…a clean, sharp-edged object such as a knife, a razoror a glass splinter.
… a nail or needle.
… force applied over a long period of time.
….damage to a blood vessel that in turn causes blood to collect under the skin.
… bruises, caused by a blunt force trauma that damage tissue under the skin.
… some blunt trauma.
Exercise 5. Give the comparative and superlative degree of the following adjectives.
Model: few – fewer – fewest; important – more important – the most important
Bright, hot, wide, easy, brave, good, active, fine, fat, bad, dirty, old, beautiful, thin, long, big, difficult, important, many, little, soon, correctly, strong, thin, thick, narrow, interesting, warm, deep, rough, great, clean, sharp.
Exercise 6. Approve or disapprove the following statements.
Injuries are far too common for some people.
At some point in most of our lives, we will receive a wound.
Whether major or minor, any injury that tears flesh is not only painful, but dangerous.
The simplest puncture can breed tetanus, and a small cut can turn septic with infection.
Knowing the basics of what types of wounds are more serious than others can help you treat them.
As mentioned above, any wound can be serious, no matter how small, if ignored.
In the case of punctures, a thorough cleansing and an update on your tetanus shot is a must.
Deep cuts, where blood is pumping with each heartbeat, need not an immediate call to 911.
Burns that are charred or where underlying tissues are exposed also need immediate medical attention.
In the case of any serious wound, seek professional medical treatment immediately.
Exercise 7. Complete the following text with the suitable words from the box; translate the text into Ukrainian:
