
Иностранный язык (Методические указания)
.pdf
МИНИСТЕРСТВО СЕЛЬСКОГО ХОЗЯЙСТВА РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ
ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
«БАШКИРСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ АГРАРНЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Кафедра иностранных языков
Б1.Б3. Иностранный язык (английский)
Методические указания для самостоятельной работы
бакалавров заочного обучения
по направлению 140100 Теплотехника и теплоэнергетика профиль Энергообеспечение предприятий
УФА – 2012
УДК 811 ББК 81.2 Англ
М 54
Рекомендовано к изданию методической комиссией энергетического факультета Башкирского ГАУ, протокол № от ноября 2012 года
Составитель: к.с.н., доцент кафедры иностранных языков Р.М. Нутфулина
Рецензент: к.с.н., доцент кафедры иностранных языков Р.Ф. Азметова
Ответственный за выпуск: заведующий кафедрой иностранных языков, к.ф.н., доцент О.Н. Новикова
От автора
Цель сборника – обучение бакалавров направления «Теплотехника и теплоэнергетика» развитию навыков самостоятельной и аудиторной работы над литературой по данному направлению, умению понимать и переводить научно-технические тексты, что соответствует требованиям программы по английскому языку и рассчитано на бакалавров, имеющих начальную языковую подготовку.
Все тексты подверглись адаптации и сокращению. Задания способствуют усвоению и закреплению лексики и дальнейшему развитию понимания текстов на английском языке.
Помощь при переводе текстов может оказать терминологический словарь, включенный в сборник.
2
|
Contents |
|
1 |
Atom is a source of energy |
4 |
2 |
Energy and its forms |
4 |
3 |
Law of conservation and transformation of energy |
5 |
4 |
Heat is a form of energy |
6 |
5 |
Sources of energy |
7 |
6 |
Electric energy |
8 |
7 |
Nuclear energy |
9 |
8 |
Solar energy |
9 |
9 |
Electricity |
10 |
10 |
Magnets and electricity |
10 |
11 |
Batteries produce electricity |
11 |
12 |
Direct current and alternating current |
12 |
13 |
Conductors |
13 |
14 |
Insulators |
14 |
15 |
Transmission of electric power |
15 |
16 |
Electric lines and their efficiency |
16 |
17 |
How electricity is generated |
17 |
18 |
Electric motors |
18 |
English – Russian vocabulary |
20 |
|
3
1Atom is a source of energy
The first source of energy which man made serve him was the energy of fire. Many thousand years passed before man learned how to use another source of energy — water. Then man made steam serve him; and then man had another servant — electricity. At that time it was impossible to imagine anything more perfect than electricity. But man would not and did not stop at electricity; he discovered another source of energy, many times more powerful — the atomic energy. We may be sure that discovery of atomic energy is just an episode in the history of human progress. But our age is the age of atomic nuclei which is to transform the world.
(520)
1. 1 Read the following international words: energy, atomic energy, human progress, electricity, material, nature, basic, culture, physics, practical, machine, operate, information, construct, mechanical.
2 Energy and its forms
1. Energy is the capacity for doing work. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: kinetic and potential. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is that of position. The kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses because of its speed. Any moving object performs work simply because it is moving. The quantity of energy depends on its mass and velocity. We know that the greater the mass and the velocity, the greater is the kinetic energy.
(420)
2. Kinetic energy is motion–of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances, and objects.
Electrical energy is the movement of electrical charges. Everything is made of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are made of even smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons. Electrical charges moving through a wire is called electricity. Lightning is another example of electrical energy.
Radiant energy is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio
4
waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Solar energy is an example of radiant energy.
Thermal energy, or heat, is the internal energy in substances––the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within substances. Geothermal energy is an example of thermal energy.
Motion energy is the movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Objects and substances move when a force is applied according to Newton’s Laws of Motion. Wind is an example of motion energy.
(870)
3. Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position –– gravitational energy. There are several forms of potential energy.
Chemical energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is the energy that holds these particles together. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are examples of stored chemical energy.
Stored mechanical energy is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands are examples of stored mechanical energy.
Nuclear energy is energy stored in the nucleus of an atom––the energy that holds the nucleus together. The energy can be released when the nuclei are combined or split apart. Hydropower, such as water in a reservoir behind a dam, is an example of gravitational potential energy.
(660)
2.1Answer the following questions
1.What do we call energy?
2.When does a body possess energy?
3.What forms of energy do you know?
4.What do we call kinetic energy?
5.What do we call potential energy?
3 Law of conservation and transformation of energy
We know a number of cases where one kind of energy is transformed into another. Whenever energy in one form is expended, an equal amount of energy in some other form takes its place.
5

We have different units in which various forms of energy are measured but after the conversion of work into heat, or chemical energy into work or into electrical energy, the amount of energy is the same as before the change. In other words, when energy is spent, there is still as much energy as before. This fact which is one of the fundamentals of physics is known as the Law of the Conservation and Transformation of Energy.
According to this law energy can neither be created, nor destroyed although its form can be changed. All the transformations, the endless number of chemical changes that are always taking place, are only changing energy from one form into another without affecting the total.
We often use machines to transfer energy from one place to another and to transform energy. The dynamo, for example, changes mechanical energy into electric energy. The energy of water is also transformed into electric energy by means of hydraulic turbines.
(950)
3.1 Answer the following questions
1.Can energy be created and destroyed?
2.What machine changes mechanical energy into electric energy?
3.When is mechanical energy converted into heat?
4.Can chemical energy be converted into heat?
4 Heat is a form of energy
Heat is a form of energy. There are three different types of heat transmission, namely: conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction. Heat may be transferred from a hotter body to a colder one by direct contact. Fast-moving molecules tend to speed up their slower neighbours on collision. We know that this method of heat transfer is called conduction.
We know that some materials are good conductors of heat and others are poor conductors. Generally speaking, metals are excellent conductors, the best conductors of electricity being also the best conductors of heat.
6

Thus, aluminium known as a good electrical conductor is likewise a good conductor of heat. On the other hand, materials like sand, asbestos, and still air are poor conductors of heat.
Convection. In gases and liquids another process of heat transfer is very effective, namely, convection. Convection is the transfer of heat by the motion of the hot body itself carrying its heat with it. A current of liquid or gas that absorbs heat at one place and then moves to
another place where it mixes with a cooler portion of the fluid and loses heat is called a convection current. Сonvection occurs only in liquids and gases.
Radiation. There is a third way by which heat travels, namely, radiation. We know the temperature of the sun is very high. We also know that, when the sun shines on the earth, the earth is warmed. The passage of heat from the sun to the earth happens by radiation. An important characteristic of radiation is that it can occur in a vacuum; it does not depend upon the presence of a substance. In addition to that, the space between the source of heat and the body to receive the heat does not rise in temperature.
(1420)
4.1Answer the following questions
1.What types of heat transmission do you know?
2.What do you call conduction?
3.What is convection?
4.What good conductors of heat do you know?
5.What is radiation?
5 Sources of energy
We use many different energy sources to do work for us. Energy sources are classified into two groups — renewable and nonrenewable. Renewable and nonrenewable energy can be converted into secondary energy sources like electricity and hydrogen.
In some countries most of our energy comes from nonrenewable energy sources. Coal, petroleum, natural gas, propane, and uranium are nonrenewable energy sources. They are used to make electricity, to heat our homes, to move our cars, and to manufacture all kinds of products.
7
These energy sources are called nonrenewable because their supplies are limited. Petroleum, for example, was formed millions of years ago. We can’t make more petroleum in a short time.
Renewable energy sources include biomass, geothermal energy, hydropower, solar energy, and wind energy. They are called renewable energy sources because they are replenished in a short time. Day after day, the sun shines, the wind blows, and the rivers flow. We use renewable energy sources mainly to make electricity.
(870)
5.1 Answer the following questions
1.What are renewable energy sources?
2.What are nonrenewable energy sources?
3.What is the difference between them?
6 Electric energy
Electric power is generated by converting heat, light, chemical energy, or mechanical energy to electrical energy. Most electrical energy is produced in large power stations by the conversion of mechanical energy or heat. The mechanical energy of falling water is used to drive turbine generators in hydroelectric stations. The heat derived by burning coal, oil, or other fossil fuels is used to operate steam turbines or internalcombustion engines that drive electric generators. Also the heat from fissioning of uranium or plutonium is used to generate steam for the turbine generator in a nuclear power plant.
Electricity is clean, inexpensive, and easily transmitted over long distances. It is used to operate lights, pumps, elevators, power tools, furnaces, refrigerators, air-conditioners, radios, television-sets, industrial machinery, and many other kinds of equipment. It has been counted that in developed countries about 43% of the electric power is generally used for industrial purposes, 32% in homes, and 21% in commercial enterprises.
(900)
6.1 Answer the following questions
1.How is electric power generated?
2.How is electrical energy produced in power stations?
3.What is electricity used for?
8

7 Nuclear energy
All the sources of energy put together is the energy locked up in the nuclei of atoms of matter itself. It is called nuclear energy.
The amount of energy which is released when the nucleus of one atom is split is very small. But scientists succeded in breaking apart the nuclei of billions of atoms and in harnessing their energy. Mankind is interested in atomic energy used only for peaceful purposes.
Many atomic power plants for producing electric energy were built in many countries of the world. There are great possibilities of using nuclear energy for transport purposes. A number of countries are working at the development and construction of various kinds of locomotives, airplanes and other means of transport. Many atomic powered ships have been already built. Nuclear energy is and will be used in medicine and in many spheres of life where the atom may find useful application.
(750)
7.1 Answer the following questions
1.What is nuclear energy?
2.Why is mankind interested in nuclear energy?
3.Where is nuclear energy used?
8 Solar energy
Solar energy is energy directly from the Sun. This energy drives the climate and weather and supports virtually all life on Earth. Heat and light from the sun account for most of the available flow of renewable energy.
Solar energy technologies harness the sun’s energy for practical ends. These technologies began from the time of the early Greeks, Native Americans and Chinese warmed their buildings by orienting them toward the sun. Modern solar technologies provide heating, lighting, electricity and even flight.
Solar power is used synonymously with solar energy or more specifically to refer to the conversion of sunlight into electricity. This can be done either through the photovoltaic effect or by heating a transfer fluid to produce steam to run a generator.
Solar photovoltaics provide 0.04% of the world’s energy usage.
(700)
9
8.1 Read the following international words: modern, energy, practical, technology, electricity, specifically, transfer, generator.
9 Electricity
The electric charge is also called electricity. We can generate electricity to illuminate our cities or we can store it in a battery to transport it. Electricity is a flow of electrons through a conductor. Copper is a good conductor so we use it in electric wires.
A simple electric circuit includes a battery with chemical paste, a carbon rod, a wire and a light bulb. The chemical paste contains an excess of electrons so when you connect the two poles of the battery, the copper wire attracts electrons. The electrons in the chemical paste repel the electrons in the carbon rod and make them flow through the соpper wire. When they arrive at the filament inside the bulb, they produce heat and emit light. That is we say that light is a photoelectric effect.
(630)
9.1 Answer the following questions
1.What is electricity?
2.Where and why do we use copper?
3.What does simple electric circuit include?
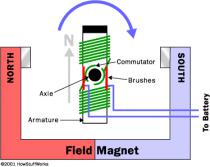
10 Magnets and electricity
10
