
- •Unit 1. Viewing the output
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •IX. What do the following abbreviations stand for? (Appendix a)
- •V. Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •Unit 3. Devices for the disabled
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •IX. What do the following abbreviations stand for?
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •IX. Here are the answers, make out the questions.
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •IX. What do the following abbreviations stand for?
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •IX. What do the following abbreviations stand for?
- •V. Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •VI. Which words in the text have the same meaning as?
- •VII. What do the following numbers in the text refer to?
- •VIII. Match each term with its proper definition.
- •IX. What do the following abbreviations stand for?
- •IV. Answer the following questions.
- •V. Agree or disagree with the following statements.
- •VI. Find in the text the English equivalents to the following Ukrainian word-combinations.
- •VII. Which words in the text have the same meaning as?
- •VIII. Here are the answers, make out the questions.
- •IX. Choose the correct form of the verb or the correct preposition.
Unit 1. Viewing the output
I. Practise reading the following words.
video, adaptor, feature, capture, monochrome, mode, cathode, graphics, viewing, multimedia, advantage, liquid, matrix, row, substrate, transistor, advances, tube, electron, continuous, sequence, perceive, fatigue, primary, phosphors, emit, analog, plasma, diode, layer, polymer, achieve, require, consumption, viewable.
II. Before reading the text try to answer these questions.
1. What is a video graphics adaptor?
2. What types of video displays do you know?
3. What new technologies are used for displaying the output?
III. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
Viewing the output
The screen of a computer is often known as the monitor, or VDU (visual display unit). Inside the computer, there is a video card, also known as a video graphics adaptor (VGA). It is an expansion card which main function is to process images and send signals to the monitor. Some video cards offer additional features, such as video capture, TV tuner adaptor, FireWire, TV output and the ability to connect multiple monitors. The first PC video card, monochrome display adaptor, was developed by IBM in 1981 and could work in a text mode representing 25x80 lines on the screen. It had 4 KB video memory and just one colour. Video graphics adaptor was widely adopted and made some corporations, such as ATI and Intel, work with these video cards improving their resolution and the number of colours. Later, when the SVGA (Super VGA) standard was adopted, video cards reached 2 MB of video memory and resolution of 1024x768 at 256 colour mode. Since 2002, the video card market has been dominated by the competition between ATI and Nvidia, with their Radeon and GeForce lines respectively (see figure 1). Speaking about the output, we should notice different types of monitors.
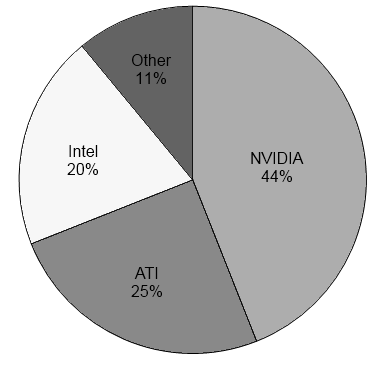
Figure 1. Manufacturers of video cards
The most common type of computer output is video displays, with the most widespread types being LCD, Plasma and OLED. But 10 years ago the most popular technology was the cathode ray tube monitor. This monitor is very similar to that of a TV set. Inside the tube there is an electron beam which scans the screen and turns on or off the pixels that make up the image. The beam begins in the top left corner and scans the screen from left to right in a continuous sequence. If the rate of this repetition is low, we can perceive a flickering, unsteady screen, which can cause eye fatigue. There are three electron guns at the back of the monitor’s tube. Each electron gun shoots out a beam of electrons; there is one beam for each of the three primary colours. CRTs are cheap, but they are heavy and can emit radiation.
Liquid crystal display was invented by John L. Janning at NCR in 1968. Later, in 1972, the first active-matrix LCD was produced in the United States by Peter Brody. Liquid crystal displays are used in wrist watches, calculators, mobile phones and computer monitors. LCD is made from flat plates with a liquid crystal solution between them. The crystals block the light in different quantities to create the image. This is similar to the way CRT and Plasma use different phosphors to create a colour. The number of colours that can be made by mixing red, green and blue sub-pixels depends on the number of distinct grey scales that can be achieved by the display. Active-matrix LCDs use TFT technology, in which each pixel has its own transistor switch. They offer better quality and take up less space, so they are replacing CRTs.
LCDs have larger effective viewable area than CRTs. Also, they produce a high quality image and do not emit harmful electromagnetic waves. LCD monitors are less expensive than CRTs because they have lower power consumption. Also, LCD monitors offer a pivoting feature that enables the unit to swivel 90° and provides a choice between the traditional landscape horizontal mode for web surfing and the portrait vertical mode for word processing and page-layout programs. To connect the liquid crystal display to the computer, you can use a traditional analog VGA, DVI and HDMI digital connectors (see fig.2).
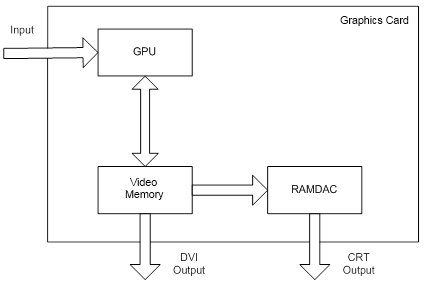
Figure 2. Digital connectors
Plasma, or plasma display panel (PDP), the latest technology used for large displays has a long history. It was invented for the PLATO Computer System at the University of Illinois by Donald Bitzer and Robert Willson in 1964. IBM developed a monochrome plasma screen that displayed orange text and graphics on a black background in the late 1980s. Modern plasma displays are RGB devices capable of displaying 32-bit colours. Plasma screens produce an image by using electrically charged gas (plasma) to illuminate triads of red, green and blue phosphors. The display electrodes create a grid that enables each sub-pixel to be individually addressed. Plasma display technology has a lot of advantages: large and very thin screen, a very sharp image and wide viewing angle.
Organic light emitting diode (OLED) monitor is a new type of displays (its electroluminescent layer is composed of organic origin film). This layer contains a polymer substance that allows suitable organic compounds to be deposited in rows and columns onto a flat carrier by a simple «printing» process. As a result, matrix of pixels can emit light of different colours. The first diode device was invented at Eastman Kodak by Dr. Ching Tang and Steven Van Slyke in the 1980s. Organic light emitting diode technology is used in TV screens, computer monitors, cell phones, PDAs and watches. OLEDs have significant advantages over traditional LCDs: they do not require a backlight to work (they can display deep black levels), they are thinner and lighter and achieve much higher contrast rate (using cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlights). Also, these displays have a faster response time (0.01 ms) than standard liquid crystal display screens (2 ms). Printing OLEDs onto flexible substrates is a starting point for new applications, such as roll-up displays and displays embedded in clothes.
