
- •Министерство образования и науки Российской Федерации
- •About myself and my study
- •Vocabulary:
- •Building materials
- •Vocabulary:
- •Shear wall and frame systems
- •Vocabulary:
- •Boulton house, cambridge, england
- •Vocabulary:
- •Assembly of elements at floor above ground level
- •Vertical section through typical upper floor
- •Saint petersburg
- •Vocabulary:
- •Urban design
- •Vocabulary:
- •Eco-architecture
- •Vocabulary:
- •Computer systems
- •Vocabulary:
- •The wide world web
- •Vocabulary:
- •Computer software and hardware
- •Vocabulary:
- •Internal combustion engine
- •Vocabulary:
- •Automobile safety
- •Vocabulary:
- •Hybrid cars
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Excavators
- •Vocabulary:
- •Power installations of construction machinery
- •Vocabulary:
- •Price elasticity of demand and supply
- •Vocabulary:
- •Fiscal policy
- •Vocabulary:
- •Foreign trade
- •Vocabulary:
- •Heat exchangers
- •Vocabulary:
- •Boilers
- •Vocabulary:
- •Air conditioning
- •Vocabulary:
- •Оглавление
- •Английский язык
Vocabulary:
alternate – ['²lt´neIt] v.– поочередно сменяться
baffle ['bxfql] n.– перегородка
due to [ÌÓ³'t³] prep.– благодаря/вследствие
engine ['enGIn] n. – двигательная установка
extremely [ÁÐ'sËÏ°ÅÎI] adv. – крайне/чрезвычайно
fluid ['ÇγÁÌ] n.– текучая среда
heat exchanger [hJt Iks'CeIGq] – теплообменник;
heat transfer area [h°t "trxnsfq 'eqrIq] – поверхность теплообмена/теплопередачи
heat transfer efficiency [h°t"trxnsfq Á'ÇÁS¶ÍÉÁ] – коэффициент теплопередачи
leak tight seal ["l°k ËÕÁË 's°l] – непроницаемая перемычка/прокладка
low pressure application [lqu "pÏÂS¶ "xplI'keISn] – установка, работающая под низким давлением
plate type heat exchanger ["pleIt taIp "h°t Iks'CeIGq] – пластинчатый теплообменник
press-fitted tube [pres"fItId 'ËjV:Ä] – запрессованная труба
shell and tube heat exchanger [Sel qnd "tj³b h°t Iks'CeIGq] – кожухотрубный теплообменник
shell side fluid ['Sel said "fl³Id] – межтрубная текучая среда
tube side fluid ['tj³b said "fl³Id] – внутритрубная текучая среда
Answer the following questions:
What two main types of constructions are mentioned in the text?
What does shell and tube heat exchanger consist of?
What does plate type heat exchanger consist of?
What is the advantage of plate type heat exchanger?
Why is plate type heat exchanger capable of transferring much more heat?
Why is plate type heat exchanger used in small, low pressure applications only?
What type of heat exchanger is becoming more common?
ТЭ, ЭЭ, ТСБ, ПВ (III семестр)
Boilers
Boilers can be classified in various ways, depending on firing method used, fuel fired, field of application, type of water circulation employed, and pressure of steam. Depending on their construction boilers can be divided into: fire tube boilers (Figure 3.), water tube boilers (Figure 4.).
Fire tube boilers have been used in various early forms to produce steam for industrial purposes. The fire tube boiler is a special form of the shell tube type boiler. A shell type boiler is a closed, usually cylindrical vessel that contains water. Hot gases pass through the tubes during the heat transfer process. The shell boiler evolved into modern forms such as the electric boiler, in which heat is supplied by electrodes embedded in the water.
Figure 3. Fire tube boilers.
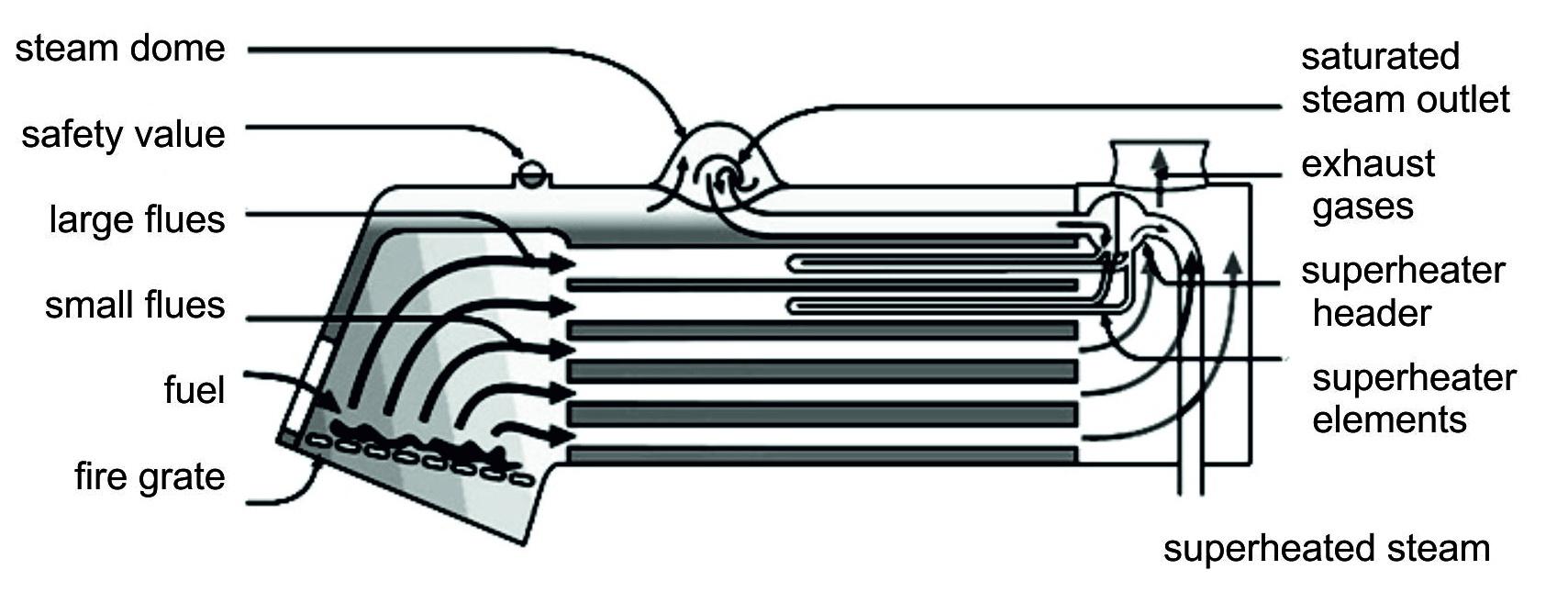
The difference between fire tubes and water tubes is simple; water flows through water tubes instead of fire. The advantage of the water tube boiler is that it can work in high steam pressure and capacities. With higher steam pressure and capacities, fire tube boilers would need large diameter of shell. With such large diameter, the shell would have to operate under such extreme pressure and thermal stresses that their thickness would have been too large.
Figure 4. Water tube boilers.
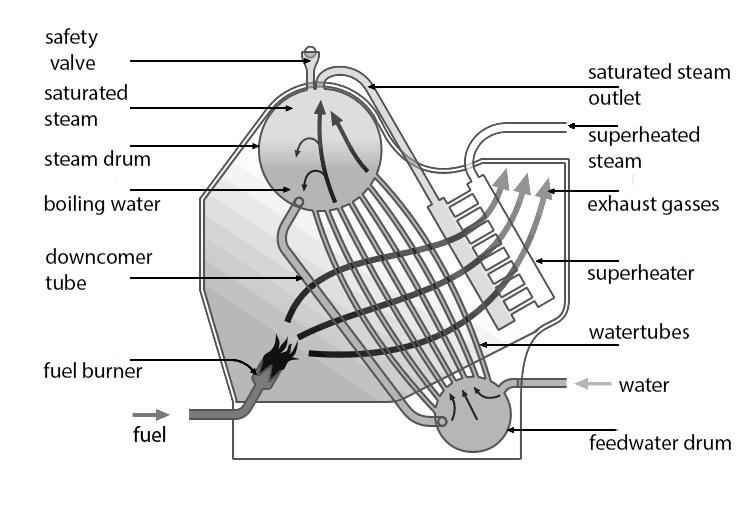
The basic purpose of any boiler is to convert the chemical energy in fuel into thermal energy that can be used to generate steam or hot water. Inside the combustion chamber, two fundamental processes must occur to achieve this objective. First, the fuel must be mixed with sufficient oxygen to allow sustained combustion. The heated gases produced by the combustion process must then transfer the thermal energy to a fluid such as water or steam. The design of the boilers depends on factors such as the type of fuel and the method selected to transfer thermal energy. Boilers are manufactured in a wide range of sizes to burn coal, oil, natural gas, biomass as well as other fuels and fuel combinations.
