
- •NEONATAL DERMATOSIS
- •OUTLINE
- •SKIN FUNCTION IN THE NEONATE
- •ECCRINE SWEATING
- •SEBACEOUS GLAND SECRETION
- •PREVELANCE OF NEONATAL DERMATOSIS
- ••Cutaneous manifestations were observed in 90.5% of the newborns.
- ••With respect to mode of delivery, Vaginally delivered neonates showed significant association with
- •TRANSIENT PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES
- •VERNIX CASEOSA
- ••Golden yellow staining - Haemolytic disease of the newborn and postmaturity.
- •FUNCTIONS
- •PERIPHERAL CYANOSIS/ ACROCYANOSIS
- ••The cyanotic hue disappears on warming the extremities.
- •HARLEQUIN COLOUR CHANGE
- ••Wide variation in the duration of attacks, but generally between 30 seconds- 20
- ••As skin matures, this vascular phenomena disappears.
- •CUTIS MARMORATA
- •MONGOLIAN SPOT
- ••Cause-arrested embryonal migration of melanocytes from neural crest to epidermis resulting in dermal
- ••Lesions also occur on the buttocks, dorsal trunk and extremities.
- •SEBACEOUS GLAND HYPERPLASIA
- •SEBACEOUS GLAND HYPERPLASIA
- •MILIA
- •MILIA
- •PALATE-EPSTEIN’S PEARL
- •DESQUAMATION (PHYSIOLOGICAL SCALING OF
- •MACULAR HEMANGIOMA
- •MINIATURE PUBERTY
- ••Scrotal hyperpigmentation and labial hypertrophy-most common findings in miniature puberty .
- ••Enlargement of breast tissue with thick milk-like secretion (witch’s milk) may be seen.
- •SUCKING BLISTERS
- •NEONATAL OCCIPITAL ALOPECIA
- ••The roots in the occipital area do not enter telogen until term, therefore
- •NEONATAL ACNE/ NEONATAL CEPHALIC
- •No additional treatment is needed -usually resolves spontaneously within four months without scarring.
- •LANUGO
- •ANETODERMA OF PREMATURITY
- ••It is non progressive and persistent.
- •SKIN DISORDERS IN THE NEONATE
- •ERYTHEMA TOXICUM NEONATORUM
- ••Commonly seen-term infants, rare in preterm and low birth weight infants.
- ••Could be an innate immune response of a newborn infant to commensal microbes
- •Diagnosis :
- •TRANSIENT NEONATAL PUSTULAR MELANOSIS
- ••It is transient, benign, self-limiting dermatoses of unknown aetiology characterised by 3 types
- •One hour after birth, flaccid vesiculopustules and superficial erosions with minimal surrounding erythema
- •MILIARIA
- ••Miliaria rubra and miliaria crystallina-common in neonates.
- •MILIARIA CRYSTALLINA
- ••Delicate and generally rupture within 24 hr, and are followed by bran-like desquamation.
- •MILIARIA RUBRA (‘PRICKLY HEAT’)
- ••Lesions occur in -flexural areas, especially around the neck and in the groins
- ••Frequently, some lesions are pustular (miliaria pustulosa), but this does not necessarily indicate
- •Management
- •DIAPER DERMATITIS (NAPKIN DERMATITIS OR
- •Three common types of diaper dermatitis are are -
- •Treatment :
- •APLASIA CUTIS CONGENITA
- ••Aplasia cutis congenita may be associated with under lying embryologic malformations like
- •BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
- ••Common skin problems seen in neonates in India.
- •IMPETIGO
- ••Varnish coloured crust is seen.
- •When bullae spread, rupture, and involve large areas, infection may spread systemically, causing
- •DIAGNOSIS :
- •STAPHYLOCOCCAL SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME(SSSS)
- ••The site of blister cleavage is the granular layer.
- ••The first sign of the disease - faint, macular, orange red, scarlatiniform eruption
- •TREATMENT :
- •OMPHALITIS
- •ECTHYMA GANGRENOSUM
- ••Predisposing factors- prematurity, renal failure, neutropenia and immunodeficiencies, necrotizing enterocolitis and bowel surgery.
- •VIRAL INFECTIONS
- •NEONATAL HERPES SIMPLEX
- ••The skin lesions appear between days 2 and 20.
- ••During an intrauterine infection, vesicles appear within 1 day of life.
- •Neonatal herpes simplex showing congenital ulceration and scarring at 10 days.
- •DIAGNOSIS
- •FETAL VARICELLA SYNDROME
- •Pregnant women who are not immune (on the basis of history, and, preferably,
- •FUNGAL INFECTIONS
- •NEONATAL CANDIDIASIS
- ••White, “flaky,” creamy patches are seen on the tongue and mucous membranes of
- ••In the surrounding normal skin there may be punctate erythematous lesions, sometimes pustular
- •CONGENITAL CANDIDIASIS
- ••Palmar and plantar pustules are regarded as a hallmark of congenital cutaneous candidiasis
- •Congenital candidiasis in a neonate born at 24 weeks’ gestation. Note the “burn-like”
- •DISORDERS CAUSED BY TRANSPLACENTAL
- •NEONATAL PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
- ••No treatment is required as the lesions have resolved spontaneously within about 3
- •NEONATAL LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
- ••It occurs in neonates up to 3 months old.
- ••A ‘spectacle like’ distribution of lesions around the eyes is especially characteristic.
- •Pathology
- ••Infants generally show little sign of residual disease after the age of 1
- •GENODERMATOSIS
- •SOURCE-IADVL
- •MISCELLANEOUS DISORDERS
- •COLLODION BABY
- ••Almost 90% of collodion babies will go on to develop a severe form
- ••Within hours, this membrane
- •MANAGEMENT
- •REFERENCES

CONGENITAL CANDIDIASIS
•This infection occurs in utero as a result of ascending infection from the genital tract of the mother causing chorioamnionitis.
•Born with a maculopapular rash often presenting within the first 12 hours.
•The lesions develop into vesicles, pustules, or bullae in 1–3 days.
94

•Palmar and plantar pustules are regarded as a hallmark of congenital cutaneous candidiasis
•Oral involvement is usually absent.
Treatment :
•Any topical anticandidal agent, e.g. nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole, or econazole, may be used.
•In case of systemic involvement, systemic antifungal agents, e.g. amphotericin, 5-flucytosine, and fluconazole, may have to be used.
95

Congenital candidiasis in a neonate born at 24 weeks’ gestation. Note the “burn-like” erosions and desquamation.
96

DISORDERS CAUSED BY TRANSPLACENTAL
TRANSFER/ MATERNAL MILK
•These include pempemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus foliaceus, herpes gestationis and lupus erythematosus.
•Because immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgM and IgE antibodies do not cross the placenta in significant amounts, this phenomenon is restricted to diseases caused by autoantibodies of IgG class.
97

NEONATAL PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
•Neonatal pemphigus vulgaris is caused due to transplacental transmission of anti Dsg antibodies to neonates from to mothers who suffered from pemphigus during pregnancy.
•Affected infants have cutaneous and/or mucosal erosions or bullae.
98
•No treatment is required as the lesions have resolved spontaneously within about 3 weeks, and circulating IgG antibodies have become undetectable by the end of the 2nd month of life.
99

NEONATAL LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
•Neonatal lupus erythematosus (NLE) is a rare syndrome comprising transient skin lesions resembling subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (LE) and/or congenital heart block .
•Associated with the transplacental passage of maternal autoantibodies to the ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) Ro SSA (>90%), La SSB or rarely U 1 RNP.
100

•It occurs in neonates up to 3 months old.
•The risk of connective tissue disease later in life is increased.
•Skin lesions - well defined areas of macular erythema, frequently annular, occurring predominantly on the face, particularly the forehead, temples and upper cheeks, and on the scalp and neck .
101
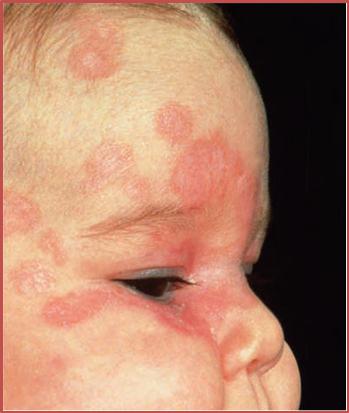
•A ‘spectacle like’ distribution of lesions around the eyes is especially characteristic.
•A degree of atrophy and/or telangiectasia are frequent long term sequelae.
•Sunlight may induce skin lesions.
102

Pathology
•Skin biopsy demonstrate the features of LE: epidermal atrophy, liquefaction degeneration of basal keratinocytes, colloid bodies and a perivascular and periappendageal lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis.
•DIF(50%) - showing dermal-epidermal junction and perivascular deposition of IgG, IgM and C3.
103
