Lens diffraction & photography
Diffraction is an optical effect which can limit the total resolution of your photography — no matter how many megapixels your camera may have. Ordinarily light travels in straight lines through uniform air, however it begins to disperse or "diffract" when squeezed through a small hole (such as your camera's aperture). This effect is normally negligible, since smaller apertures often improve sharpness by minimizing lens aberrations. However, for sufficiently small apertures this strategy becomes counterproductive — at which point your camera optics are said to have become diffraction limited. Knowing this limit can help you to avoid any subsequent softening, and the unnecessarily long exposure time or high ISO speed required for such a small aperture.
Background
Parallel light rays which pass through a small aperture begin to diverge and interfere with one another. This becomes more significant as the size of the aperture decreases relative to the wavelength of light passing through, but occurs to some extent for any size of aperture or concentrated light source.
|
|
|
Large Aperture |
Small Aperture |
Since the divergent rays now travel different distances, some move out of phase and begin to interfere with each other — adding in some places and partially or completely canceling out in others. This interference produces a diffraction pattern with peak light intensities where the amplitude of the light waves add, and less light where they cancel out. If one were to measure the intensity of light reaching each position on a line, the data would appear as bands similar to those shown below.
![]()
![]()
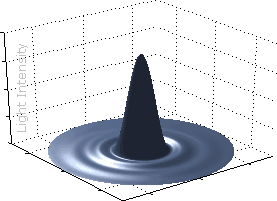
For an ideal circular aperture, the 2-D diffraction pattern is called an "airy disk," after its discoverer George Airy. The width of the airy disk is used to define the theoretical maximum resolution for an optical system (defined as the diameter of the first dark circle).
Airy Disk |
3-D Visualization |
|
|
|
Spatial Position |
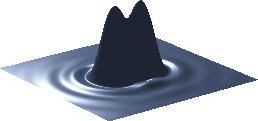
When the diameter of the airy disk's central peak becomes large relative to the pixel size in the camera (or maximum tolerable circle of confusion), it begins to have a visual impact on the image. Alternatively, if two airy disks become any closer than half their width they are also no longer resolvable (Rayleigh criterion).
|
|
Barely Resolved |
No Longer Resolved |
Diffraction thus sets a fundamental resolution limit that is independent of the number of megapixels, or the size of the film format. It depends only on the aperture's f-stop (or f-number) setting on your lens, and on the wavelength of light being imaged. One can think of it as the smallest theoretical "pixel" of detail in photography. Even if two peaks can still be resolved, small apertures can also decrease small-scale contrast significantly due to partial overlap, the secondary ring and other ripples around the central disk (see example photo).