
zhurova_t_v_angliiskii_yazyk_dlya_studentovgeologov (1)
.pdfФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ УХТИНСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ
Т.В. Журова
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК ДЛЯ СТУДЕНТОВ-ГЕОЛОГОВ
Учебное пособие
Ухта 2009
2
УДК 802.0 (075) Ж 92
Журова, Т.В. Английский язык для студентов-геологов [Текст]: учеб. пособие/ Т.В. Журова. – Ухта: УГТУ, 2009. – 107 с.
ISBN 978-5-88179-538-2
Учебное пособие предназначено для работы со студентами геологического факультета на этапе бакалавриата и магистратуры.
Пособие состоит из введения и двух частей.
Введение содержит тексты и задания, которые раскрывают ключевые понятия профессии геолога.
Первая часть пособия включает в себя восемь разделов, которые содержат тексты профессиональной направленности, подкрепленные яркими иллюстрациями, и серию упражнений, нацеленных на освоение лексического и грамматического материала.
Вторая часть пособия содержит тексты для дополнительной внеаудиторной работы к разделам I - YIII. Тексты, отобранные автором научны, содержат интересный, познавательный материал профессиональной направленности.
Данное учебное пособие соответствует программе и отвечает современным требованиям обучения студентов неязыковых вузов.
Рекомендовано к изданию Редакционно-издательским советом Ухтинского государственного технического университета.
Рецензенты:
Вороговская Р.П. - зав. кафедрой иностранных языков Института управления, информации и бизнеса;
Ломайкина И.С. - ст. преподаватель кафедры ДОУ и ПЛ Коми Республиканской Академии государственной службы и Управления при главе РК
©Ухтинский государственный технический университет, 2009 ©Журова Т. В., 2009
ISBN 978-5-88179-538-2
3
Contents
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Introduction………………………………………………………………… 4
Part I
Unit I…………………………………………………………………………..…….7
Грамматика: Времена группы Simple, Continuous, Perfect (Active, Passive).
Текст “Earth”.
Unit II………………………………………………………………………………16
Грамматика: Conditional sentences I, II, III types.
Текст “Age of the Earth”.
Unit III……………………………………………………………………………..25
Грамматика: The Infinitive
Текст“Rocks and Their Classification”.
Unit IV……………………………………………………………………………..33
Грамматика: The Complex Subject, The Complex Object with the Infinitive
Текст “Igneous Rocks”
Unit V………………………………………………………………………………42
Грамматика: The Participle.
Текст “Sedimentary Rocks”.
Unit VI…………………………………………………………….……………….50
Грамматика: The Absolute Participial Construction
Текст “Metamorphic Rocks”.
Unit VII…………………………………………………………….………………58
Грамматика: Modal verbs and their equivalents
Текст “Rock Weathering”.
Unit VIII…………………………………………………………….……………..65
Грамматика: The Gerund
Текст “Petroleum”.
Part II
Professional translation
Geology and its subdiciplines………………………………………….…………...71 History of Geology…………………………………………………………………78 Petrology……………………………………………………………………………80 Earth science………………………………………………………………………..89 Erosion……………………………………………………………………………...93 Weathering………………………………………………………………………….96 Oil and gas geology………………………………………………………………..100 Bibliography……………………………………………………………………….106
4
Introduction
Read the text, trying to get the main idea.
What is Geology?
Definition of Geology:
Geology is the study of the Earth, the materials of which it is made, the structure of those materials, and the processes acting upon them. It includes the study of the organisms which inhabit our planet. A very important part of geology is the study of how Earth’s materials, structures, processes and organisms have changed over time.
Geology is commonly divided into a number of sub – disciplines:
1)those concerned with the chemical composition of the solid Earth, which include the study of minerals (mineralogy) and rocks (petrology);
2)those having to do with the structure of the solid Earth, as, for example, the study of the relationships of rocks and geologic features (structural geology) and the science of volcanic phenomena (volcanology);
3)those concerned with landforms and the processes that produce them (geomorphology and glacial geology);
4)those dealing with geologic history, including the study of fossils (paleontology), the development of sedimentary strata (strastigraphy), and the evolution of planetary bodies and their satellites (astrogeology); and
5)economic geology and its various branches – e.g., mining geology and petroleum geology.
Some other sciences are closely connected with geology such as geodesy, geophysics, and geochemistry.
The various sub-disciplines of geology are not only integrated with one another but also with other branches of the Earth sciences and with such fields as physics, chemistry, biology, and mathematics.
Geology provides a better understanding of the Earth‘s evolution and its present features. It also serves society in a variety of practical ways. Exploration for deposits of commercially valuable minerals is broadly guided by geologic principles and conducted with geophysical and geochemical methods. The search for fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) is strongly influenced by those aspects of geology dealing with the deposition and deformation of sedimentary rocks and with the flow of underground fluids. Significant findings of seismological research have helped engineers to design structures that are better able to withstand earthquakes.

5
Exercise1. Answer the questions.
1.What does geology deal with?
2.Which sciences concern with chemical composition of the Earth?
3.What does structural geology deal with?
4.What do geomorphology and glacial geology study?
5.What sciences deal with the study of fossils, the development of sedimentary strata and the evolution of planetary bodies?
6.What are some branches of economic geology?
7.What other sciences which are closely connected with geology do you know?
8.What are the various sub-disciplines of geology integrated with?
9.What is the search for fossil fuels influenced by?
10.How do significant findings of seismological research help engineers?
Exercise 2. Summarize the main idea of the text.
Exercise 3.Look through the text again. Complete the sentences below:
-Mineralogy and petrology deal with …
-The structure of the solid Earth studies …
-Geomorphology deals with …
-Mining geology and petroleum geology are included into …
-Paleontology requires the use such disciplines as … … … .
What Does a Geologist Do?
Pre-reading task.
You have chosen the geology as your future specialty. Think what a geologist can do. Give at least three possible answers. Now read the text and say if you are right.
Geologists work to understand the history of our planet. The better they can understand
Earth’s history the better they can foresee how events and processes of the past might influence the future. Here are two examples:
1) The processes acting upon the Earth cause hazards such as landslides, earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Geologists are working to understand these processes well enough to avoid building important structures where they will be damaged. If geologists learn a lot about volcanic

6
mudflows of the past then that information can be very useful in predicting the dangerous areas where volcanic mudflows might strike in the future. The map at left shows areas that are thought to be at risk from future mudflows around Mount Rainier. Intelligent people should be cautions when considering activities or property development in these areas.
2) Geologists have worked hard to learn that oil and natural gas are formed from organic materials deposited along the margins of continents and in shallow seas upon the continents. They have also learned how to recognize the types of rock that are deposited in these near-shore environments. This knowledge enables them to recognize potential oil and natural gas source rocks. In the photo oil field workers are placing a tool into an oil exploration well. This tool will be lowered down the hole and will record tiny amounts of radioactivity released from the rocks below (rocks rich in organic materials frequently contain tiny amounts of radioactive materials). The information obtained from the tool will help them assess the oil and natural gas production potential of the rocks below. If they do these tests at many locations within a region they might be able to map an oil or natural gas field.
Answer the questions.
1.What is the task of a geologist?
2.What do processes acting upon the Earth cause?
3.Why do geologists study these processes?
4.How are oil and natural gas formed?
5.What does knowledge about gas and oil formation enable geologists to recognize?
6.Why is a tool lowered down in the hole?
7.How will the information obtained from the tool help geologists?
8.What do geologists do when they finish their tests connected with production potential of the rocks below?
7
Geology as a Career.
Geology can be a very interesting and rewarding career. The minimum training required is a college degree in geology. Pre-college students who are interested in becoming a geologist should take college preparatory courses in earth science, biology, chemistry, physics and math. Courses related to writing, environmental science, computers, geography and mapping are also valuable.
Geologists work in a variety of settings which include: natural resource companies, environmental consulting companies, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and universities. Many geologists do field work at least part of the time. Others spend their time in laboratories, classrooms or offices. All geologists prepare reports, do calculations and use computers. Although a bachelor's degree is required for entry level employment, many geologists earn masters or doctorate degrees. The advanced degrees provide a higher level of training, often in a geology specialty area such as paleontology, mineralogy, hydrology or volcanology. Advanced degrees will often qualify the geologist for supervisory positions, research assignments or teaching positions at the university level. These are some of the most desirable jobs in the field of geology.
Exercise 1. Answer the questions.
1.Is geology an interesting career?
2.What should pre-college students study if they are interested in becoming a geologist?
3.Where can a geologist work?
4.What degree is required to enter employment?
5.What do the advanced degrees provide?
Exercise 2. Give a short summary of the text.
Part I
Unit I
I. Vocabulary
Translate the international words into Russian.
Geology, biological resources, physics, atmosphere, conservation, rational, scale, planet, solar system, spherical mass, gravitation, distance, rotation, temperature, fluctuation, process of erosion, constantly, topographical forms, chemical composition, volcanic action, seismic, physical activity, to orient, mineral, to indicate
8
a)Learn the vocabulary.
1.to alterизменять
2.bedпласт
3.earth’s crustкора земли
4.essentially – главным образом
5.to faultразламывать, сдвигать, нарушать
6.to foldсгибать, складывать
7.interiorвнутренний
8.moderateумеренный
9.to occurпроисходить, случаться
10.to powerуправлять, являться природным двигателем
11.particular – особый
12.relativelyотносительно, сравнительно
13.rockгорная порода
14.solidтвёрдый, плотный
15.source – источник
16.to subsidenceоседание
17.substantial – существенный, значительный
18.surfaceповерхность земли
19.sufficientдостаточный
20.to thrustнадвигать, давить
21.upper mantelверхний слой мантии
22.to be in order fromбыть по порядку
23.vastобширный, громадный, значительный
b)Translate the word combinations.
The study of the earth crust, the upper mantel of the earth crust, moderate temperatures, to power the Hydrologic Cycle, the surface of the planet, the geology of the beds, sufficient gravitational attraction, the interior of the earth, on a vast scale,substantional atmosphere, relatively minor fluctuations, subsidence of the parts.
II. Translate the sentences. Put questions to the words in italics.
1.The Earth’s crust is a potential source of minerals.
2.The study of the biological recourses, the physics of the sea, the study of natural resources have developed on a vast scale.
3.The Earth is the fifth largest planet of the solar system.
4.The Earth consists essentially of a nearly spherical mass of more or less solid rocks.
5.The Earth’s temperatures are moderate with relatively minor fluctuations.
6. Solar heat powers the Hydrological Cycle.
7. The Hydrological Cycle makes water continuously available to living things over most of the planet’s surface.

9
8.The science of the study of the Earth has made particular progress.
9.The Earth’s crust is constantly being altered by thrusting, folding, faulting.
10.The Earth seems unique among the planets.
III. Read the text. |
|
|
|
|
|
Earth |
|
|
|
|
The science of the study of the |
|||
|
Earth has made particular progress in |
|||
|
recent years. |
|
|
|
|
It has developed into large group of |
|||
|
individual sciences, closely related and |
|||
|
oriented towards the study of the Earth’s |
|||
|
crust and upper mantel, and their |
|||
|
composition-particularly that of the |
|||
|
Earth’s crust which is potential source of |
|||
|
minerals. |
|
|
|
|
The study of the world’s oceans |
|||
|
and the geology of their beds, their |
|||
|
biological resources, the physics of the |
|||
|
sea and the physics of the atmosphere, |
|||
An animation showing the rotation of |
the study of |
natural resources, |
their |
|
conservation |
and rational use |
have |
||
the Earth. |
||||
developed on a vast scale. |
|
|||
|
|
|||
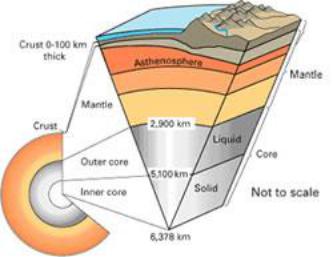
The earth, the fifth largest planet of the solar system, the third in order from the Sun, consists essentially of a nearly spherical mass of more or less solid rock. It has sufficient gravitational attraction (because of its mass) to hold substantial atmosphere; because of its distance from the Sun, its rotation, and the nature of the atmosphere, its temperatures are moderate, with relatively minor fluctuations. Solar heat, without which the Earth would be a frozen lifeless world, powers the Hydrological Cycle, which makes water continuously available to living things over most of the planet’s surface and, through the process of erosion, keeps working changes constantly on and in the crust. The crust, with its broad variety of topographical forms and chemical composition, is being altered further by thrusting, folding, faulting, and uplift or subsidence of its parts, as well as by volcanic action resulting from the planet’s internal heat. Although little is precisely known about the Earth’s interior, seismic evidence indicates that physical activity is continuous. Altogether the Earth seems unique among the planets in the variety of its characteristics and of the processes occurring over, on, and beneath its surface.
Notes
10
1.and their composition-particularly that of the Earth’s crust - и их строения-
особенно строения земной коры
2.keeps working changes-продолжает вызывать изменения
3.resulting from-являющийся результатом
IV. Find English equivalents to the following words and word combinations in the text.
1.изучение коры земли
2.сохранение природных ресурсов
3.из-за расстояния от солнца
4.умеренные температуры
5.относительно небольшие колебания
6.безжизненный мир
7.вода, доступная живым организмам
8.широкое разнообразие
9.недра земли
10.тесно связанный
V. Match the synonyms. |
|
1. individual |
a) happen |
2. essentially |
b) to change |
3. power |
c) difference |
4. variety |
d) mainly |
5. to alter |
e) to separate |
6. action |
f) to regulate |
7. evidence |
g) activity |
8. to occur |
h) layer |
9. bed |
i) proof |
10. sufficient |
j) adequate |
VI Word building |
|
a)Form the adjectives from the nouns using the suffix – less. Translate them. E.g. life - lifeless. (жизнь – безжизненный)
End, hope, use, child, cord, care, power, color, help, fruit, mother.
b)Form the adverbs from the adjectives using the suffix- ly. Translate them. E.g. essential - essentially.
