
Энергоэффективные ограждающие конструкции_EN
.pdf
Energy Efficient Building Envelope |
Kiev, 13.5.2010 |
|
|
Dr. Ing. R. Himmler
energydesign stuttgart – Ingenieurgesellschaft mbH
Gropiusplatz 10
70563 Stuttgart Germany
www.energydesign st.com robert.himmler@energydesign st.com
Seite 1

Energy Efficient Pilot Project Ukraine Structure
Cooperation
Contracted for
Implementation
Consultancy
Consultancy
Working Group
m-g-h
ingenieure + architekten GmbH
stuttgart
Ministry for Construction Ministry for Environment
Energy Efficient Pilot Project
Design
Building Design Team
Building Owner
Architect
Structural Engineer
HVAC Engineer
Contractor
Seite 2

Objectives of the „Energy Efficient Pilot Project“
Development of energy efficient building concepts during the planning stage and implementation
Awarness raising within the relevant national and municipal institutions, associations, chambers and the general public
Training and instruction of architects, engineers, municipalities and construction companies
Seite 3

Building Envelopes – Nowadays
Berlin |
|
|
|
Kiev |
Abu Dhabi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seite 4

Hot and Humid Climate
Seite 5

Cold and Dry Climate
Seite 6
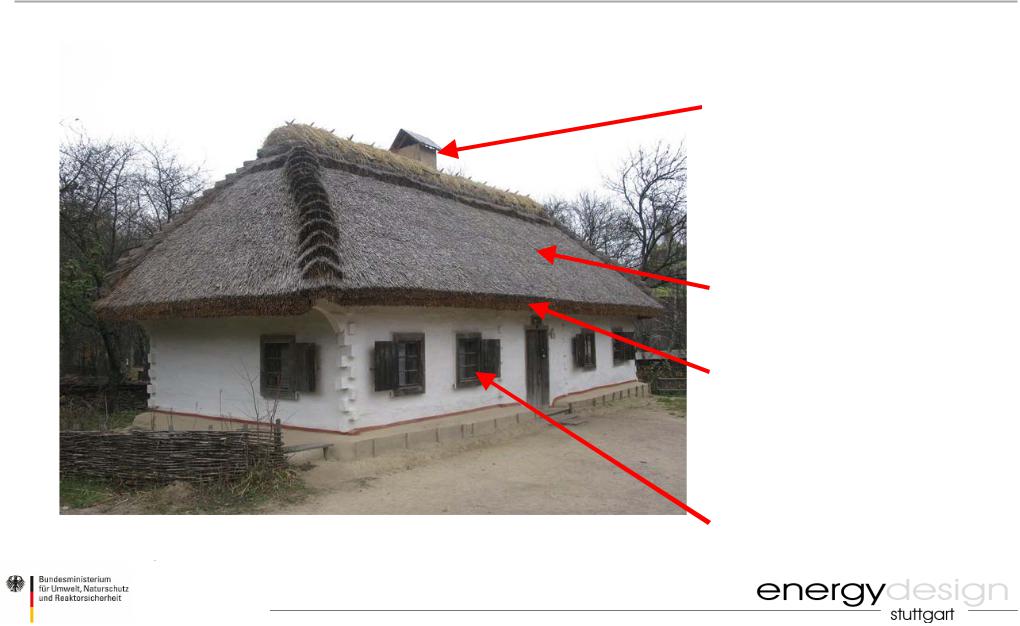

Traditional Buildings in Ukraine
CO2 neutral energy supply
thermal insulation
passive shading system
sufficient window/wall area
Seite 7
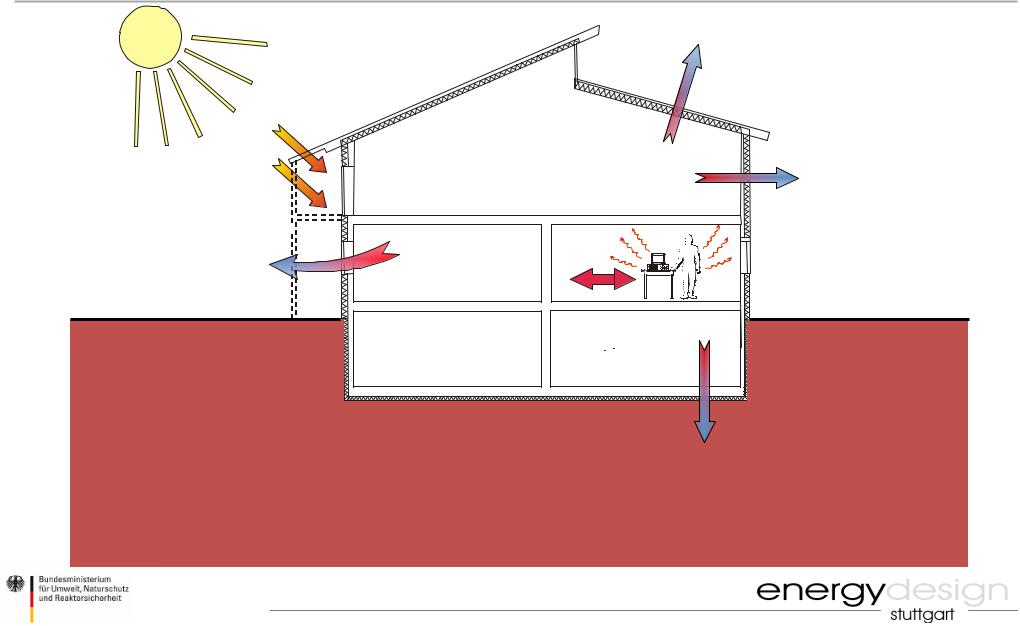
Energy Balance of a Building
Transmission
QS
QT
Solar
QV
Ventilation
Qi |
Internal Gains
QT
Heat Loss |
- |
Heat Gains |
= |
Qh |
|
QT + QV |
- |
η ( QS + Qi ) |
= |
Qh (Heating Demand) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seite 8
Heating Demand – Energy Balance
Heating Energy [kWh/m2]
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Heat Losses |
|
Heat Gains |
= Heating Demand (Qh) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
passiv |
|
20 % |
|
|
|
|
|
solar |
|
|
|
|
Ventilation |
|
QS |
|
|
Nutzbare |
|
|
QV |
50 % |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
30 % |
Gewinne |
|||
|
|
|
|
internal |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Q i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trans |
|
50 % |
Heating |
50 % |
|
mission |
Demand |
|
|||
QT |
|
|
Q |
h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: TU Braunschweig, IGS
Seite 9

Compact Building Design Surface to Volume Ratio
A Area of Building Envelope
V Volume of Building
Source: TU Braunschweig, IGS
Seite 10
