
- •Английский язык
- •In Search of the Perfect Home
- •Vocabulary Practice
- •Blarney Castle
- •Design Active vocabulary
- •Design Elements Point Active vocabulary
- •Active vocabulary
- •Color spaces
- •Active vocabulary
- •Active vocabulary
- •Active vocabulary
- •Active vocabulary
- •Types of design Fashion design Active vocabulary
- •Interior design Active vocabulary
- •Active vocabulary
- •Web design Active vocabulary
- •Gardening
- •Logo Active vocabulary
Logo Active vocabulary
brand |
фирмалық марка |
фирменная марка |
trace |
із, белгі |
след ,черта |
identify |
анықтау |
определять |
to stem |
шығу |
происходить |
legible |
айқын |
разборчивый |
font |
жиынтық |
комплект |
valid |
шынайы |
действительный |
A logo is essentially a visual brand identity of a company. The origins of logos can be traced to the 19th century, when industries added a symbol to represent their companies and to help customers easily identify their products. The trend caught on, and today corporations, services, products, agencies, universities, and colleges all have a specially designed identifying emblem or logo.
The idea probably stemmed from royal courts and the nobility, who for centuries had specific coats of arms emblazoned across everything they owned, from saddles to stables, to farms, castles, manors, furniture, jewelry, and dinnerware.
Since the logo represents a distinct identity, it must have the essential elements of: simplicity, proportionality, flexible color palette, easily legible fonts, and uniqueness. A logo must be designed so that it not just represents the company, but sets it apart. Originality and distinctiveness are the keys to a successful logo. The design elements such as font and color should lend themselves to redesigning as well as to representation in single or multiple colors.
Even before selecting a designer for the logo you need to clarify certain basic thoughts. What should the logo convey? What is the basic identity of my company today and what are the expansion plans? What are my objectives and strategy? Study your product and its customers, brainstorm with those who are committed to the success of your company, and never forget the competitors.
Remember, the logo is essentially a business tool so it must reflect professionalism, competency, and commitment. The logo must survive time and be valid even centuries later.
In logo design, it would be prudent to use vector graphics, as they allow resizing and retain design integrity. Keep away from complicated and intricate logo designs. Limit colors to two or three, this is not just economical but practical. Also chose colors that are in keeping with your industry. Choose a font that is universal and uncluttered.
Here are some common associations: blue represents trust, loyalty, and power; yellow energy, joy, and hope; while green represents growth, sustenance, and regeneration. Among shapes, a circle is associated with connection, community, trust, and safety; a rectangle represents strength; and a triangle power and aggression. Keep such aspects in mind while discussing possible design elements.
Glossary in Design
A
Authors Alterations. The term refers to changes (not corrections) made by a client during the proofing process. AA's are normally charged to a client as billable time.
Absolute Colorimetric Absolute Colorimetric is a rendering intent that leaves colors that fall inside the destination gamut unchanged. It does not expand or compress the whole gamut. Each color is transformed into itself, if it exists in the destination gamut. Otherwise, it is transformed to the closest color at the gamut boundary. In short, out of gamut colors get clipped.
Absorbency The capacity of paper to accept liquids like inks.
Acid-free paper Paper, which has had the acid removed from the pulp during production so that it has a neutral 7.0 pH.
Acquire Module Software (created by a scanner manufacturer), that expands the functions of the Adobe Photoshop program.
Acrobat Application software developed by Adobe to create PDF files. Acrobat Reader is used to read the PDF files.
Actual weight The true weight of any volume of paper used to determine price.
Additive Color The additive primary colors are red, blue and green. These three additive colors represent the three main components of white light in the additive color module. Black is produced by the absence of the primary colors. In theory, any color can be created by mixing these three colors.
Additives Additives are ingredients of paper such as clay fillers, sizing, dyes and other chemicals.
Alias When the curves and other lines in a graphic become jagged, the resolution of the graphics file is too low. The graphic is then referred to as "aliased".
Alignment The align command is used to adjust the position of objects or text in relation to each other. The various ways objects or text can be aligned are typically left, right, center, top and bottom.
Alkaline Paper The preferred choice for books, maps and documents, alkaline paper is usually used where aging resistance is preferred.
Alpha A fourth color component in the RGB color model that represents opacity. By changing Alpha values, images can be rendered completely transparent to completely opaque.
Alpha channel Alpha channels are used to create and store masks. Masks enable you to isolate or protect parts of an image you want to apply changes to, be it color changes, filters, opacity to a certain area on an image etc.
ALT-attribute An attribute specified in the image tag (HTML). The alt attribute is used to specify the text that must be displayed while an image on a web site loads. The alt attribute also adds functionality where the user's browser does not display images or where images have been turned off.
Ambient Light Also known as "available light" or "existing light". It's the surrounding light within an environment. Ambient light is used to read proofs.
Anchor Point Anchor points allows the user to manipulate paths to change it's shape. It (anchor points) appears along a path at every curve of a path and at the beginning and end of a path. Anchor points does not print out.

Animated GIF A very basic animated image, used primarily in web design. Animated GIFs consist of a set of GIF images placed in sequence.
Animation A series of graphic images pieced together in a timed sequence to give the appearance of continuous movement.
Anti-alias Softening of the jagged edges in images that have become aliased.
Aqueous Coating Aqueous Coating is a water-based coating applied after printing. It helps the underlying ink from rubbing off. Such a coating can give a gloss, dull or matte finish. It can be applied while the paper is still on press, or after it's off press.
Archival Paper Archival paper is typically acid-free and has a quality lifetime of about 100 years or longer. This paper is used to keep critical records for many years.
Archiving Data To archive data means to store copies of information for long periods of time.
Art Director The person responsible for managing the creative and production process for a given project as well as the people working on the project.
Auto Trace A function in graphic design software that automatically traces images. Paths are created along the edges of a scanned sketch. The paths are then cleaned up and the scanned file are discarded off. Now you have an outlined sketch of the image you scanned.
backing-up data The act of safeguarding your work against equipment malfunction. Data can be backed-up (copied) on various storage mediums like Floppy disks and storage tapes to compact disks.
Banner Banners are graphic images created to be placed as advertisements for products on websites.
Bevel Bevel is a function in graphic design software that, when applied to an image, gives the image the appearance of being raised out of the surface. A common example is buttons on websites. The appearance of the bevel is created by the application of lighter and darker colors to the image.
![]()
Bezier The bezier (or Pen) tool draws curved line segments that can be reshaped by changing its anchor points and/or direction lines.
Bitmap(BMP) Bitmap images are resolution dependent, unlike vector graphics which are resolution independent. A bitmap does not need to contain a bit of color-coded information for each pixel on every row. It only needs to contain information indicating a new color as the display scans along a row. This means that an image with much solid color will tend to require a small bitmap.
Bleeding When an image or printed color extends beyond the trimmed edge of a page, it is called a "bleed". Bleeding ensures that the print extends to the edges of the paper. The paper is usually trimmed to the desired size after printing.
Brightness The brightness (light/dark) of an image, the intensity of a light source or color luminance
Burn A tool used (in Adobe Photoshop) to darken an area of an image.
canvas size The full area of an image.
cartoon logo Typically a logo where a cartoon character - like a dog, robot etc. - is developed as a mascot. The mascot character is then combined with a rendering of the company name and slogan to create a cartoon logo. Cartoon logos can also be made up of nothing but text, presented in a "cartoonish" way.
cast shadow Similar to a drop shadow but with added perspective to create the illusion of a third dimension.
![]()
clipping path A function that allows a shape to mask part of an image. The masked part of the image can be edited but won't let you work past the borders of the clipping path.
cloning pixels A function in image editing software that can copy a part of the image and place it elsewhere. It can be used to remove blemishes on a models skin, text on a scanned image etc.
CMYK CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Black, the four process color inks.

color cast A color cast changes the hue of a selected part (or the whole) of an image while keeping the saturation and brightness intact.
color correction Correction to a color cast created by the scanner on the scanned image. The preview image on the computer display is adjusted. Color correction is usually done in CMYK.
Color map (color palette) A display of all the colors available in a computer program.
Color model A system used to describe and reproduce color.
Color palette A set of colors that make up an image or animation. It is also the set of colors available to be applied to images.
Color space Color space is a particular way to describe color. Examples of color spaces include: RGB, CMYK, HSB, CIE LAB.
colorcurve system The colorcurve system addresses the tendency of some colors to appear different on a variety of surfaces, materials and in different lighting conditions. The system is based on light reflectance curves and not on ink formulations.
Colorfastness If something is colorfast the color won't run when it gets wet and it won't fade in sun/bright light.
comp (comprehensive) Comp's are made to see what a prospective design project will look like for example the layout of the image, use of color, the size and the paper that will be used. It is also named a dummy.
composite image A composite image is a graphic image (or photograph), made up of a combination of images.
compound path Illustration software enables users to create compound paths from two or more paths. A compound path is an image with a see-through hole in the middle. An example of a compound path is the shape of the letter "A". If you put an "A" or any image with a compound path onto a colored background, the background color shows through.
construction logos Logos created specifically for construction companies. Construction logos typically share many of the design characteristics of real estate logos.
continuous tone Black and white photographs often contain gradient tones from black to white which are called continuous tones.
Contrast The difference between light and dark areas in an image. The wider the tonal range is in an image, the lower the contrast will be.
control handle The handle that extends from an anchor point that is used to create curved shapes in a path. Stretching the control handle will affect the depth of the curve.
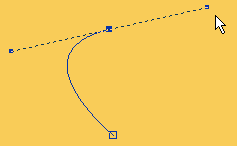
Crop A tool that enables the user to trim away the edges or part of an image.

Density The higher the density of an image, the greater the opacity. The lower the density, the more transparent the image is.
Dither The mixing of adjacent pixels to simulate additional colors to fill the gaps between two colors. For instance, if you want to display a full color graphic on a 256-color monitor, the computer will simulate the colors he cannot display. If there is a part in an image that displays incorrectly because a red and a yellow pixel are lying next to each other, creating a definite line from a distance, dithering would put an orange pixel in between to smooth out the line and the colors.
device dependant color space A color space where the same color will display differently on different devices. Scanner RGB and display RGB, for example, will display the same color value differently.
Dodge To bleach (lighten) a part or the whole of an image.
DPI (dots per inch) DPI is the number of dots (or pixels - PPI) that fit horizontally and vertically into a one-inch measure. The more dots per inch, the more detail is captured and the sharper the image.
drop shadow Similar to a cast shadow but without added perspective to create the illusion of a third dimension.
Dummy A dummy counts as an example of a piece of design work (brochure, ad, book cover etc.) that needs to be approved by the client. Once the client approves the dummy, the designer creates and prints the final design.
Duotone Duotones are made by printing an image with two colors, usually black and a second color. The resulting image has more depth than it would have had with only a monotone color (mostly black ink on white paper).
Emboss Embossing an image, gives it a three dimensional (3-D) quality. The 3-D effect is created with highlights and shadows on the edges of the image.
![]()
Export Exporting allows the user to save the file in another format to be opened in other programs.
F
Feathering A graphic software tool used to make the edges of an image appear blurry.
Fill A graphic software tool used to fill selected parts of images or their backgrounds with a color.
filterA filter is applied to images or art works to easily create special effects or to achieve a look that would be too difficult to create manually.
Flash Vector graphic animation software from Macromedia that creates browser-independent graphics (graphics that look the same across all browsers). An advantage of Flash animation is that their download time are relatively fast.
Focaltone A color matching system used for process color.
Font A font is a complete set of characters in a particular style and typically consists of a full letter set, number set and all other special characters you get by pressing the shift, control or option keys. Examples of fonts include "Arial", "Courier New" etc.
foreground color Color applied to objects in the foreground of the designed layout. You can fill in the color of these images with the painting tool, when the type is created or when the stroke command is applied.
format text Format text is a function available in most page layout software, allowing the user to change fonts and point sizes of all copy elements.
four-color process The printing process that reproduces colors by combining, cyan, magenta, yellow and black. If you look through a magnifying glass, you'll see that the printed image consists of dots in these four colors. These dots are printed on top of each other, next to each other or just close to each other, depending on the color and tonal values wanted. For example; by printing a blue dot over a yellow dot will give you green etc. To created the shadows in the image, all the colors (with or without black - depending on the intensity of the shadow) will be printed on top of each other to create a dark brownish color. The closer the colored dots are printed to each other, the darker it will appear. The further apart the colored dots are printed from each other, the lighter that part of the image will appear.
freehand drawing tool A tool found in Illustration software allowing the user to draw freeform shapes as if with a pencil.
G
Gamma An adjustment that makes the tonal distribution lighter or darker. Gamma adjustments are made to monitors, scanners or during an image editing process.
Gamut Gamut is the range of available color on an output device. Each device has its own gamut capabilities. If the gamut fall out of that particular devices range, it is shown inaccurately on the display or cannot be printed. We then say a color is "out of gamut".
gamut transformation A function of Color Management Systems that converts out of gamut colors to colors within the gamut of the targeted printer.
get picture command A command in Quark Xpress that imports a file into a picture frame.
get text command A command in Quark Xpress that imports a text file into a text frame.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) GIF images display up to 256 colors. GIF images generally have very small file sizes and are the most widely used graphic format on the web. The low quality resulting from compression makes them unsuitable for professional printing.
Gradient A function in graphic software that allows the user to fill an object/image with a smooth transition of colors, for example a dark blue, gradually becoming lighter or red, gradually becoming orange, then yellow.

graphic background In web page design, some web pages are designed with a graphic background on the web page and the text on top of the graphic. In most cases the graphic background can make the text hard to read.
graphic design Visual representation of an idea or concept. The term is used as a collective name for all activities relating to visual design, including web design, logo design etc.
grayscale Grayscale images contains black, white, no color and up to 256 shades of gray.
H
Hexadecimal Hexadecimal describes a numbering system containing 16 sequential numbers as base units. These numbers are used to color web pages for example, red is #FF0000.
high-resolution image An image with a high level of sharpness/clarity.
HLS A color space consisting of hue, lightness and saturation.
HSB A color space consisting of hue, saturation and brightness.
Hue Hue is the actual color of an object. Hue is measured as a pure color (on the color wheel) in degrees, for example degrees/variations of blue which is from a green-blue or sea-blue up to a purple-blue.
image assembly A hybrid image constructed from parts of other images.
image map An image map is a single graphic image (on a website), containing multiple clickable hyperlinks.
Invert Reversal of the tonal values or colors of an image. On an inverted image, black becomes white, blue becomes orange etc.
J
JPEG (Joint Photographic Electronic Group) A common compression method that shrinks a file's storage size by discarding non-important picture detail. Excessive jpeg compression can cause poor image quality
K
Kerning Adjusting the lateral (horizontal) space between letters.
Layers A function within graphic software that allows the user to assemble, organize and re-edit their artwork.
Leading The vertical spacing (measured in points) between lines of text.
letter spacing
lightness The lightness or brightness of a color.
line weight Line weight is a term referring to the thickness of a printing line. Sometimes shapes are drawn with a line weight of zero and then the fill color is used to define the shape.
Logos Unique visual business identifiers. A logo is an image that acts like a business signature, identifying the company and differentiating it from the competition. Although not a requirement, many logos illustrate the nature of the business and/or the nature of its products/services.
LogoAnts A popular online logo design service.
Lossless Refers to a form of data compression where the detail is retained and no data is lost after file downsizing. The lossless compression method is commonly used in TIFF and GIF formats.
Lossy A form of data compression where detail is removed as the file size are reduced. A common lossy compression method is JPEG.
low-resolution image A low-resolution image is a low-detail scan made from, for example a photograph.
Luminosity The brightness of an area determined by the amount of light it reflects or emits.
LZW (Lemple-Zif-Welch) A useful compression technique that compress images that contain large areas of single color, for example screenshots. This technique is supported by TIFF, GIF and PDF.
magic wand tool A tool in graphic software that allows the user to select parts of an image, for example areas with the same color.
Margins Guidelines in page layout software to show the user the body copy areas. It also allows the user to specify the dimensions. Margins/guidelines do not print.
Mask See clipping path.
master page A feature found in page layout software that allows the user to create a consistent page layout. Repeating elements like page numbers are created once on a master. This allows the user to avoid adding the numbers to each page manually.
medical logos Logos created specifically for use within the medical industry. The term is used to refer to hospital logos, clinic logos and healthcare logos in general.
monitor RGB The working space that reflects the current color profile of a monitor.
Mouseover A web graphics special effect that changes color on a graphic when you place your cursor over it.
Multimedia Multimedia is a form of communication that combines text, still or moving images, sound etc.
N
neon glow A tool in graphic software that gives a graphic image the appearance of neon lighting.

Noise Noise is a term used to describe the occurrence of pixels that contain random colors.

non-printing guides Non-printing guides are alignment aids (rulers or margin guides) found within page layout software.
non-reproducible colors Non-reproducible colors are colors present in an original photograph, that fall outside of the gamut.
Object An image usually consists of objects. If the user was to create an image of a flower, the stem and leaves could be treated as objects by themselves, or the leaves could all be treated as one object. In graphic design images are usually built up, object by object.
Opacity The density of a color or tonal value. The opacity of an image or object can range from transparent (0% opacity) to opaque (100% opacity). The ability to edit the opacity of individual objects allows the designer to create images that seem to flow into and through one another.
Outline The outline is the outer edge of text or a graphic.
P
page layout An example of a page layout is the pages in magazines or brochures. Every single page layout was created on a blank page by placing text, text columns, images etc. on the page. The whole design of a single page in a magazine is a page layout.
page size A setting in graphic software that enable the user to define the size of the page s/he is creating their artwork on.
Pantone matching system The Pantone matching system is used for specifying and blending match colors. It provides designers with swatches of over 700 colors and gives printers the recipes for making those colors.
paste board A paste board is the area around a page surface in a page layout program. This area allows the user to put down elements that is to be used in the page layout.
Path A path is the shape of a single element in an illustration. A path will not show unless it has a fill or line weight assigned to it.
patterned fill A custom fill usually defined by the user.
![]()
Pixel The smallest picture element (used to display an image on a computer), that can be independently assigned a color.
PNG Portable Network Graphics format. PNG (usually pronounced "ping"), is used for lossless compression. The PNG format displays images without jagged edges while keeping file sizes relatively small, making them popular on the web. PNG files are however generally larger than GIF files.
Posterize A tool in graphic software that reduces the number of shades of gray or colors to a specific number.
PPI Pixels Per Inch. A measurement of the resolution of a scanned image.
pre-designed logos Made famous by web sites such as Biz-Logo and ShelfLogos, pre-designed logos are logos that are created beforehand and offered for sale, usually online via the designer's web site. Some confusion exists between pre-designed logos and template logos. While these terms are sometimes used interchangably, pre-designed logos generally refer to exclusive logos while template logos refer to logos that are resold.
primary colors The primary colors are combined to produce the full range of other colors (non-primary colors), within a color model. The primary colors for the additive color model is; Red, Green and Blue. The primary colors for the subtractive color model is; Cyan, Magenta and Yellow.
printable color See Gamut
Q Quark Express Quark Express is page layout software used mainly for magazine and brochure layouts.
quick mask A screen display mode in Photoshop in which a translucent colored mask covers selected or unselected areas of an image.
Rasterize An image is said to be rasterized when converted from vector image to a bitmapped image. When opening a vector image in a bitmap-based editing program, you are usually presented with a dialog box of options for rasterizing the image.
real estate logos Logos created specifically for real estate companies. Real estate logos often contain standard real estate images, such as a roof, house, or a building.
Resample A function available in image editing that allows the user to change the resolution of the image while keeping its pixel count in tact.
Resolution The resolution of an image is an important factor in determining the attainable output quality. The higher the resolution of an image, the less pixilated it will be and the curves of the image will appear smoother.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) RGB is the model used to project color on a computer monitor. By mixing these three colors, a large percentage of the visible color spectrum can be represented.
rich media Rich media are banner ads that use technology more advanced than standard GIF animation, for example; Flash, Shockwave, Streaming video etc.
rotate A function within graphic software that enables a user to rotate an image or pixel by any number of degrees.
royalty-free photos or images Intellectual property like photos and graphic images that are sold for a single standard fee. These can be used repeatedly by the purchaser only, but the company that sold the images usually still owns all the rights to it.
Ruler Alignment or measurement aids found in page layout software.
S
Saturation Saturation is the color intensity of an image. A color with high saturation will appear brighter and more vibrant than the same color with low saturation. Colors in grayscale images have no saturations (white, grays and black).
scaling images See resizing.
Selection Selection refers to an area of an image that is selected (isolated) so it can be edited while the rest of the image is protected.
selective color correction adjustment A setting available in graphic software that allows the user to adjust a specific color in an image. For example, you can remove the blue in green grass without affecting the blue of the sky.
shadow detail Shadow detail refers to the amount of detail contained in the dark areas of an image. If the shadow is lightened too much in an attempt to expose more detail, the risk is there to decrease the overall contrast of the image.
subtractive color A term describing the three subtractive primary colors; Cyan, Magenta and Yellow. As opposed to the three additive colors; Red, Blue and Green.
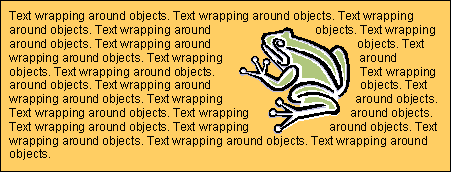
text wrap A term used in page layout software, referring to the way text can be shaped around the edges of images.
Thumbnail A thumbnail is a small version of the original image.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) A common graphic file format used for saving bitmapped images such as scans, photographs, illustrations and logos.
Tint A color is tinted by adding white to make the color lighter.
Tolerance Tolerance is the range of pixels a tool in graphic software operates in. In other words the range of shade or color pixels a Magic Wand selects etc.
tonal distribution Tones can be redistributed during the scanning or image editing stage, to lighten dark images or to darken light images.
true color system A true color system is a 24-plane graphics sub-system which produces the entire range of 16.7 million colors.
U
unsharp masking A very sophisticated sharpening method that sharpens images without the graininess that appears with most other sharpening methods.
V
Value With reference to color, the term is used to describe brightness.
vector graphic Vector graphics are drawn in paths. This allows the designer to resize images freely without getting pixilated edges as is the case with bitmapped images. The vector format is generally used for in printing while the bitmap format is used for onscreen display.
white point The white point, on a monitor, is the combination of RGB at full intensity.
white point adjustment A white point adjustment determines the amount of highlighted detail in an image.
YIQ A color model sometimes used in television broadcast systems. Colors are seperated into a luminance (Y) and 2 color values (I and Q).
Z
Zoom Most imaging software allows you to adjust zoom in order to "move closer" or "move further away" from an image. Usually when you open an image, the zoom level is set to 100% (actual size).
