
- •In your own words …
- •List the major components …
- •List operations …
- •Call the minimal number of levels of virtual machine..
- •D escribe the functional structure of von Neumann machine.
- •Formulate and analyze Moor’s Law.
- •Instruction
- •Interpreter
- •1 7) Describe the functional structure of Computer components …
- •22) Do we mean under the Interrupts? What is the main reason of using the Interrupt Mechanism?
- •What’s the Main Cycle of Instruction Processing (mcip)?
- •19)Describe the architecture of “Hypothetical Machine”. What is the difference between translator and interpr…
- •OpCode I Address
- •2 3) Draw up diagrams of the Program Flow Control without interrupts and with interrupts, describe each fragment of
- •25) Describe the mechanism of work with interrupts.
- •57. Describe the typical Disk data layout 29. Draw a scheme of dma Transfer
- •What is the interconnection structure, and by which factors is it determined?
- •List the types of exchanges (input and output)
- •What kind of buses does the System Bus include?
- •What do we call the width of a bus?
- •What operation does the control signal “I/o read” set?
- •What problems may arise, when only one (single) bus is used in a computer system?
- •List and describe main generic types of buses.
- •Which methods of arbitration are used now?
- •Describe existed methods of access to different types of memory.
- •Which parameters are used for the estimation memory devices performance?
- •What is ram? Describe distinguishing characteristics of ram. What’s the difference between dram…
- •48)Enumerate elements of Cache Design.
- •4 9)Draw up a block-diagram of Pentium processor and explain functions of its main nodes
- •50) How is ensured the Data Cache Consistency?
- •56. How is evaluated the Disk Access Time... Disk Access Time is the main Characteristic of Disk Performance.
- •60. Describe the process of Virtual Memory..
56. How is evaluated the Disk Access Time... Disk Access Time is the main Characteristic of Disk Performance.
If removable heads are used and disk drive is operating, then to read/write, the head must be positioned at the desired track and at the beginning of the desired sector on that track. The time it takes to position the head at the track is known as seek time. In either case, The time it takes for the sector to reach the head is known as rotational latency. Disk Access Time is equal to the sum of Seek time and Rotational Latency time. RAID (Six[seven] levels of RAID). The RAID scheme consists of six levels. These levels do not imply a hierarchical relationship but designate different design architectures that share three common characteristics:
RAID is a set of physical disk drives viewed by operating system as a single logical drive.
Data is distributed across the physical drives of an array.
Redundant disk capacity is used to store parity information, which guarantees data recoverability in case of a disk failure.
RAID systems of different levels differ by methods of realisation the second and the third characteristics.
58. How are sector positions within a track.. Data are transferred to and from the disk in blocks, accordingly data are stored in block-size regions known as sectors. To avoid imposing unreasonable precision requirements the adjacent sectors are separated by intra—track(record) gaps. In order to identify positions within a track there are must be starting points on the tracks and ways for identification the start and the end of each sector. These requirements are handled by means of control data recorded on the disk. Thus, the disk is formatted with some extra data used only by the disk driver, and they are not accessible to the user. In Fig. Winchester Disk Track Format each track contains 30 fixed-length sectors of 600 bytes each. Every sector holds 512 bytes data, plus control information useful to the disk controller. The ID field is a unique identifier or address used to locate a particular sector. The SYNCH byte is special bit pattern that determines the beginning of the field. The track number identifies a head, since this disk has multiple surfaces. The ID and data fields contain an error-detecting code (CRC).
60. Describe the process of Virtual Memory..
A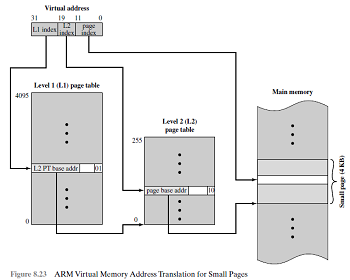 virtual memory address translation method based on the concept of
fixed length pages: each virtual address generated by the processor,
whether it is for an instruction fetch or an operand fetch/store
operation, is interpreted as virtual page number (high—order
bits) followed by an offset(low-order bits) that specifies
the location of a particular byte (or word) within a page.
Information about the main memory location of each page is kept in a
page table. This information includes the main memory address
where the page is stored and the current status of the page. An area
in the main memory that can hold one page is called a page frame.
The starting address of the page table is kept in a page table
base register.
virtual memory address translation method based on the concept of
fixed length pages: each virtual address generated by the processor,
whether it is for an instruction fetch or an operand fetch/store
operation, is interpreted as virtual page number (high—order
bits) followed by an offset(low-order bits) that specifies
the location of a particular byte (or word) within a page.
Information about the main memory location of each page is kept in a
page table. This information includes the main memory address
where the page is stored and the current status of the page. An area
in the main memory that can hold one page is called a page frame.
The starting address of the page table is kept in a page table
base register.
