
In addition:
Ca3P2 + 6HCl = 2РН3 + 3 CaCl2
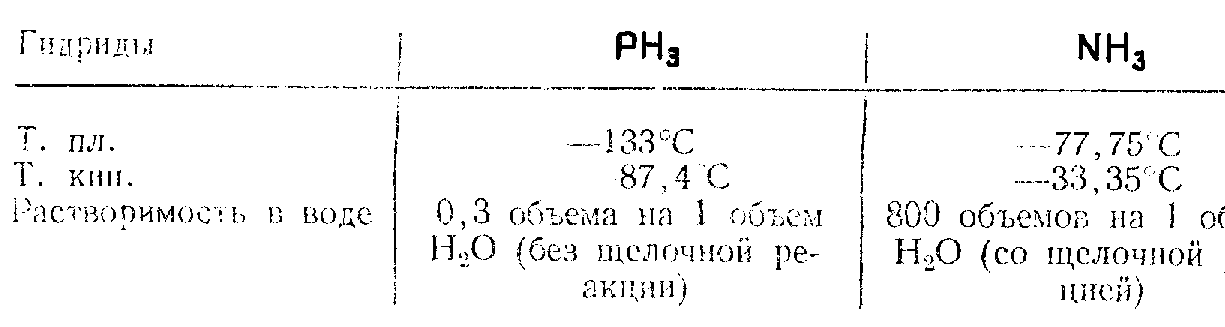
Properties. Let us compare its physical properties with NH3:
PH3 molecule can be treated as an NH3 analogue. Difference in the properties of PH3 and NH3 is associated with the following peculiarities of their structure:
• the length of bond N—H (0.1014 nm) is much shorter than the length of P—H bond (0.142 nm)
• NH3 polarity (dipole moment is 1.47 D) significantly exceeds the polarity of PH3 (0.55 D).
This is attributed to the absence of sp3-hybridization of valence orbitals in PH3, which is typical of NH3. Indeed, PH3 molecule is pyramidal, H-P-H = 93.5o ( 90o) (in NH3 – 107.3o). It indicates the decrease of contribution of s-orbital in the hybrid bonds of PH3 formation, i.e. unshared electron pair of P is s-orbital (in case of NH3 at the sp3-orbitals).
This PH3 structure considerably complicates formation of donor-acceptor bonds with electron donors. Therefore, PH3 has very weak basic properties.
The bond p—h is less strong (322 kJ / mol) than n—n (390 kJ / mol), ph3 practically does not form h-bonds. As, Sb, Bi Compounds e (-3)
The oxidation state –3 of these elements is found in arsenides, antimonides bismutides of s-elements of I and II groups. Metal-like compounds are formed in most of other cases (s-elements form salt-like compounds).
In the series of nitrides, phosphides, arsenides, antimonides, and bismutides of the same type gap width decreases, indicating an increase of contribution of delocalised bond (unlike covalent bonding that is localised along the bond axis of molecular structure compounds):
AlN AlP AlAs AlSb
E, eV 3.8 3.0 2.16 1.6
Most of these compounds decompose under the action of acids.
Hydrogen compounds.
As, Sb, Bi do not interact with hydrogen, so EH3 is available only indirectly:
Mg3Е2 + 6HCl = 3MgCl2 + 2H3Е
or under the action of Zn on compounds of arsenic in acidic medium:
As2O3 + 6Zn + 12HCl = 2AsH3 + 6ZnCl2 + 3H2O
This is known as the Marsh reaction (test for arcenic).
Arsine, AsH3, stibine, SbH3, bismuthine, BiH3, are gases with a sharp smell. They, especially AsH3, are one of the strongest inorganic poisons (generally, all volatile compounds and soluble compounds of arsenic are extremely poisonous). These compounds are also strongly endothermic, and therefore very unstable. Generally, in the series AsH3—SbH3—BiH3 stability decreases. BiH3 decomposes at the moment of liberation and its properties are not well studied.
|
dE-H, nm |
ЕЕ-Н, kJ/mol |
Ноf, kJ/mol |
НЕН |
ЕН3, D |
NH3 |
0.101 |
390.4 |
-46.4 |
107.3o (sp3) |
1.47 |
PH3 |
0.142 |
328.5 |
5.4 |
93.3 o ( - ) |
0.58 |
AsH3 |
0.152 |
279.2 |
66.5 |
92 o |
0.22 |
SbH3 |
0.171 |
254.6 |
145 |
91 o |
0.12 |
BiH3 |
|
|
230 (evaluation) |
|
|
In the series of nonmetallic elements As—Sb—Bi is revealed the nonmetallicity weakening of EH3 compounds. The structure of these molecules is similar to NH3 and PH3, (i.e., pyramidal structure with the atom of an element at the top and hydrogen atoms below). However, Ra is increased in the series N—P—As ... Bi and E-H polarity, the strength of bond is reduced; nonbonding orbital occupied by two electrons becomes less directed and the valence angle HEH is decreased either.
The important property of EH3 is their high reducing ability. For instance, arsine, AsH3, can even reduce phosphorous acid H3PO3 to hypophosphorous H3PO2, although phosphorous acid itself is a very active reducing agent:
2 AsH3 + 3 Н3РО3 = 3 Н3РО2 + 2 As + 3 Н2О ( Go = -60 kJ / mol)
EН3 decomposes easily: 2EН3 = 2E + 3H2O
All hydrides EН3 are dissolved well in water, but do not interact chemically. They burn in the air:
2EН3 + 3О2 = E2О3 + 3Н2О
In the series NH3—PH3—AsH3—SbH3—BiH3 donor properties of molecules are weakened, so the typical of NH3 synthesis reaction is not observed in case of AsH3 and SbH3.
Properties of hydrides can be generalized as follows:

