
- •Electron configurations of carbon subgroup
- •Some physical properties of c subgroup elements
- •Physical properties
- •Occurrence
- •Silicon
- •Interaction with o2:
- •Interaction with chlorine:
- •Interaction with sulfur:
- •Compounds Carbon
- •Hydrogen compounds Carbon
- •Compounds Silicon
- •Si has no interaction with Zn, Al, Sn, Pb, Ag, Au and so it can be recrystallised from their melts. Hydrogen compounds Silicon
- •Chemical compounds
- •Oxygen containing compounds
- •Oxygen containing compounds
- •Chemical compounds
- •Compounds with halogens, sulfur, and nitrogen Carbon
Chemical compounds
Compounds with hydrogen
Germanium, tin, and lead
Ge, Sn and Pb do not react with H2 directly. The common method of obtaining hydrides:
decomposition of their compounds by diluted acids:
Mg2Е + 4HCl = ЕH4 + 2MgCl2
Hydrides in the series Ge—Sn—Pb elements are low stable. In the series SiH4 (silane) - GeH4 (germane) - SnH4 (stannane) - PbH4 (plumbane) stability decreases so that the existence of PbH4 has been confirmed indirectly (increase of fugitivity of Pb in the stream of hydrogen):
GeH4 = Ge + H2 (rapidly at 300 oC)
SnH4 = Sn + H2 (rapidly at 150 ° C)
PbH4 = Pb + H2 (immediately at STP)
Ge has the maximal number of compounds with hydrogen, with the homologous series of germanes from GeH4 to Ge9H20. All of them have chemical properties that are similar to GeH4 (gas b.p. = -90 oC).
Preparation:
GeO2 + Na[BH4] + HCl + H2O = GeH4 + H3BO3 + NaCl
Germanes are rapidly oxidised:
GeH4 + O2 = GeO2 + 2H2O
Degree of hydrolysis of germanes is lower compared with silanes. GeH4 is stable even in 30% solution of alkali, while SiH4 is easily decomposed even by water.
SnH4 and Sn2H6 are only known in case of tin. SnH4 is a strong reducing agent that in 15% NaOH and dilute acids reduces HgCl2 easily:
SnH4 + 3HgCl2 = 3Hg + SnCl2 + 4HCl
There are many derivatives of hydrogen compounds, including relatively stable tetraethyllead, Pb(C2H5)4, used as antidetonator of fuel for internal combustion engines.
Oxygen containing compounds
Carbon
Carbon forms compounds СО, СО2, С3О2, С5О2, С6О9 and cyclic С12О12 and (C4O3)n.. To inorganic belong mono- and dioxide of carbon. others are derivative of organic substances.
carbon Dioxide (carbon dioxide) CO2.
It forms at burning of coal and all organic substances.
Preparation. In industry: roasting of limestone:
СаСО3 = СаО + СО2 Н = 180 kJ/mol
In a laboratory:
СаСО3 + 2HCl = CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O (Kipp apparatus)
Structure. CO2 consists of symmetric linear unpolar molecules (distance of C—O is 0,113 nm): It has sp-hybridization: two -bonds are formed at overlapping of 2 sp-hybride orbitals of C and two 2px-orbitals of O.Two other localized -bonds are formed at overlapping of 2py and 2pz-orbitals of C with 2py and 2pz-orbitals of O.
Properties. At ordinary conditions, CO2 is colourless, uncombustible gas with a weak sourish smell and taste. It is heavier then air - specific density in respect to air makes up 1,529.
Therefore, in the absence of air motion CO2 is going on the bottom of hollows, where it forms (caves, wells, mines and others. As a result, there is known Dog’s cave near Naples - a man is not hurt, dogs perish. It follows to be very careful at the entrance in such premises, because CO2 does not support breathing, at concentrations higher then 3% it causes heavy disorder of organism functioning. At concentration 10%, the loss of consciousness and death through the stop of breathing comes quickly.
CO2 is easily liquefied at 20 and pressure 57 atm. into a colourless mobile liquid with density 0,766 g/cm3. In the liquid state, it is stored in the balloons painted in a black with yellow inscription carbonic acid.
At rapid evaporation “dry ice” is created, which in the preliminary compressed state slowly evaporates and is used therefore as an effective cooling medium. Sublimation of “dry ice” at ordinary conditions occurs at –78,48 C.
Chemically, CO2 is rather inert. It does not support burning, because it is the final product of combustion (it is used as a fire-extinguisher media). In its atmosphere burn only the substances, affinity to oxygen at which are greater than at carbon, for example, magnesium:
CO2 + Mg = MgO + C H298 = –811,7 kJ/mol
At ordinary conditions, CO2 is well dissolved in water ( 1:1 on a volume). Its saturated water solution has concentration 0,04 M CO2, pH of solution = 3,7.
At CO2 dissolution is formed partly H2CO3, anhydride of which it is:
CO2 + Н2О Н2СО3
This reaction equilibrium is very strongly displaced to the left, therefore greater part of CO2 is found simply in the dissolved state, and not as H2CO3. Taste of this solution is slightly sour.
Carbonic acid
H2CO3 is weak dibasic acid:
Н2СО3 Н+ + НСО3- К1 = 4,2•10-7
НСО3- Н+ + СО32- К2 = 4,8•10-11
At higher temperatures an equilibrium is displaced toward the practically complete removal of CO2 from the solution (to the left), and in an alkaline medium as a result of binding of ions H+ - to the right.
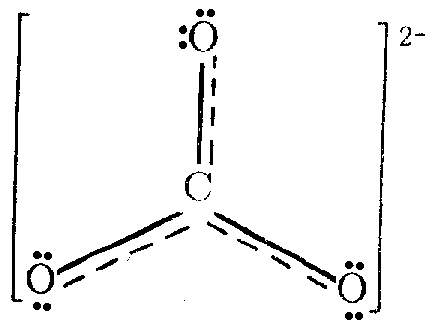 In
the anion СО32-
atom of carbon is found in the state of sp2-hybridization:
In
the anion СО32-
atom of carbon is found in the state of sp2-hybridization:
p-Electrons, which remains by one at every atom, form delocalized p-p bonds which substantially increase the strength of the structure. This ion is flat in accordance with sp2-hybridization.
To H2CO3 correspond two types of salts - neutral, carbonates with an ion СО32- and acidic – hydrogen carbonates which contain an ion HCO3-. Most salts of carbonic acid are colourless.
Carbonates. Among them, the water-soluble are only salts of alkali metals (excepting Li2CO3) and ammonium. In solution carbonates hydrolyze strongly:
СО32- + Н2О НСО3- + ОН- рН > 7
Often this reaction is complicated by the reactions of double exchange between two-charged cations of weak bases and soluble carbonates:
2CuCl2 + 2Na2CO3 + H2O = (CuOH)2CO3 + CO2 + 4NaCl
In the case of multicharge cations (Fe3+, Cr3+, Al3+, Ti4+, Zr4+) hydroxide carbonates are not form even, but as a result of complete hydrolysis are precipitated hydroxides:
2AlCl3 + 3Na2CO3 + 3H2O = 2Al(OH)3 + 3CO2 + 6NaCl
2Al3+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O = 2Al(OH)3 + 3CO2
Thermally, the more stable are carbonates, the more active are metals, from which they are formed. So, Na2CO3 is melted without decomposition, CoCO3 decomposes on CoO and CO2 at 825, and Ag2CO3 - at 100. (Analogy with nitrates).
At action of strong acids all carbonates are decomposed with the elimination of CO2.
Hydrogen carbonates. All known hydrogen carbonates are soluble. In nature, they are slowly formed at interaction of insoluble carbonates with carbonic acid:
СаСО3 + СО2 + Н2О = Са(НСО3)2,
therefore, they are always present in natural water. The most used among them is NaHCO3 - washing soda. Its hydrolysis occurs so:
НСО32- + Н2О Н2СО3 + ОН- (Кh)
НСО32- Н+ + СО32- (Кd)
it is needed to confront them, in this case Kh >> Kd, therefore pH ~ 8.
Like carbonates hydrogen carbonates are decomposed by strong acids. At heating higher then 60 they begin to decompose with evolving carbon dioxide:
NaHCO3 Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
On that thermal decomposition is based one of methods of removal of hardness of water.
carbon Monooxide (charcoal gas).
Forms at interaction of CO2 with an incandescent coal:
CO2 + C CO Hо = 171,5 kJ/mol
The reaction is reversible, its shift to the right is predetermined by an entropy factor, and to the left – by enthalpy. Below 400 reaction is practically fully displaced to the left, and higher than 1000, to the right. At ordinary conditions, CO is fully stable substance.
Preparation.
In industry: in great scale - in the form of generator and aquatic gases.
Generator gas forms at incomplete combustion of anthracite coal or `coke in large furnaces (generators). It is the mixture of gases: 25% CO, 70% H2, 4% CO2, other - N2, CH4, O2.
Water-gas forms at passing of water steam above incandescent carbon:
С + Н2О = СО + Н2 Н298 = 117,6 kJ/mol
In a laboratory: at decomposition of formic or oxalic acid or their salts at intearaction with hot concentrated H2SO4:
НСООН = СО + Н2О
Н2С2О4 = СО + СО2 + Н2О
Structure. A molecule CO is extraordinarily stable (one of most stable among the known molecules). It sustains heating to 6000. Energy of bond (1069 kJ/mol) is more than in H2 (938 kJ/mol) and to the triple bond between atoms:



C
 O
O

 2s 2p
2s 2p
2s 2p
2s 2p





 C
O
or C
O
C
O
or C
O
In accordance with a method of Valence bonds two bonds are formed at coupling of two unpaired electrons of carbon and two - of O and both are displaced toward oxygen; another bond forms according donor-acceptor mechanism: to two-electronic orbital of oxygen is overlapped with a lone electron orbital of carbon. This pair is displaced to carbon, and on the whole the molecule of CO is weakly polar ( = 0,37•10-29 C.m).
Properties. Small polarity and capacity for polarizing predetermine low b.p. -191,5 and low solubility in water (3,3 vol. at 100 vol. H2O).
C
CO + PdCl2 + H2O = Pd + CO2 + 2HCl
At ordinary conditions, CO is nonsaltforming oxide, it is unreactive with water, acids and alkalis. With alkalis, it reacts only at elevated temperatures, and at the presence of catalysts:
СО + NaOH = HCOONa,
So, CO acts as the anhydride of formic acid.
For CO there are characteristic reactions of addition and oxidation, where it is reduced:
Fe2O3 + 3CO = 2Fe + 3CO2
NiO + CO = Ni + CO2
CO + Cl2 = COCl2 (phosgene)
COCl2 is slowly decomposed by water, quicker by alkalis and it is a typical chloroanhydride:
COCl2 + H2O = CO2 + 2HCl
Phosgene is very poisonous substance and was used as a chemical weapon.
CO finds wide application in the organic syntheses. It is used as a reagent for preparation of paraffins, petrol, methyl alcohol, aldehydes, a lot of acids (formic, oxalic, vinegar, propionic, adipinic, acrylic), hydrogen cyanide and many other products.
At higher pressures CO reacts with powdered metals with formation of complex metal carbonyls: Fe(CO)5, Co2(CO)8, Ni(CO)4, Cr(CO)6 and others. Ligand in these compounds uses unshared electronic pair of carbon. Carbonyls are easily decomposed; they find application for preparation of pure metals. Like CO, all of them are very poisonous.
