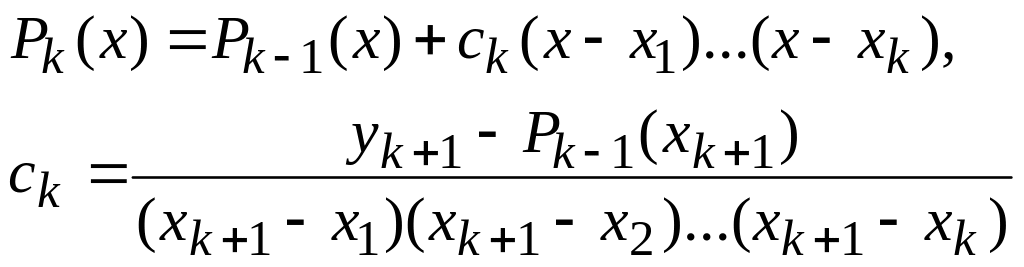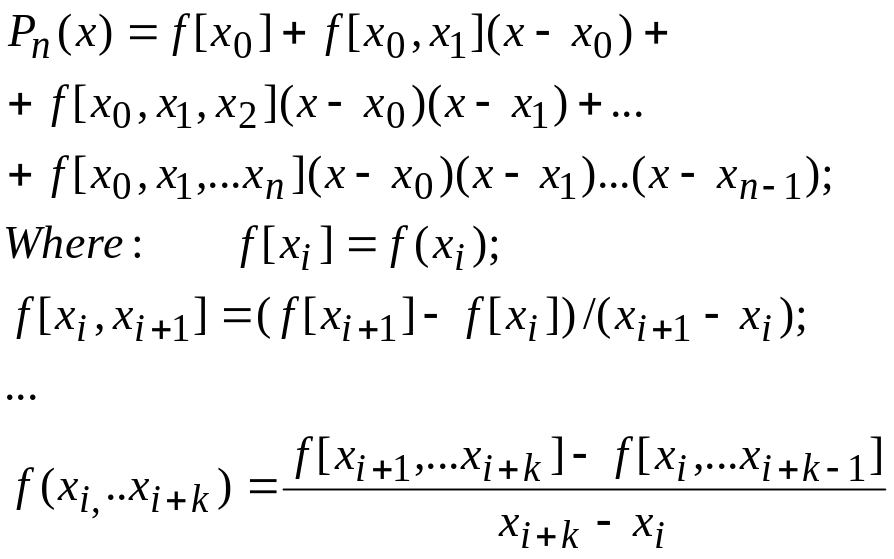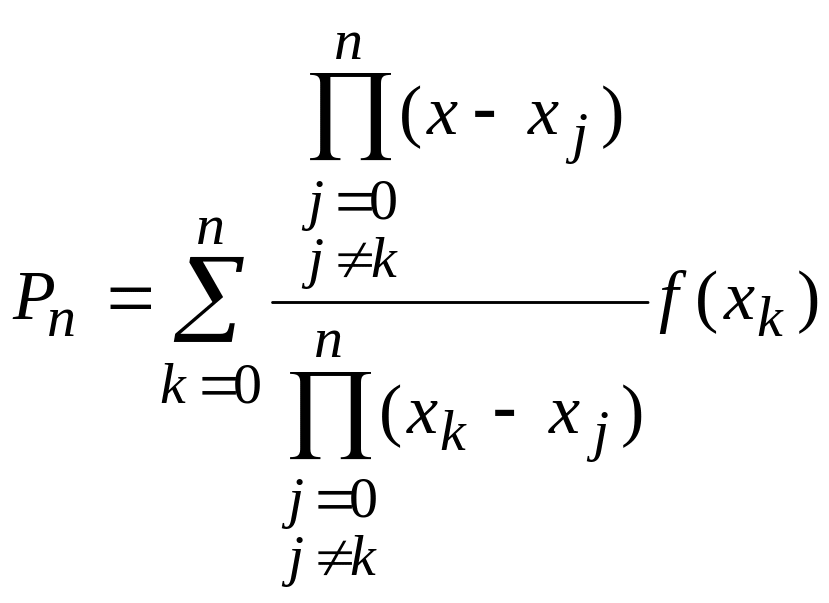- •Contents
- •Introduction
- •Syllabus
- •Error and Accuracy of Calculations
- •Practise Part 1. Error and Accuracy of Calculations
- •Part 2. Numerical Integration
- •Part 3. Solution of Linear Algebraic Equations
- •Part 4. Solution Methods of Non-Linear Equations
- •Part 5. Integration of Ordinary Differential Equations
- •Table 5.2 Summary of important information
- •Part 6. Interpolation and Extrapolation of Functions
- •Computer labs
- •To the Student
- •The laboratory tasks Lab 1. Numerical Integration.
- •Variant 3. Numerically evaluate the following definite integral accurate to 4 significant digits.
- •Variant 4. Evaluate the integral from Var. 3 using Simple Monte Carlo approximation. Lab 2. Solution of Linear Algebraic Equations.
- •Variant 2. Solve the linear system from Var. 1 using Jacobi iteration. Check your results.
- •Variant 3. Solve the linear system from Var. 1 using Gauss - Seidel iteration. Substitute your results back into the original equations to verify your solution.
- •Lab 3. Solution Methods of Non-Linear Equations.
- •Lab 4. Integration of Ordinary Differential Equations.
- •Lab 5. Interpolation and Extrapolation of Functions.
Part 6. Interpolation and Extrapolation of Functions
TABLE 6.1 Comparison of the characteristics of alternative methods
Method |
Error Associated with Data |
Number of Points Matched Exactly |
Programming Effort |
Comments |
Newton's Divided Difference Polynomial |
Small |
n + 1 |
Easy |
Usually preferred for exploratory analyses |
Lagrange Polynomials |
Small |
n + 1 |
Easy |
Usually preferred when order is known |
Cubic Spline |
Small |
Piecewise fit of data points |
Moderate |
First and second derivatives are equal at knots |
TABLE 6.2 Summary of important information
Method |
Formulation |
Error |
Newton (Gregory-Newton) Interpolating Polynomial |
|
|
Newton's Divided Difference Interpolating Polynomial |
|
|
Lagrange Interpolating Polynomial |
|
|
Spline Interpolation |
A linear spline:
(i = 1, n). A
quadratic spline:
A
cubic spline:
|
|
Example 1
Given the data:
x |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
f(x) |
0 |
5 |
22 |
57 |
116 |
Calculate f(2.5) using the Lagrange polynomial of order 4.
Employ inverse interpolation using Newton's divided difference interpolating polynomial to determine the value of x that corresponds to y = f(x) = 20.
Solution. a) To find an approximate value for f(2.5), we compute P4(2.5).
![]()
![]()
![]()
b) In this case we use the Newton polynomial reversing the variables:
![]()
Construct a table for computing the divided differences.
y |
f[y] |
f[.,.] |
f[.,.,.] |
f[.,.,.,.] |
f[.,.,.,.,.] |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
5 |
2 |
|
-6.417·10-3 |
|
|
|
|
0.05882 |
|
1.024·10-4 |
|
22 |
3 |
|
-5.817·10-4 |
|
-8.472·10-7 |
|
|
0.02857 |
|
4.127·10-6 |
|
57 |
4 |
|
-1.236·10-4 |
|
|
|
|
0.01695 |
|
|
|
116 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
Hence ,
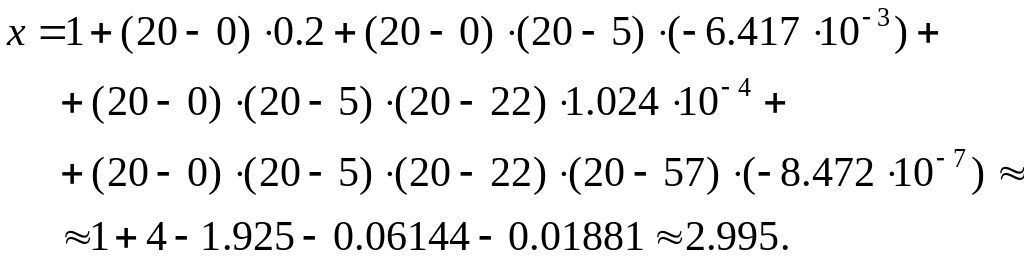
Example 2
Fit the data in the table below with a) first-order splines, b) quadratic splines, c) use the results to estimate the value at x = 3.3, d) compute percent relative errors for the numerical results.
x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
f(x) |
0 |
0.5 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
0.941176 |
0.961538 |
Note
that the values in the table were generated with the function
![]() .
.
Solution.
a) The slopes for all intervals can be computed (see Table 6.2), and the resulting first-order splines are:
![]()

b) Now fit quadratic splines to the same data using formulas:
![]() ;
;
![]()
Select
![]() ,
then:
,
then:
![]()
Hence,
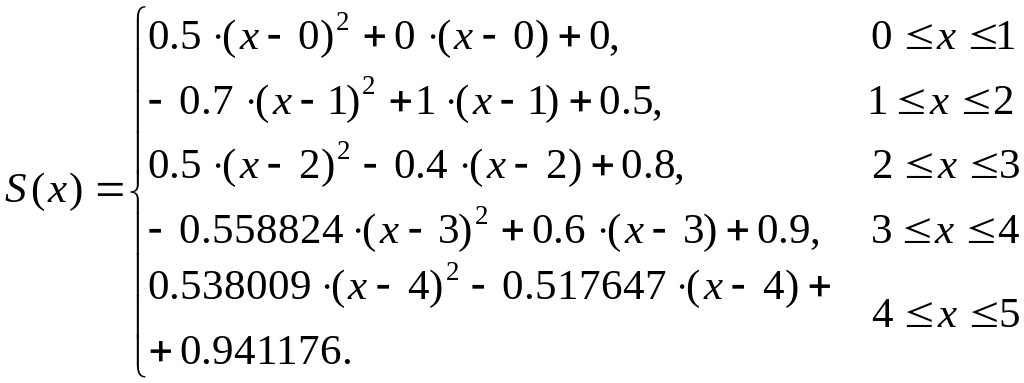
The correct value of the function at x = 3.3 is f(x) = 0.915896.
The result of first-order splines at x = 3.3 is f(x) = 0.93. The percent relative error is εt = 1.5%. The result of quadratic splines at x = 3.3 is f(x) = 1.029706. The percent relative error is εt = 12.4%.
Problems
Given the data:
x |
1 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
f(x) |
1 |
5 |
7 |
8 |
2 |
1 |
Calculate f(4.4) using a) Newton (Gregory-Newton) interpolating polynomial, b) Newton's divided difference interpolating polynomial.
Employ inverse interpolating to determine the value of x that corresponds to f(x) =1.0 for the following tabulated data:
x |
1.0 |
1.2 |
1.4 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
f(x) |
0.5652 |
0.7147 |
0.8861 |
1.1964 |
1.5906 |
a) Use the linear splines; b) Use the Lagrange polynomial.
3. Develop cubic splines for the following tabulated data:
x |
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
6 |
f(x) |
4.75 |
4 |
5.25 |
19.75 |
36 |
a) Calculate f(2.5) and f(4.0); b) Verify that S3(5) = S4(5).