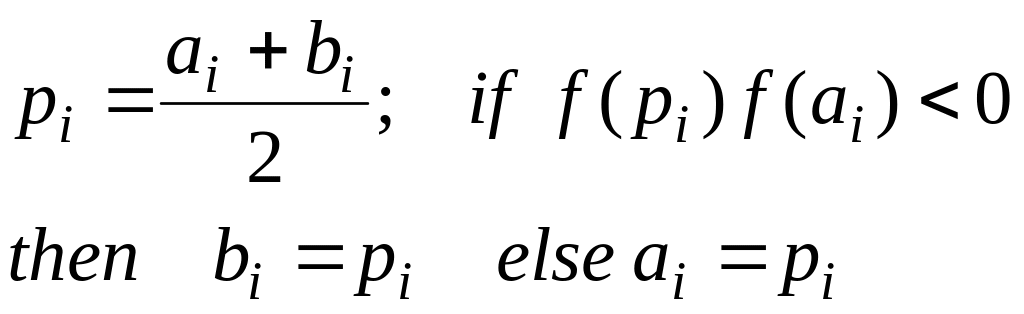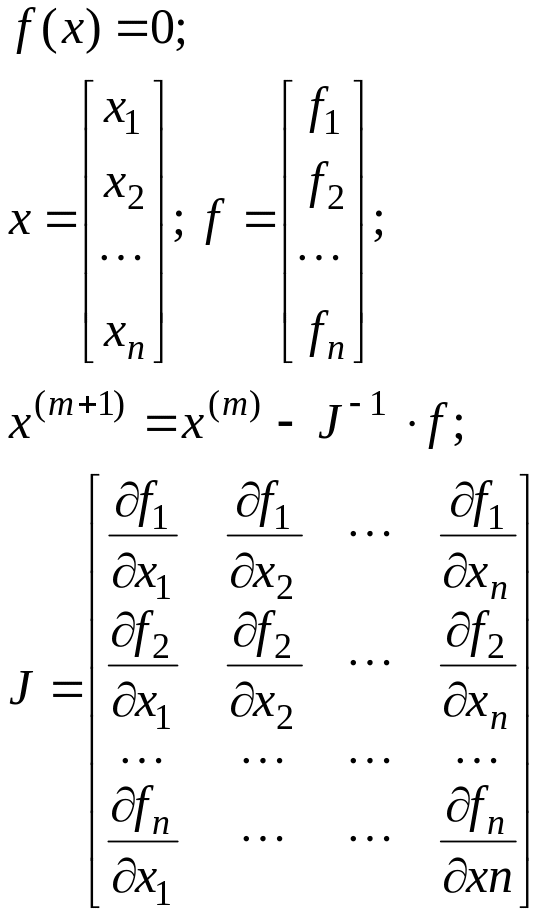- •Contents
- •Introduction
- •Syllabus
- •Error and Accuracy of Calculations
- •Practise Part 1. Error and Accuracy of Calculations
- •Part 2. Numerical Integration
- •Part 3. Solution of Linear Algebraic Equations
- •Part 4. Solution Methods of Non-Linear Equations
- •Part 5. Integration of Ordinary Differential Equations
- •Table 5.2 Summary of important information
- •Part 6. Interpolation and Extrapolation of Functions
- •Computer labs
- •To the Student
- •The laboratory tasks Lab 1. Numerical Integration.
- •Variant 3. Numerically evaluate the following definite integral accurate to 4 significant digits.
- •Variant 4. Evaluate the integral from Var. 3 using Simple Monte Carlo approximation. Lab 2. Solution of Linear Algebraic Equations.
- •Variant 2. Solve the linear system from Var. 1 using Jacobi iteration. Check your results.
- •Variant 3. Solve the linear system from Var. 1 using Gauss - Seidel iteration. Substitute your results back into the original equations to verify your solution.
- •Lab 3. Solution Methods of Non-Linear Equations.
- •Lab 4. Integration of Ordinary Differential Equations.
- •Lab 5. Interpolation and Extrapolation of Functions.
Part 4. Solution Methods of Non-Linear Equations
TABLE 4.1 Comparison of the characteristics of alternative methods
for finding roots of algebraic and transcendental equations
Method |
Initial Guesses |
Convergence Rate |
Stability |
Accuracy |
Breadth of Application |
Comments |
Graphical |
|
|
|
Poor |
Real roots |
May take more time than the numerical method |
Bisection |
2 |
Slow |
Always |
Good |
Real roots |
|
Secant |
2 |
Medium to fast |
Possibly divergent |
Good |
General |
Initial guesses do not have to bracket the root |
False-position |
2 |
Medium |
Always |
Good |
Real roots |
|
Newton-Raphson |
1 |
Fast |
Possibly divergent |
Good |
General |
Requires evaluation of f(x) |
Newton-Raphson for Nonlinear Systems of Equations |
n |
Fast |
Often diverge if the initial guesses are not sufficiently close to the true roots |
Good |
General |
Requires evaluation of J(x) |
TABLE 4.2 Summary of important information
Method |
Formulation |
Errors and Stopping Criteria |
Bisection |
|
|
Secant |
|
|
False Position |
if
|
or |
Newton-Raphson |
|
|
Newton-Raphson for Nonlinear Systems of Equations |
|
|
Example 1
Determine the real
root of
![]() :
:
Graphically.
Using the bisection method (three iterations).
Using the secant method (three iterations).
Using the false position method (three iterations).
Using the Newton-Raphson method (three iterations).
Solution. a) The graphical approach for determining the roots of an equation.
-
x
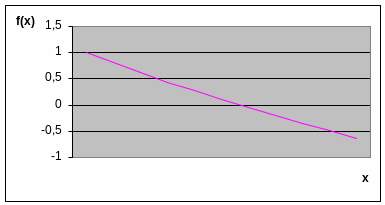
f(x)
0
1
0.1
0.804837
0.2
0.618731
0.3
0.440818
0.4
0.27032
0.5
0.106531
0.6
-0.05119
0.7
-0.20341
0.8
-0.35067
0.9
-0.49343
1
-0.63212
The root is
![]() .
.
b) Bisection method.
Using bisection, the results can be summarized as
Iteration, i |
ai |
bi |
xi |
f(ai) |
f(bi) |
f(xi) |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
-0.63212 |
0.106531 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.75 |
0.106531 |
-0.63212 |
-0.277633 |
2 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
0.625 |
0.106531 |
-0.277633 |
-0.089738 |
3 |
0.5 |
0.625 |
0.5625 |
0.106531 |
-0.089738 |
0.007283 |
Thus, after three iterations the root is x
0.5625, f(x)
= 0.007283 0,
![]() .
.
c) Secant method.
Use the secant method to
find the root with initial estimates of
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
First iteration:
![]()
![]()
Second iteration:
![]()
Note that both estimates are now on the same side of the root.
![]()
![]()
Third iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
False position method.
Use the false position method with guesses of a0 = 0 and b0 = 1.
First iteration:
![]()
![]()
Second iteration:
Therefore, the root lies in the first subinterval, and p1 becomes:
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Third iteration:
![]() .
.
Therefore, the root lies in the first subinterval:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Newton-Raphson method.
The first derivative of the function can be evaluated as
![]() which can be substituted along with the original function into
equation (see table 4.2) to give:
which can be substituted along with the original function into
equation (see table 4.2) to give:
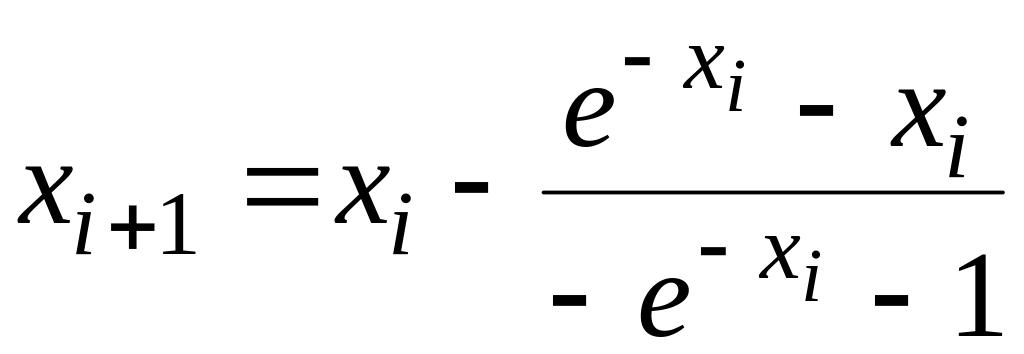 .
.
Starting with an initial guess of x0 = 1, this iterative equation can be applied to compute
i |
xi |
f(xi) |
a, % |
0 |
1 |
-0.63212 |
|
1 |
0.537883 |
0.0461 |
85.9 |
2 |
0.566987 |
0.000245 |
5.1 |
3 |
0.567143 |
4.54110-8 |
2.810-2 |
Thus, the method rapidly converges on the true root.
Notice that the percent relative error decreases at each iteration much faster than it does in another methods.
Example 2
Use the Newton-Raphson method for nonlinear system to determine the roots of equations:
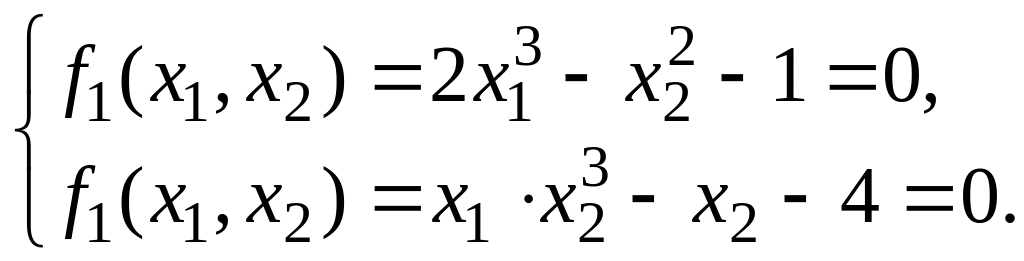
Solution. Graphical method gives us solution (point): M(1.2; 1.7). For this system Jacobian matrix is
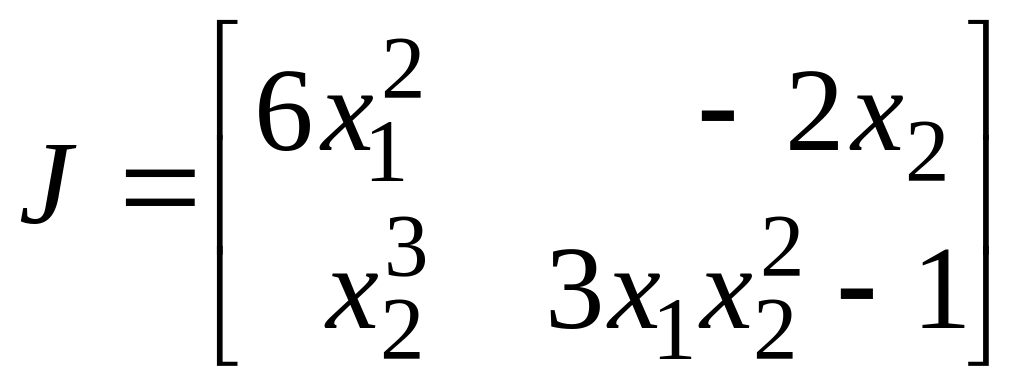 .
.
Hence, at the initial guesses we approximated roots as
![]() then
then
![]() .
.
First iteration:
Thus, the determinant of
the Jacobian for the first iteration is
![]() .
The values of the functions can be evaluated at the initial guesses
as
.
The values of the functions can be evaluated at the initial guesses
as
![]() .
.
Hence, ![]() .
From the formula:
.
From the formula:
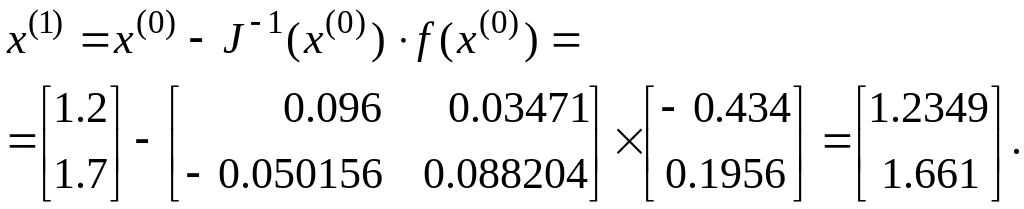
Check, how the results are converging to the true values:
![]() .
.
![]() .
.
Second iteration:
Repeat this process and we will have
![]()
The computation can be repeated until an acceptable accuracy is obtained.
Problems
Determine the real roots of
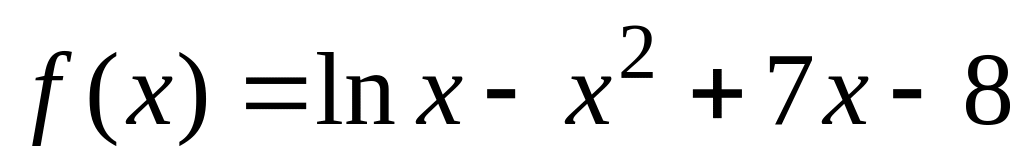 :
(a)
graphically,
(b)
using
the Newton-Raphson method, and (c)
using
the secant method. Compare and discuss the rate of convergence.
:
(a)
graphically,
(b)
using
the Newton-Raphson method, and (c)
using
the secant method. Compare and discuss the rate of convergence.Locate the first positive root of
 .
Use four iterations of (a)
the
bisection method, and (b)
the
false position method. Discuss and also perform an error check of
your final answer.
.
Use four iterations of (a)
the
bisection method, and (b)
the
false position method. Discuss and also perform an error check of
your final answer.Determine the roots of the nonlinear system of equations using the Newton-Raphson method:
![]()
Use graphical approach to obtain your initial guesses. Discuss and estimate the rate of convergence.