
Unit 9. Graphical User Interface
Warm-up
Task 1. Answer the following questions:
-
What does the GUI stand for?
-
How do you pronounce this abbreviation?
-
What is special about a GUI? Why were GUIs developed?
-
What common features of the GUI do you know? Can you make a list of them?
-
Why the GUI is popular among users? Give reasons.
-
What other types of user interface do you know? What are their character features?
Reading
Task 2. Read the text and compare your answers in Task 1:
Abbreviated GUI (pronounced GOO-ee). A program interface that takes advantage of the computer's graphics capabilities to make the program easier to use. Well-designed graphical user interfaces can free the user from learning complex command languages. On the other hand, many users find that they work more effectively with a command-driven interface, especially if they already know the command language.
Graphical user interfaces, such as Microsoft Windows and the one used by the Apple Macintosh, feature the following basic components:
-
pointer: a symbol that appears on the display screen and that you move to select objects and commands. Usually, the pointer appears as a small angled arrow. Text-processing applications, however, use an I-beam pointer that is shaped like a capital I.
-
pointing device: a device, such as a mouse or trackball, that enables you to select objects on the display screen.
-
icons: small pictures that represent commands, files, or windows. By moving the pointer to the icon and pressing a mouse button, you can execute a command or convert the icon into a window. You can also move the icons around the display screen as if they were real objects on your desk.
-
desktop: the area on the display screen where icons are grouped is often referred to as the desktop because the icons are intended to represent real objects on a real desktop.
-
windows: you can divide the screen into different areas. In each window, you can run a different program or display a different file. You can move windows around the display screen, and change their shape and size at will.
-
menus: most graphical user interfaces let you execute commands by selecting a choice from a menu.
The first graphical user interface was designed by Xerox Corporation's Palo Alto Research Center in the 1970s, but it was not until the 1980s and the emergence of the Apple Macintosh that graphical user interfaces became popular. One reason for their slow acceptance was the fact that they require considerable CPU power and a high-quality monitor, which until recently were prohibitively expensive.
In addition to their visual components, graphical user interfaces also make it easier to move data from one application to another. A true GUI includes standard formats for representing text and graphics. Because the formats are well-defined, different programs that run under a common GUI can share data. This makes it possible, for example, to copy a graph created by a spreadsheet program into a document created by a word processor.
Many DOS programs include some features of GUIs, such as menus, but are not graphics based. Such interfaces are sometimes called graphical character-based user interfaces to distinguish them from true GUIs.
Listening
Task 3. You are going to hear a lecture about graphical user interfaces. Listen carefully and decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F) in relation to the information in the recording.
-
Some time ago only experts could use computers.
-
If you want to use a program easily, a good user interface is critical.
-
You have to memorize commands in order to execute an application.
-
From the first, Macintosh computers had a user-friendly interface based on graphics and intuitive tools.
-
WIMP stands for Windows, Image, Mouse and Pointer.
-
The creation of applications with a high level of consistency is impossible.
-
You can launch the desired program by clicking its icon.
-
GUIs stimulate users to be more creative and productive.
Task 4. Read the extract from the tapescript and fill in each gap with an appropriate word.
Today, the most 1) __________ GUIs are the Macintosh, Microsoft Windows and IBM OS/2 Warp. These three platforms include similar 2) __________: a desktop with icons, windows and 3) __________, a printer selector, a file 4) __________, a control panel and various desk 5) __________. Double-clicking a folder opens a window which contains programs, documents or further nested folders. At any time within a folder, you can 6) __________ the desired program or document by 7) __________ the icon, or you can 8) __________ it to another location.
The three 9) __________ differ in other areas such as device installation, network 10) __________ or compatibility with application programs.
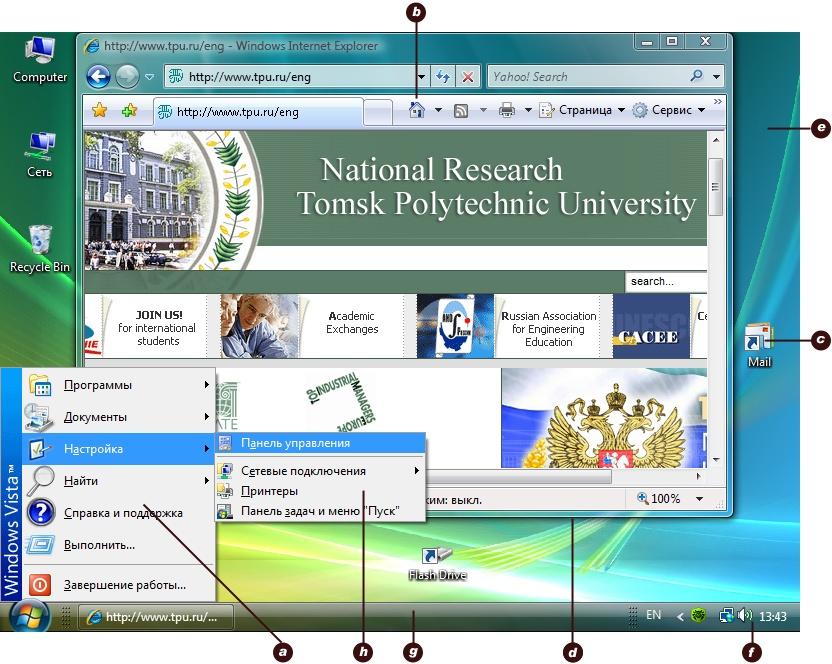
Task 5. Study this diagram of a graphical user interface on the next page. Identify these features:
|
|
|
|
Language work
|
Verbs + object + infinitive; Verbs + object + to-infinitive
|
|
|
New developments in computing are often designed to make something easier. These verbs are often used to describe such developments:
allow permit let enable help
Study these examples:
|
Allow, enable and permit are used with this structure: verb + object + to-infinitive Let is used with this structure: verb + object + infinitive Help can be used with either structure. |
Task 6. Complete the gap in each sentence with the correct form of the verb in brackets.
-
The Help facility enables users ………… (get) advice on most problems.
-
Adding more memory lets your computer ………… (work) faster.
-
Windows allows you ………… (display) two different folders at the same time.
-
The operating system provides several of its own commands that help you ………… (use) the computer.
-
The Shift key allows you …………. (type) in upper case.
-
The MouseKeys feature enables you ………… (use) the numeric keypad to move the mouse pointer.
-
ALT + TAB allows you ………… (switch) between programs.
-
The StickyKeys feature helps disabled people ………… (operate) two keys simultaneously.
-
ALT + PRINT SCREEN lets you ………… (copy) an image of an active window to the Clipboard.
-
Trackball enables you ………… (select) objects on the display screen.
-
Most graphical user interfaces let you ………… (execute) commands by selecting a choice from a menu.
-
Computer graphics help users ………… (understand) complex information quickly by presenting it in a clear visual form.
Task 7. Describe the function of these features using ‘enabling’ verbs:
|
|
|
Speaking
Task 8. Work in groups. Complete the questionnaire for yourself. Then take turns in your group to explain how to perform each of these actions. You may need these verbs:
choose drag and drop hover
right/left/double-click on pull down select
|
Do you know how to: |
Yes |
No |
|
1. create a new document? |
|
|
|
2. quit a program? |
|
|
|
3. shut down the system? |
|
|
|
4. save a file onto a floppy disk? |
|
|
|
5. arrange the icons? |
|
|
|
6. display the time? |
|
|
|
7. pull down a menu? |
|
|
|
8. in Windows, show Tooltips? |
|
|
|
9. download information from the Internet? |
|
|
|
10. print out a document? |
|
|
Writing
Task 9. Study these instructions for moving a file from one folder to another using Windows Explorer. Then write your own instructions for one of the actions in Task 7.
To move a file
-
If you want to move a file that was saved in a different folder, locate and open the folder.
-
Right-click the file you want to move; then click Cut on the shortcut menu.
-
Locate and open the folder where you want to put the file.
-
Right-click the folder; then click Paste on the shortcut menu.
Word-play
Task 10. Solve the crossword puzzle using the clues below.
Across
-
a list of options displayed on a computer screen
-
drag and ……
-
a set of instructions written in a computer language that control the behaviour of a computer
-
a label that appear on the screen when the user holds the mouse pointer over an icon in a Microsoft Windows system
-
the hardware or software that connects two systems and allows them to communicate with each other
-
a Microsoft Windows desktop component that indicates what programs are currently being used and allows the user to switch between them
-
using light for reading or storing information
-
the main output device used to display the output from a computer on a screen
-
to move data from one location to another with a mouse
-
to press and release the button on a mouse
Down
-
the main graphical user interface background screen that dislays icons for other programs
-
optical …… recognition
-
an arrow-shaped cursor
-
the act of identifying what something is
-
a computer program designed to be used for a particular purpose
-
the layout of a document including page numbers, line spaces, margins, paragraph alignment, headers and footers, etc.
-
a stationary device that works like a mouse turned upside down
|
|
1 |
|
6 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Task 11. Translate the following text into English. You may use the dictionary if it is necessary.
