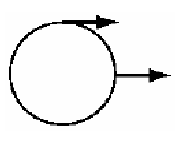
- •If vector b is added to vector a, which two of the following choices must be true in order for the resultant vector to be equal to zero?
- •In inelastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In elastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In rotational motion, the quantity, which plays the same role as the inertial mass in linear motion, is called ___________.
- •If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 Ohm, what is the current in the wire?
- •If a loop in a basic dc generator suddenly begins rotating at a faster speed, the induced voltage
A ball is thrown upward. While the ball is in free fall, does its acceleration
Increases
Decreases
Increases and then decreases
Decreases and then increases
Remain constant
After a ball is thrown upward and is in the air, its speed in all path
Increases
Decreases
Increases and then decreases
Decreases and then increases
Remain the same
If vector b is added to vector a, which two of the following choices must be true in order for the resultant vector to be equal to zero?
A nd B are parallel in the same direction and have same magnitude
A and B are parallel in opposite directions, but have same magnitude
A and B have the same magnitude
A and B are perpendicular but have same magnitude
None of them is right
A car moves along y-axes. In the figure, velocity of the car as a function of time is shown in three parts (I, II, III). Which statement is ALWAYS true?

Velocity is constant in part II
A car drives backward in part I
Velocity is negative in part III
Velocity is negative in part I
Nothing is true
What is the cross product of two vectors A and B, if the angle between them is 30 degree, and magnitudes are |A|=4, |B|=2
5.6
4
0
8
2.5
When a box rests on the floor, it is acted upon by the gravitational and the _________________ force.
Centrifugal
Acceleration
Normal
Inertia
Friction
Motion is produced by
all forces
unbalanced forces
balanced forces
the absence of force
none of them
Force is that agent which produces or tends to produce the __________.
Speed in the body
Acceleration in the body
Constant velocity in the body
Constant angular velocity in the body
mass
A force of 3N acts perpendicularly to a force of 4N. Their resultant has magnitude of ______
1N
5N
7N
9N
25N
In inelastic collision between the two bodies __________.
Only momentum of the system is conserved
Only the kinetic Energy of the system is conserved
Both the kinetic Energy and Momentum of the system remain the same
Total energy is not conserved
Angular momentum is conserved
Work done by a grass cutter is maximum when he pulls it __________.
Making an angle 450 with the floor
Making an angle 900 with the floor
Along a line parallel to the floor
Making an angle 600 with the floor
Making an angle 550 with the floor
A man does the work if he ___________.
Goes to fifth floor of the building
Goes to fifth floor of the building and comes back to ground floor
Remain on the ground floor
Goes to the basement and comes back to ground floor
Goes to fourth floor of the building and comes back to ground floor
In elastic collision between the two bodies __________.
Only momentum of the system is conserved
Only the kinetic Energy of the system is conserved
Both the kinetic Energy and Momentum of the system remain the same
Total energy is not conserved
Angular momentum is conserved
When the constant force and displacement are parallel to each other, then work is __________.
Minimum
Maximum
None of these
Depends on force magnitude
Changes with time
In rotational motion, the quantity, which plays the same role as the inertial mass in linear motion, is called ___________.
Inertia
Angular momentum
Moment of inertia
Torque
Center of mass
Pairs of forces of equal magnitude act on identical cylinders as shown in the figures. In which example is the cylinder in translational and rotational equilibrium?
Four identical particles, each with mass m, are arranged in the x, y plane as shown. They are connected by light sticks to form a rigid body. If m = 2.0 kg and a = 1.0 m, the rotational inertia of this array about the y-axis is:

4.0 kg m2
12 kg m2
9.6 kg m2
4.8 kg m2
none of these
Three identical objects, each of mass M, are fastened to a massless rod of length L as shown. The rotational inertia about one end of the rod of this array is:

ML2/2
ML2
3ML2/2
5ML2/4
3ML2
How defines period of physical pendulum?


No correct answer
Find a sample of the physical pendulum:

None of them
A sound wave can be characterized as
A transverse wave
A longitudinal wave
A transverse wave or a longitudinal wave, depending on the nature of its source
One that carries no energy
A wave that does not require a medium to be transmitted from one place to the other
Sound travels faster in
a vacuum
water
steel
air
Sound travels at about the same speed in all of the above media.
A woman sits on a spinning stool with her arms folded. When she extends her arms, which of the following occurs
She increases her moment of inertia, thus increasing her angular speed
She increases her moment of inertia, thus decreasing her angular speed.
She decreases her moment of inertia, thus increasing her angular speed
She decreases her moment of inertia, thus decreasing her angular speed
Her angular speed remains constant by conservation of angular momentum
The pressure at the surface of the ocean is 1 atm (1 x 105 Pa). At what approximate depth in the ocean water (ρ = 1025 kg/m3) would the absolute pressure be 2 atm?
1 m
5 m
10 m
100 m
1000 m
What is the direction of angular momentum for the bowling ball that rotates about z-axis?

+y
–y
+x
–x
+z
–z
A parallel-plate capacitor with air between the plates has an area A=2.00·104 m2 and a plate separation d=1.00 mm. Find its capacitance.
C=1.77 pF
C=1.77 F
C=1.77 mF
C=1.77 nF
No correct answer
Find the equivalent capacitance between a and b for the combination of capacitors shown in Figure. All capacitances are in microfarads.

6.0 μF
6.0 F
5.0 μF
6.0 nF
No correct answer
A parallel-plate capacitor has plates of dimensions 2.0 cm by 3.0 cm separated by a 1.0-mm thickness of paper. Find its capacitance (k = 3.7, ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
20 pF
20 F
40 pF
60 pF
80 pF
Find the electric flux though the spherical surface, covers the point-like charges q1=5 nC and q2=-2 nC. (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2)
339 N·m2/C
0.339 N·m2/C
339 N/C
339 N·m2
No correct answer
Find the attractive force F between nuclei of hydrogen atom and electron. Radius of hydrogen atom is r=0.5·10-10 m; modules charge of nuclei are equal and opposite to charge sign of electron (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
F=92.3·10-9 N
F=92.3 N
F=92.3·10-9 N/m2
F=92.3·10-9 N
No correct answer
Two point-like charges in air (ε=1) at the distance r1=20 сm from each other interact with some force. At what distance r2 one needs to place this charges in oil (ε2=5) to get the same force of interaction?
r2=8.94 сm
r2=8.94 m
r2=8.94·103 m
r2=8.94·10-3 m
No correct answer
What times the gravitational force between two protons less the electrostatic force of their repulsion? The charge of proton is equal on module and opposite on sign of charge of electron.



No correct answer
The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom are separated (on the average) by a distance of approximately 5.3·10-11 m. Find the magnitudes of the electric force between the two particles. (ke=8.99·109 N·m2/C2)
8.2·10-8 N
8.2 N
8.2·10-9 N
8.2·109 N
No correct answer
Calculate the resistance of an aluminum cylinder that has a length of 10.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 2.00·10-4 m2 (ρ=2.82·10-8 Ohm·m).
R=1.4·10-5 Ohm
R=1.4·10-3 Ohm
R=1.4 Ohm
R=1.4·105 Ohm
No correct answer
Calculate the resistance of a glass cylinder that has a length of 10.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 2.00·10-4 m2 (ρ=3·1010 Ohm·m).
R=1.5·1013 Ohm
R=1.5·10-13 Ohm
R=1.5·1014 Ohm
R=1.5·103 Ohm
No correct answer
Calculate the resistance per unit length of a 22-gauge Nichrome wire, which has a radius of 0.321 mm (The resistivity of Nichrome is 1.5·10-6 Ohm·m).
4.6 Ohm/m
4.6 Ohm
4.6 Ohm·m
4.6·10-3 Ohm/m
No correct answer