
03b_И_debate
.pdf
MANAGEMENT
Applied Summer School
Business in Europe
A Single European Currency – A Debate
Prof. Vito Bobek
University of Apllied Sciences FH Joanneum
vito.bobek@fh-joanneum.at

MANAGEMENT
Key Issues
•Why to have convergence criteria?
•What are the basic effects of a single currency?
•What are the motivations for joining the Euro?
•The case for EMU entry
•The case against EMU entry
•Optimal currency areas
•Tensions for the single currency in 2009-2010

MANAGEMENT
Basics on the Euro
•A single currency requires a common interest rate for the Euro Zone – i.e. a common monetary policy
•17 member nations are inside the Euro Area
•The European Central Bank (ECB) sets official interest rates to meet an inflation target of 2%
•The approach of ECB is different to that of the USA Federal Reserve (dual target)
•The US Federal Reserve tends to set interest rates to maintain growth and avoid deflation.

MANAGEMENT
Euro Zone Interest Rates
Percent
Interest Rates for the Euro Area and for the UK
Per Cent
8.0 |
|
8.0 |
|
Bank of England Rates
7.0 

















































































































 7.0
7.0
6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.0 |
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.0 |
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.0 |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
Euro Zone Interest Rates |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 |
99 |
00 |
01 |
02 |
03 |
04 |
05 |
06 |
07 |
08 |
09 |
Source: Reuters EcoWin

MANAGEMENT
Judging the Success of the Euro
•The Euro project should be judged according to whether it achieves its long term aims:
1.Sustained non-inflationary growth
2.Lower long-term interest rates and higher rates of investment
3.Lower unemployment
4.Expansion of the EU single market
•The Euro on its own in insufficient to achieve these – structural economic reforms in Europe are also required and many are taking place.

MANAGEMENT Nominal v Real (Structural)
Convergence
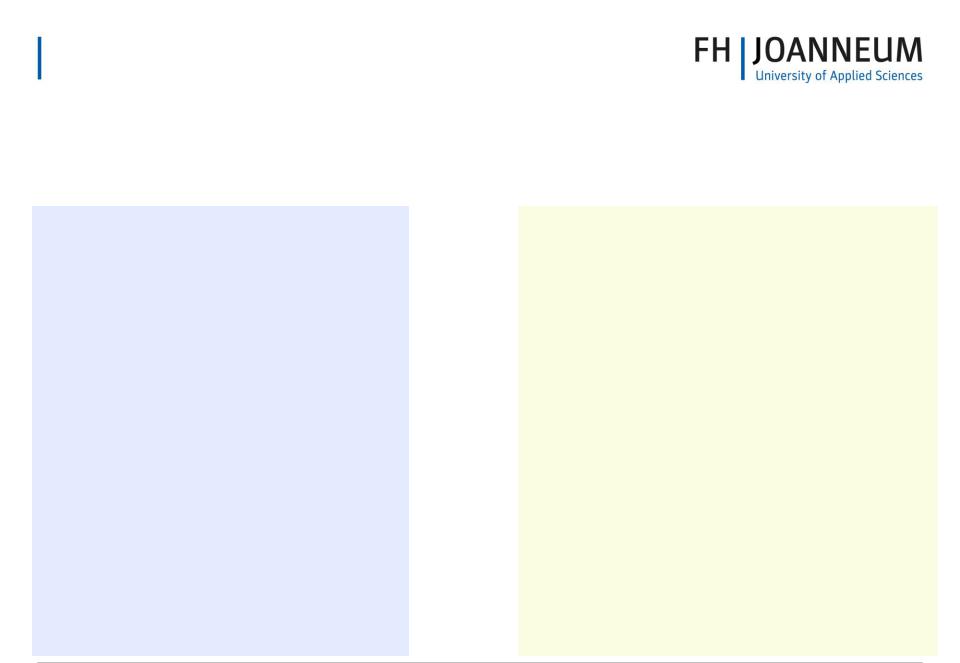
Nominal Economic Indicators
•(Those required under the Maastricht Treaty)
•Consumer price inflation
•Short term interest rates
•Fiscal (Budget) deficit
•Gross government debt
•Exchange rate stability
MANAGEMENT
Nominal vs. Real (Structural) Convergence
Nominal Economic Indicators
•(Those required under the Maastricht Treaty)
•Consumer price inflation
•Short term interest rates
•Fiscal (Budget) deficit
•Gross government debt
•Exchange rate stability
Real Economic Indicators
•(Important in the long term)
•Trend growth of GDP
•Labour market performance
•Trend growth of labour productivity
•Trade balances in goods and services
•Investment/GDP ratios
•Housing market structure.

MANAGEMENT
Is the Euro an Optimal Currency Zone?
•An optimal currency zone occurs when:
–(1) Countries have achieved real convergence
–(2) They respond in similar ways to external economic shocks or macro policy changes
–(3) They have sufficient flexibility in both their product markets and labour markets to deal with these shocks
•High geographical mobility of labour
•High occupational mobility of labour
•Wage and price flexibility in factor markets
–(4) Countries are prepared to use fiscal transfers to even out some of the regional economic imbalances within the European currency union

MANAGEMENT
Optimal Currency Zones (2)
•By most criteria, the current Euro Zone does not come close to an optimal currency zone!
–The core group of EU countries are broadly similar (Germany + France + Netherlands + Belgium)
–But peripheral countries have big structural differences
–And there are barriers to the mobility of labour
–Little wonder that tensions are rising in the Euro Area as recession bites
MANAGEMENT
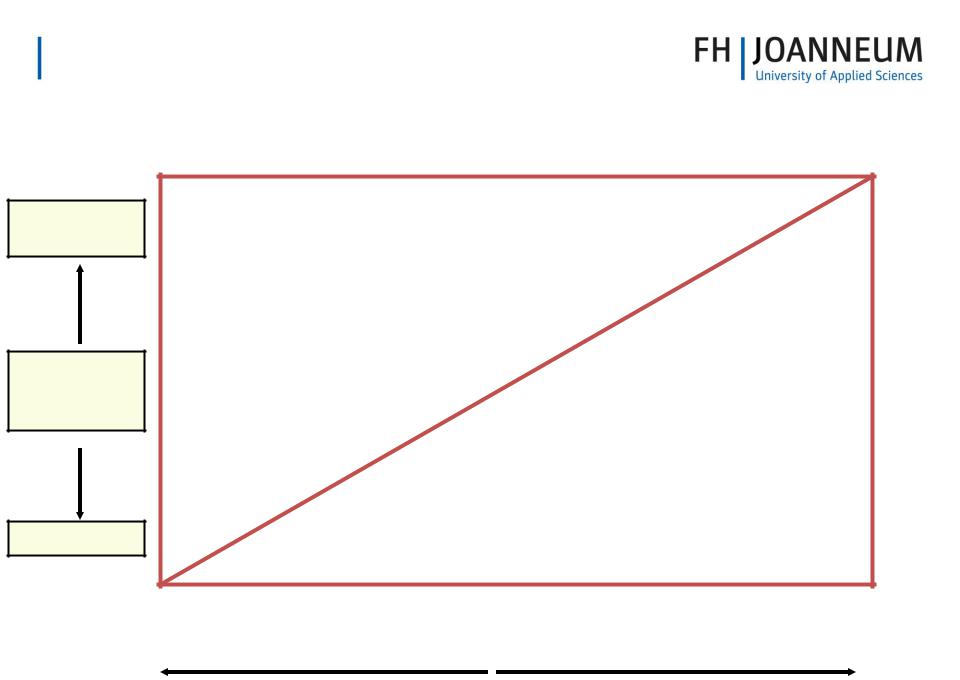
Optimal Currency Zones
Highly
Flexible
Labour
Market
Flexibility
Inflexible
|
Divergent |
|
Real Economic Convergence |
|
Convergent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
