
03a_EMU
.pdf
MANAGEMENT
Applied Summer School
Business in Europe
Economic and Monetary Union
Prof. Vito Bobek
University of Apllied Sciences FH Joanneum
vito.bobek@fh-joanneum.at

MANAGEMENT
THE EURO
•The euro – Europe's new single currency - represents the consolidation and culmination of European economic integration.
•Its introduction on January 1, 1999, marked the final phase of Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), a threestage process that was launched in 1990 as EU member states prepared for the 1992 single market.

MANAGEMENT
The EURO
Early 1990’s
•1990: Aimed at boosting cross-border business activity, the first stage of EMU lifted restrictions on movements of capital across internal EU borders.
•1994: The European Monetary Institute was established in Frankfurt to pave the way for the European Central Bank.
•1999: the Euro was introduced as the single currency for eleven EU member states: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain.

MANAGEMENT
The EURO
1999-Present
•1999-2002: The Euro and the previous national currencies were concurrently used in participating states.
•2002: The participating countries had their previous national currencies withdrawn permanently as legal tender.
•EU member states not yet using the Euro as currency: Denmark, Sweden, United Kingdom + 7 new member countries (2004 and 2007)
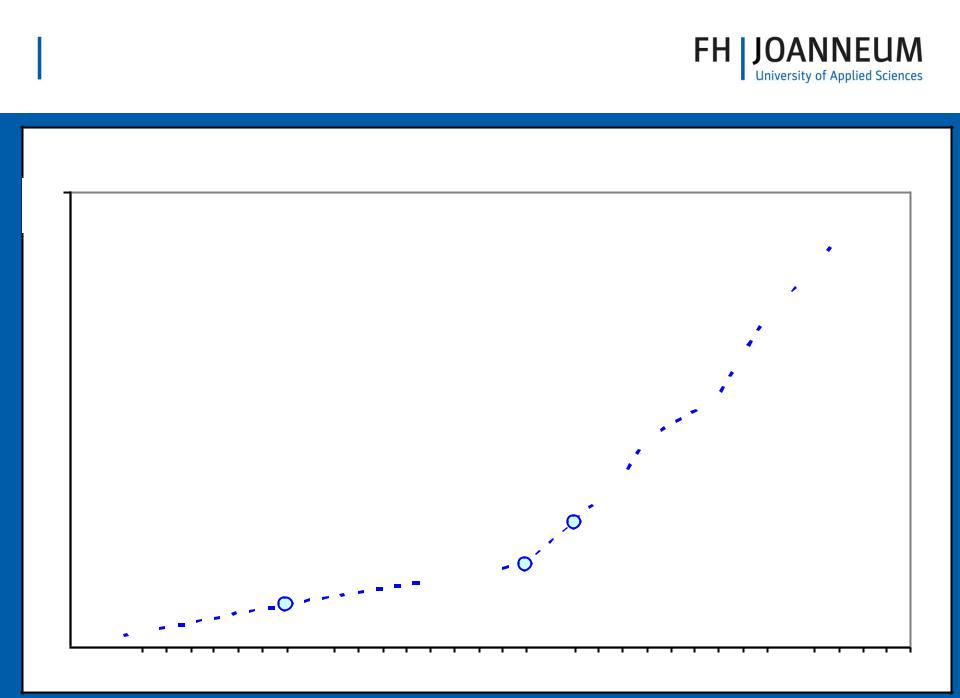
MANAGEMENT
event11
Werner Plan
0 


 1970
1970
Timeline for European monetary integration
Euro coins and notes  Greece joins
Greece joins 

EMU starts  Decision on members, conversion rates, creation ECB
Decision on members, conversion rates, creation ECB
Stability and growth pact 
EMI (precursor ECB) 

 Maastricht ratified
Maastricht ratified
Maastricht treaty



 Delors Committee
Delors Committee
EMS starts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1980 |
1990 |
2000 |
|||||

MANAGEMENT
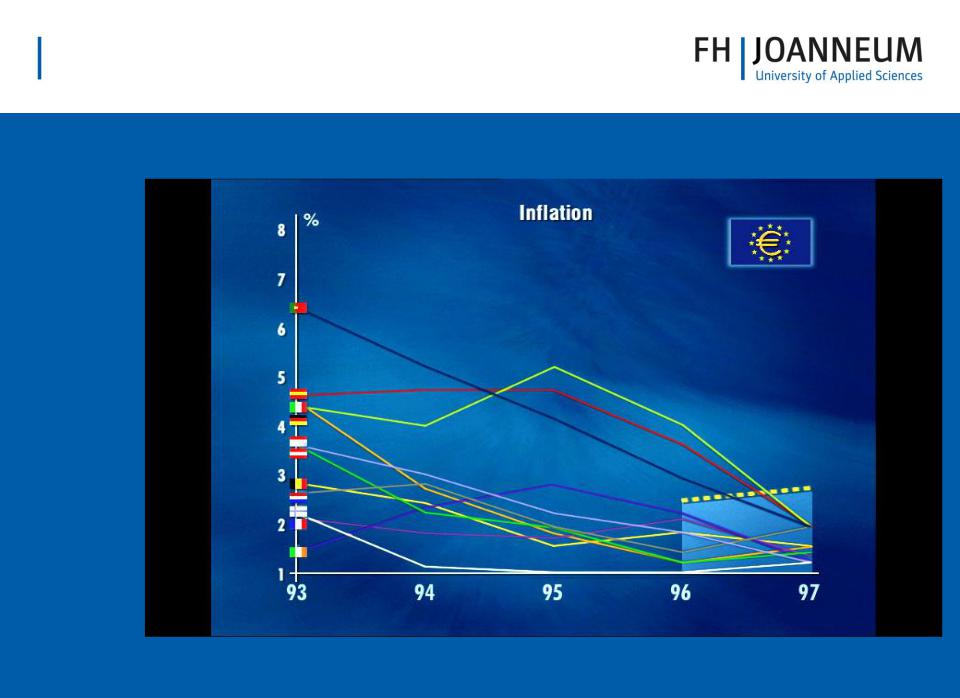
Convergence Criteria – Joining the Euro
•Flexibly applied for original Euro members – but more strictly applied in the case of new member states
•Inflation:
–Average inflation over previous year must not exceed by more than 1.5% that of the three lowest inflation countries
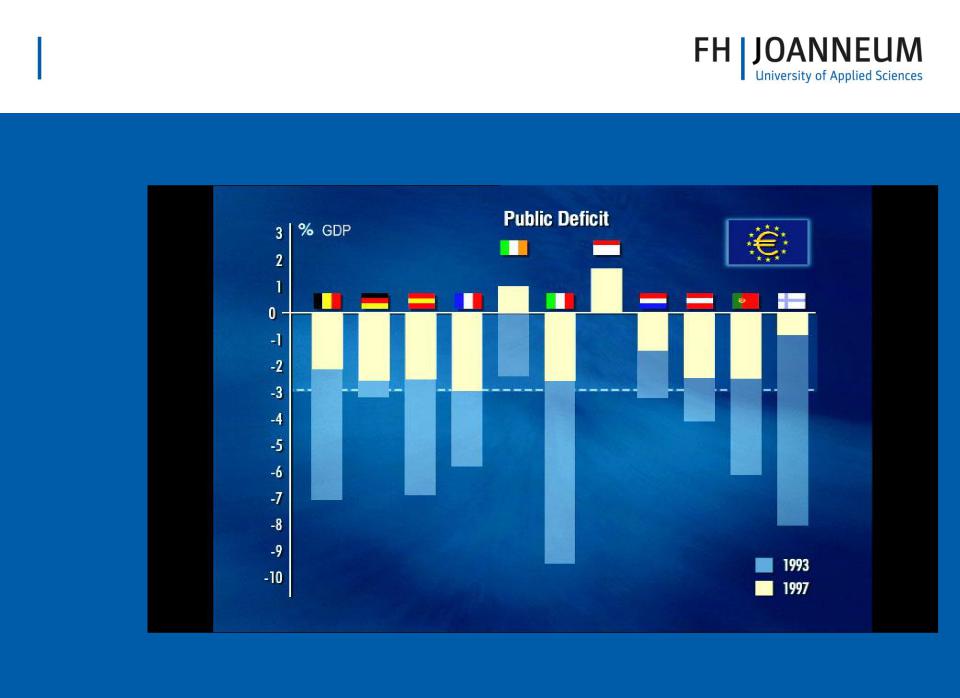
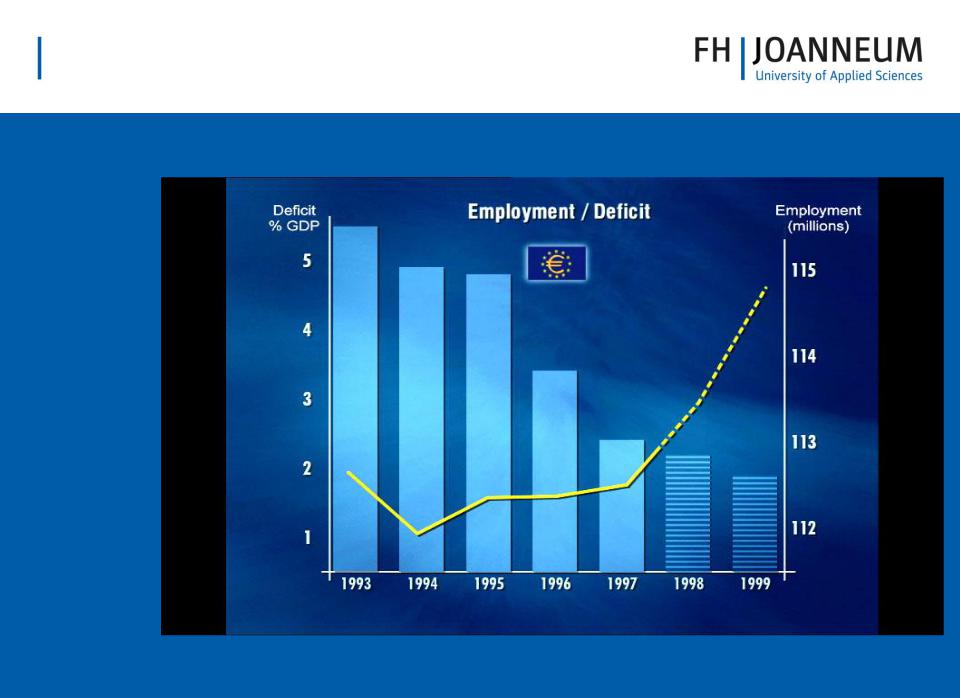
•Government Finances
–Budget deficit must not exceed 3% of GDP
–Gross government debt must not exceed 60% of GDP
•Interest Rates:
–Average yield on govt bonds must not exceed by more than 2% bond yields of three lowest inflation countries
•Exchange Rate Stability:
–Currency must have adhered to fluctuation margins of the ERM II in two previous years without severe tension.
MANAGEMENT
MANAGEMENT
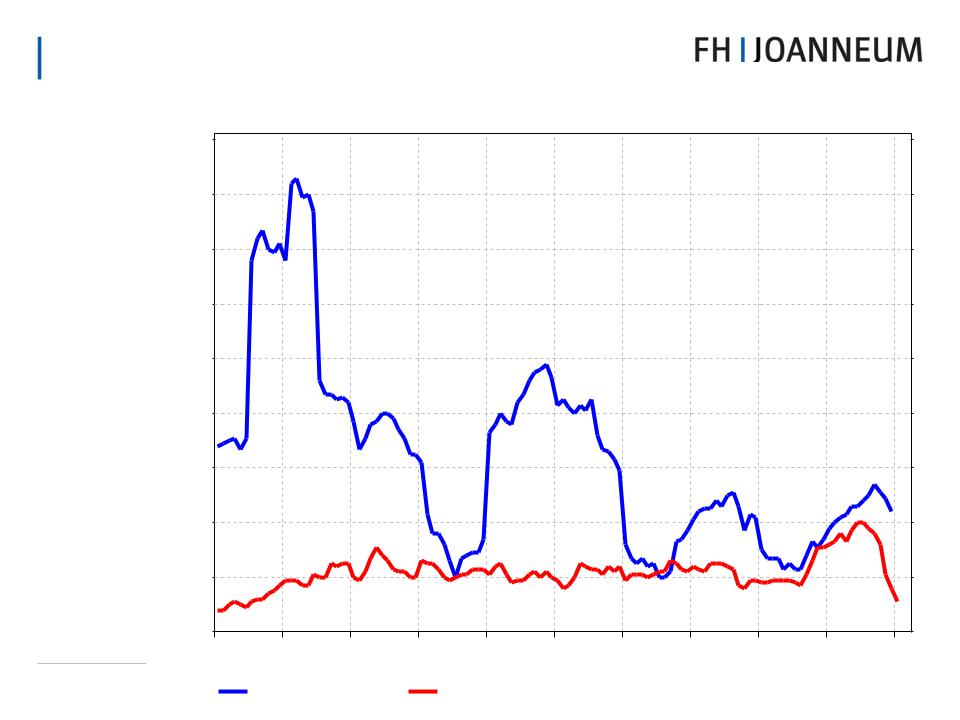
InflationSlovakconvergenceRepublic - Consumer–PriceSlovakiaInflation
Annual percentage change in the consumer price index
|
18.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.0 |
|
16.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.0 |
|
14.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.0 |
|
12.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.0 |
Percent |
10.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.0 |
8.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.0 |
|
4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.0 |
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
99 |
00 |
01 |
02 |
03 |
04 |
05 |
06 |
07 |
08 |
|
|
Slovak Republic |
Euro Zone |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Source: Reuters EcoWin
MANAGEMENT
MANAGEMENT
