
- •My studies
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •St. Petersburg
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Building materials
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •An industrial building under construction
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Sir Christopher Wren (1632-1723)
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Components of the Automobile
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Excavators
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Road construction
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Types of bridges
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •City water supply
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •The Heating system of a Modern House
- •Vocabulary:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Sewerage
- •Words to the text:
- •Questions to the text:
- •Hardware and software
- •Vocabulary:
- •Question to the text:
- •Computer
- •Vocabulary:
- •Question to the text:
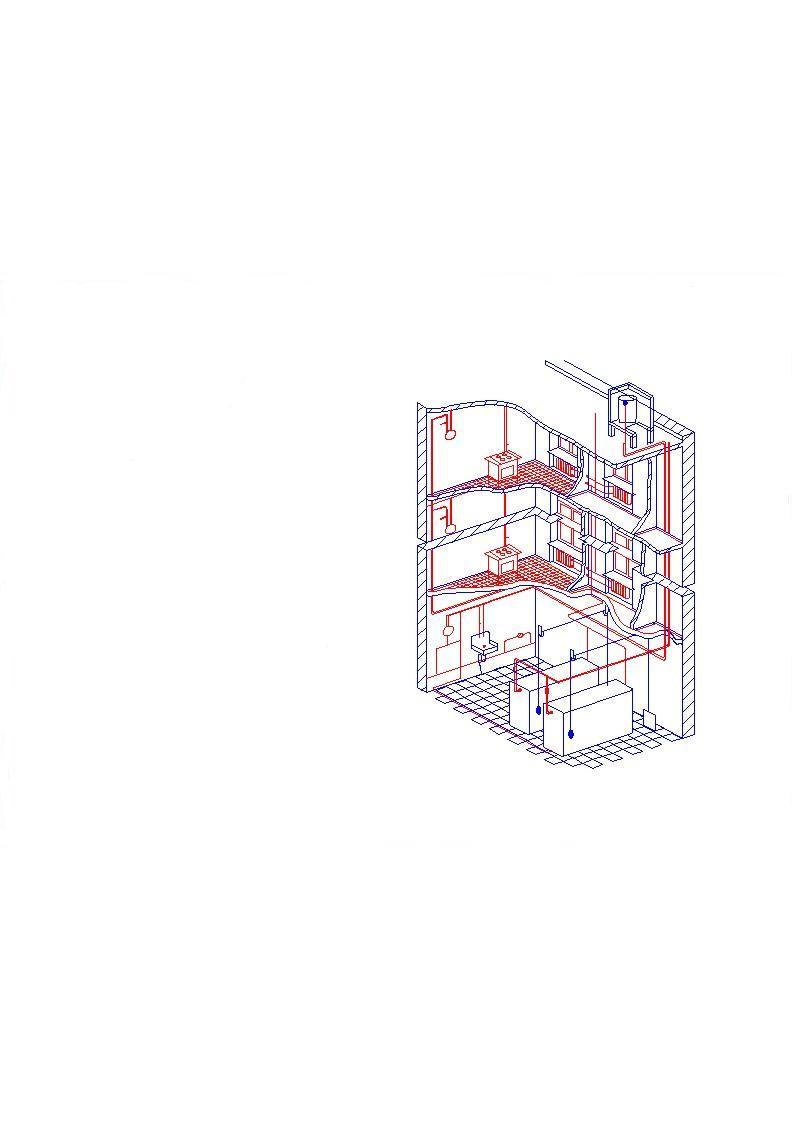
The Heating system of a Modern House
In this picture one can see a two-pipe heating system of a three-storied modern house. It is a circulation system. The overhead method of distribution is applied in that system. In the top right-hand corner one can see the storage tank of the system.
Water is heated in the basement. One can see two such boilers in the basement of this house.
The heated water is brought to the attic through the main riser. One can see that riser against the wall.
The main riser circles the attic one can see it in the top part of the picture.
Return risers extend down from it to the basement.
The supply radiators are situated under the windowsills.
The cooled water from the radiators drains down through the special pipes. These pipes. These pipes are provided under the radiators.
The cooled water is drained into the boiler. Here it is heated again and is forced into the main riser once more.
Draft in the boilers is controlled by means of a weighted belt-tightener, system located above the boilers. There is counter-weight on the left. There is a damper on the right. Water is a brought into the building by a pump. One can see this pump on the wall.
Vocabulary:
two-pipe treating system – двухтрубная система отопления
circulation system – циркуляционная система
heating system – система отопления
overhead method of distribution – метод верхней разводки (распределения)
storage tank – питательный резервуар
apply (v) – применять, прилагать
main riser – основной (главный) стояк
attic (floor) (n) – чердак
extend – расширяться, удлиняться, тянуться
return riser (n) – обратный стояк
supply radiator – радиатор
provide (v) – обеспечивать, предусматривать
drain down (v) – вытекать, сливаться
by means of – посредством, с помощью
draft (n) – тяга воздуха
counterweight – противовес, контргруз
weighted belt-tightener – натяжной ролик с грузом
circle (v) – окружать
Questions to the text:
What type of system can one see in the picture?
It is a circulation system. Isn’t it?
Is the overhead method of distribution applied in that system?
Where can one see the storage tank of the system?
How many boilers are there in the basement of this house?
Where is the heated water brought to?
How is the heated water brought to the attic?
Does the main riser circle the attic?
Do the return risers extend down from the main riser to the basement?
Where are the supply radiators situated?
How does the cooled water drain from the radiators?
Where is the cooled water heated again? Where is it forced to?
How is draft controlled in the boilers?
What is there on the left? What is there on the right?
Is water brought into the building by a pump?
Where can one see the pump?
Sewerage
Great amount of water is required by a community for domestic, industrial and fire extinguishing purposes. In the course of its usage water gets additional pollution, physical and chemical properties of water are changed. Such changed water is called sewage.
According to its source sewage may be subdivided into domestic, industrial or rain waters. These waters must be collected, removed and purified.
Collection, removal and treatment of sewage is carried out by a complex of engineering works called sewerage. A sewerage system consists of the following principal elements:
collectors of a sewage situated in building
a sewerage net
pumping stations
purifying plants.
